Foreword
Introduction
Breast anatomy
Introduction
Gross anatomy
Breast tissue
Microscopic anatomy
Vascular and lymphatic supply
Development of the breast
Changes in the breast with ageing
Clinical breast examination (CBE)
Breast cancer screening versus early diagnosis
Performing a breast examination
Practical tips when performing breast examinations
Common abnormalities
Interpretation: normal/negative cases
Interpretation: abnormal/positive cases
Documentation
Pitfalls and limitations
Breast imaging
Introduction
Evolution of breast imaging
Techniques
Principles of mammography
Mammography technique
Reporting and final assessment categories
Breast pathology
Mammography unit
Basic functioning
Mammography procedure
Mammography interpretation
Scheduling a woman for mammography
Obtaining mammographic images
Technical adequacy of acquired mammographic views
Additional mammographic views
Pitfalls
Incorrect MLO positioning
Inadequate breast compression
Screen artefacts on mammographic image
Overstretched RCC and RMLO views
Opacities from body parts causing artefacts in the examination field
Breast tissue inadequately pulled onto the image receptor
Image processing
Introduction
Getting organized
Understanding the normal mammogram and the physiological variations
Interpreting the abnormal mammogram
Mammography lexicon
Breast ultrasound
Introduction
Indications
Equipment: Basic components and functioning
Technique
Benefits
Limitations
Learning breast ultrasound
Normal anatomy
Breast changes in special stages of life
Breast changes in special stages of life (2)
Interpreting the abnormalities
Ultrasound lexicon
Introduction
Cytopathology of the breast
Histopathology of the breast
Case studies
BI-RADS 1
BI-RADS 2
Quiz
Acknowledgements
Authors
Suggested citation
Copyright
Cystic
Solid
Fat-containing solid
Calcified benign mass
Calcifications – typically benign
BI-RADS 3
BI-RADS 4
Skin
Vascular
Coarse or popcorn-like
Large rod-like
Round
Rim
Dystrophic
Milk of calcium
Suture
Diffusely scattered calcifications bilaterally
Miscellaneous
4A-Low suspicion for malignancy
4B-Moderate suspicion for malignancy
4C-High suspicion for malignancy
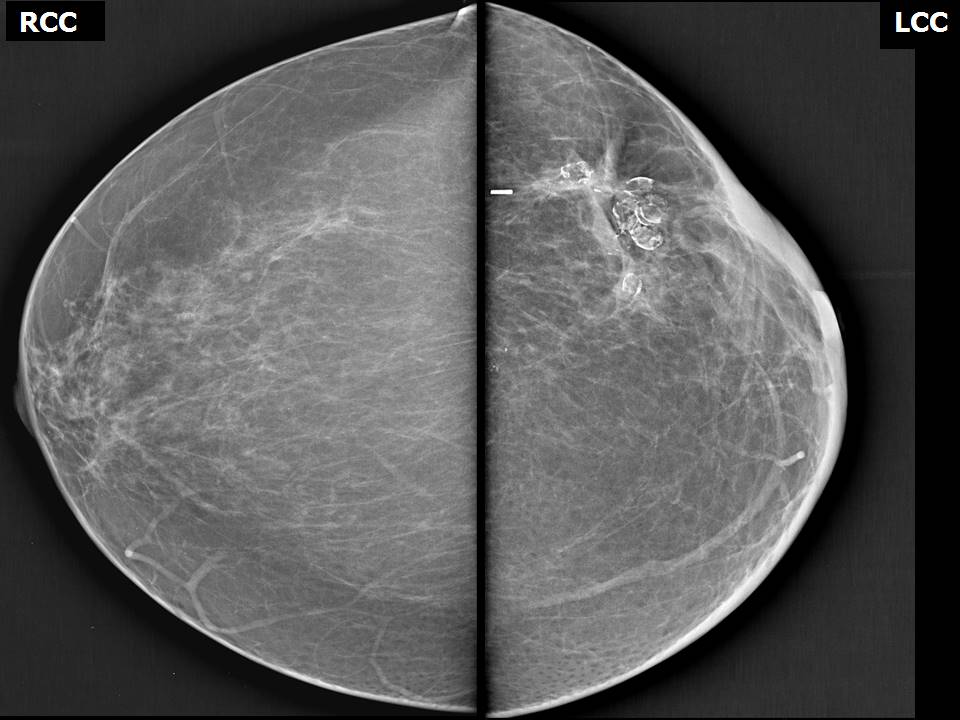
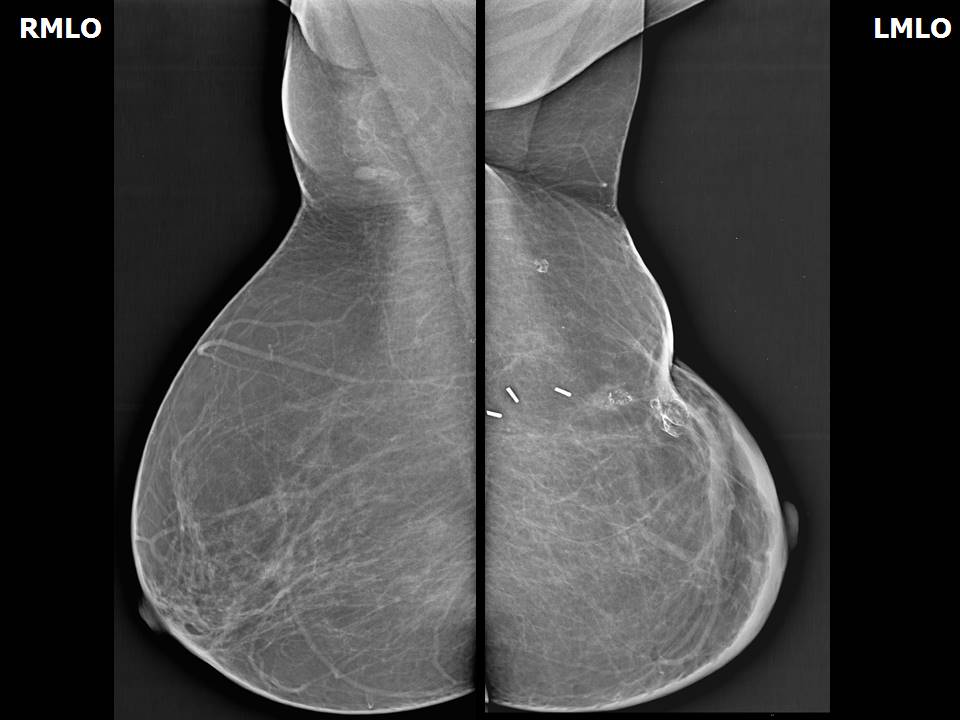
BI-RADS 5
IBC-Microcalcifications
IBC-Skin thickening
IBC-Skin retraction
IBC-Nipple retraction
IBC-Architectural distortion
IBC-Spiculated margin
IBC-Indistinct margin
IBC-Obscured margin
IBC-Microlobulated margin
IBC-Metaplastic carcinoma
IBC-Nipple erosion
IBC–Occult primary in breast with nodal metastases
IBC with metastatic intramammary node
IBC with coarse heterogeneous calcifications
IBC with Paget disease
IBC with neuroendocrine differentiation
IBC in neurofibromatosis
Encapsulated papillary carcinoma
Multifocal
Multicentric
Invasive cribriform carcinoma
Infiltrating lobular carcinoma
Inflammatory carcinoma
Malignant phyllodes
Medullary carcinoma
Mucinous carcinoma
Bilateral synchronous carcinoma
Calcification of suspicious morphology
BI-RADS 6
Miscellaneous cases