Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Learning
.png)
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends

Click on this icon to display a case study
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
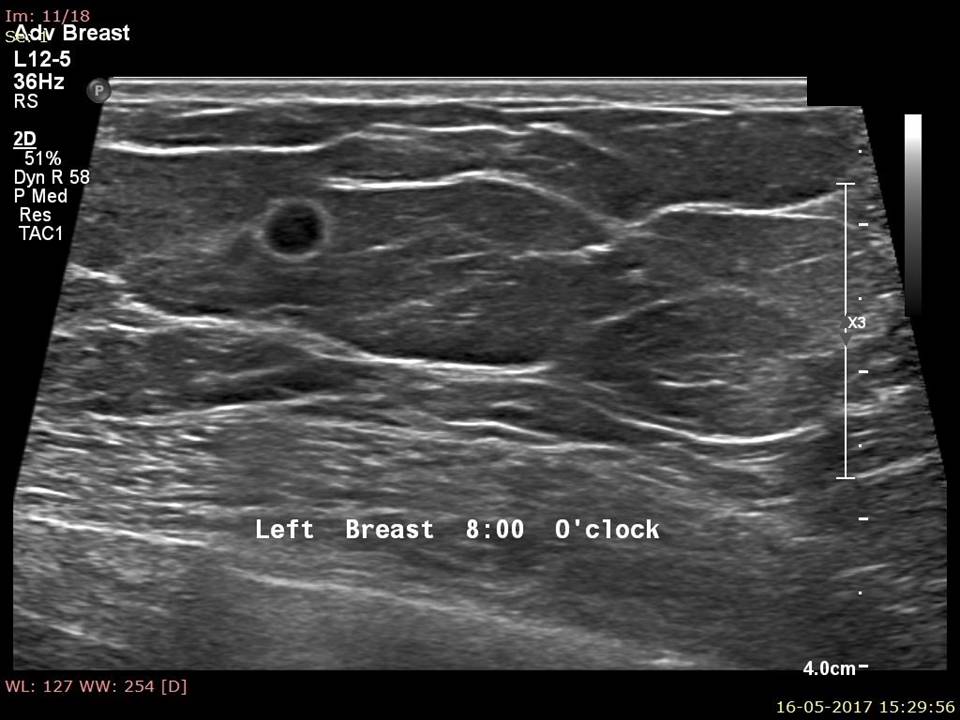
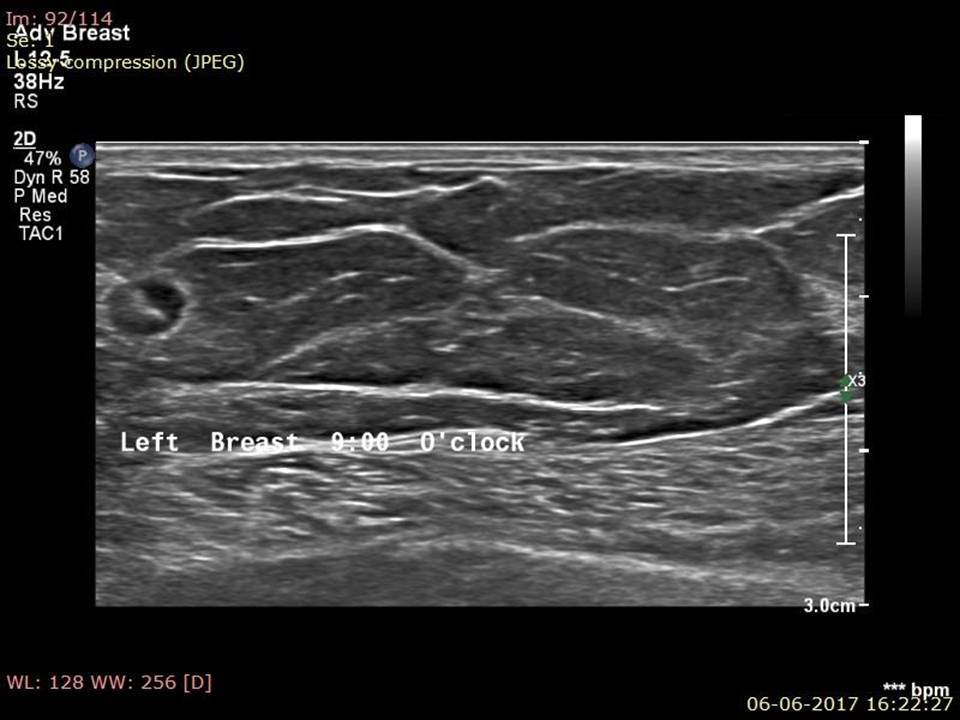
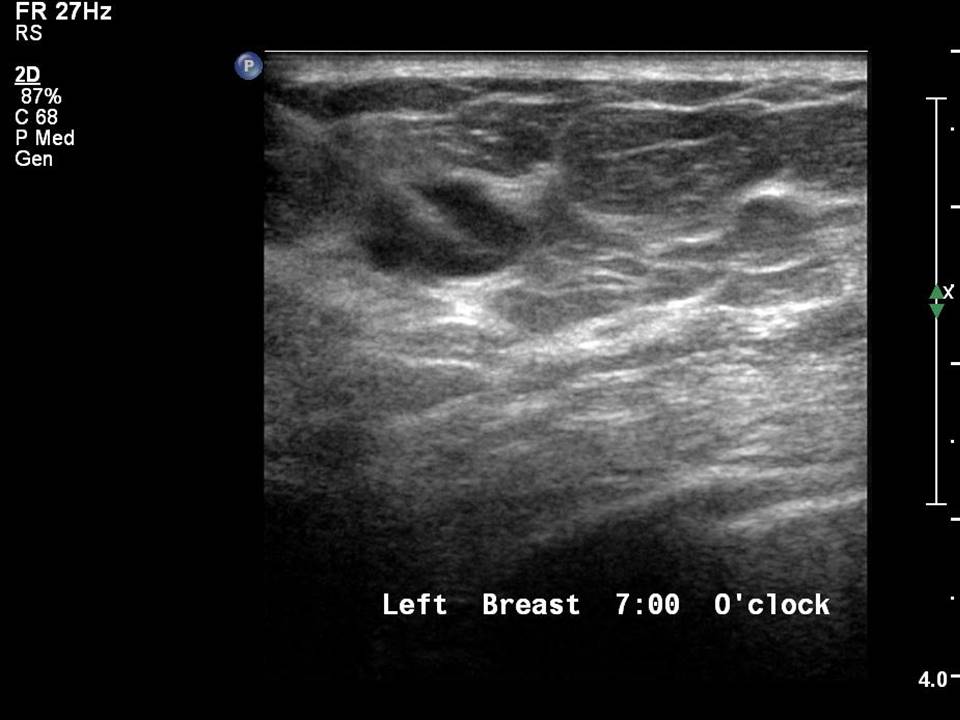
Filter by language: English / РусскийBreast imaging – Breast ultrasound – Ultrasound-guided interventional procedures – Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) |
Indications for FNAC
Steps
Further details about the advantages and disadvantages of FNAC are given later. |
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on this icon to display a case study
25 avenue Tony Garnier CS 90627 69366, LYON CEDEX 07 France - Tel: +33 (0)4 72 73 84 85
© IARC 2025 - Terms of use - Privacy Policy.
© IARC 2025 - Terms of use - Privacy Policy.