Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Filter by language: English / Русский
Go back to the list of case studies
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
| Case number: | 181 |
| Age: | 37 |
| Clinical presentation: | Premenopausal woman with average risk of breast cancer presented with a right breast lump first noticed 1 month ago with progressive rapid increase in size. On examination, a hard non-tender lump was palpable in the right breast. |
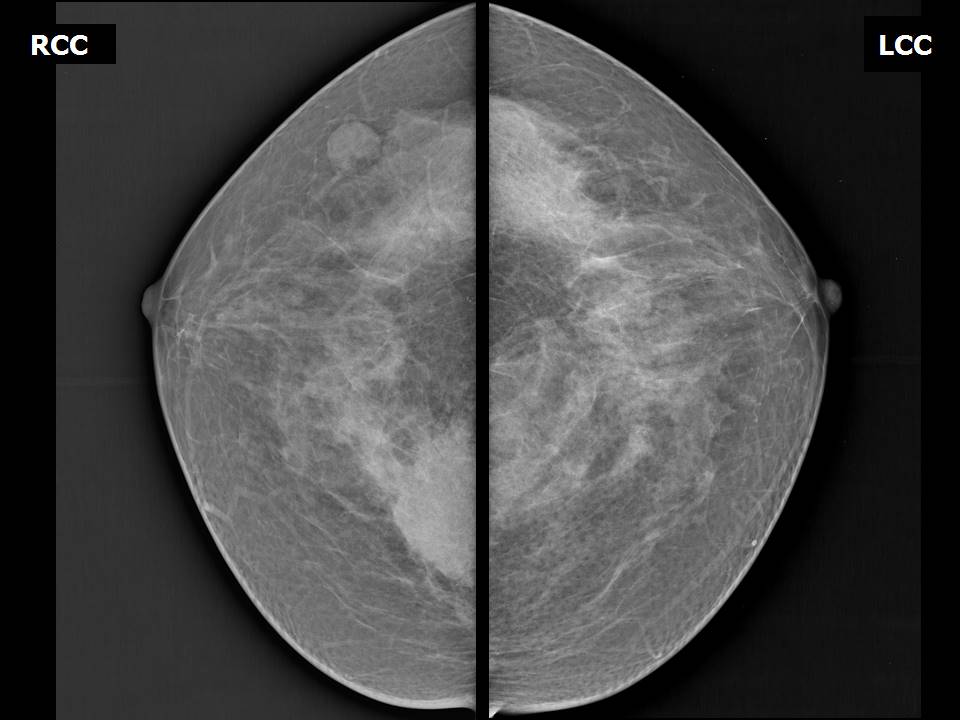
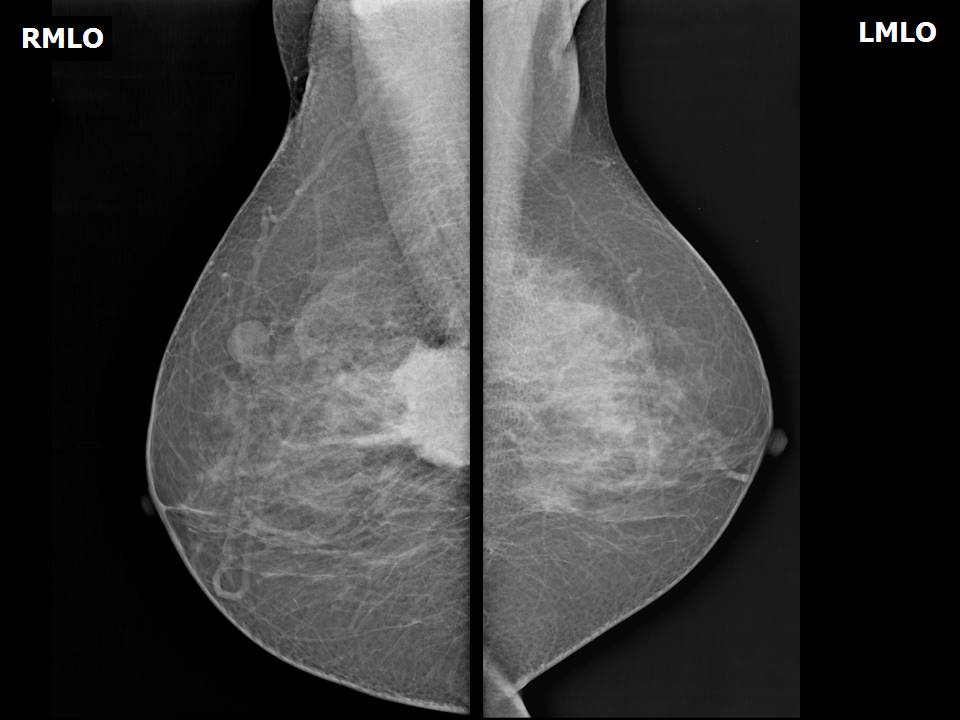
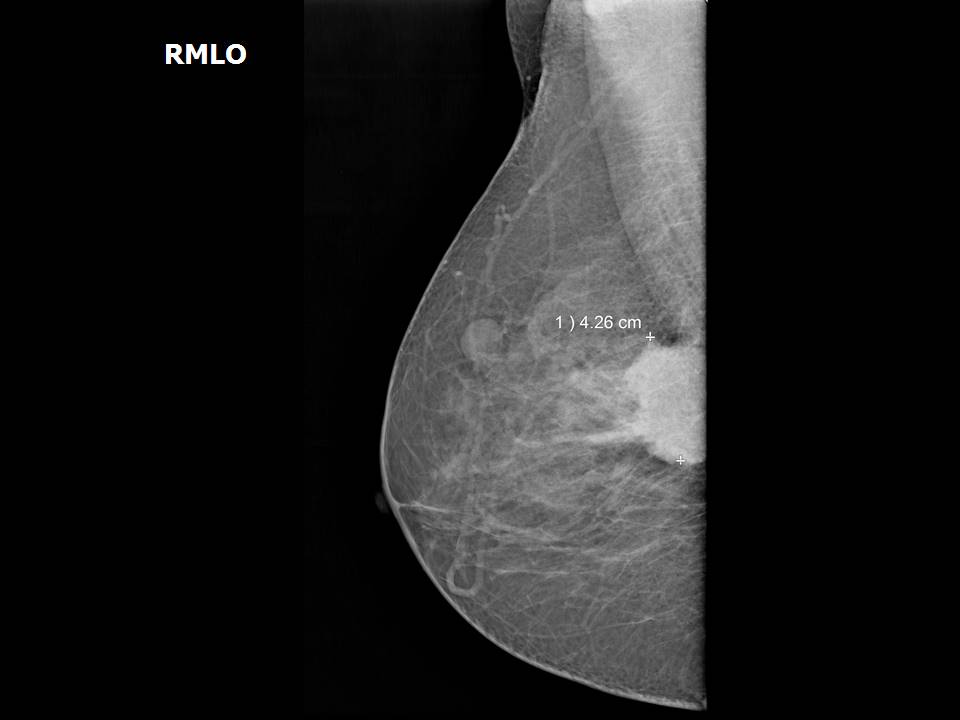
Mammography:
| Breast composition: | ACR category c (the breasts are heterogeneously dense, which may obscure small masses) | Mammography features: |
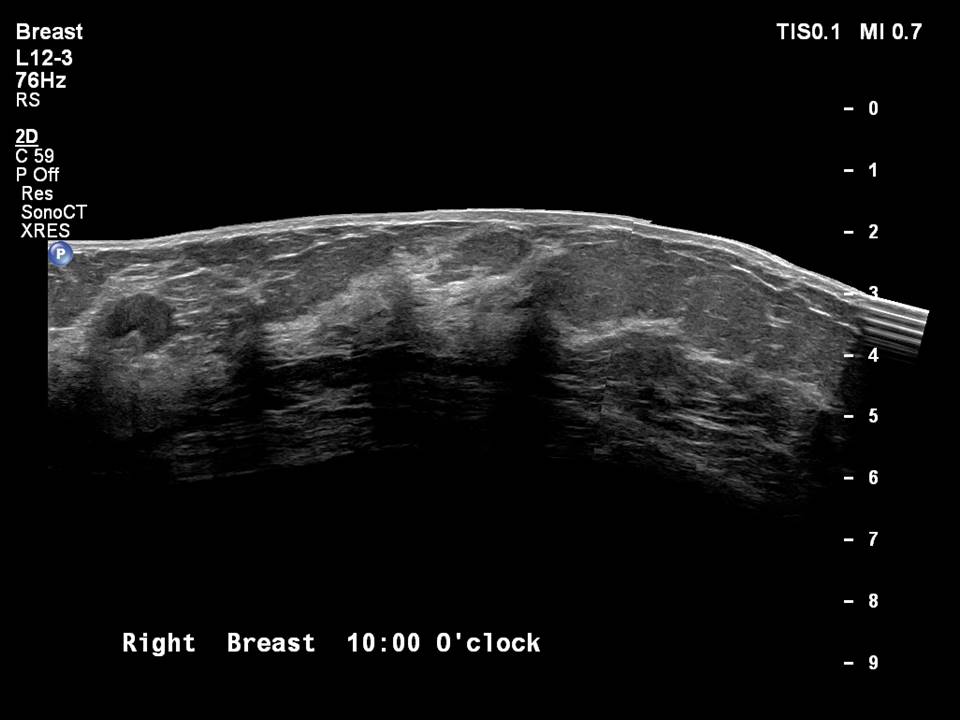
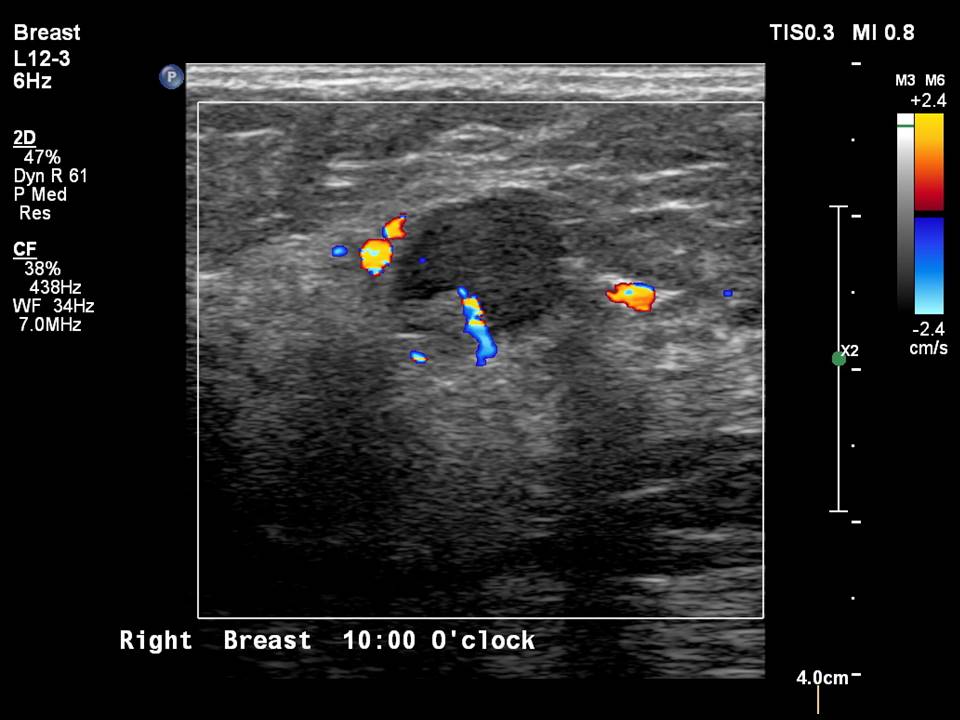
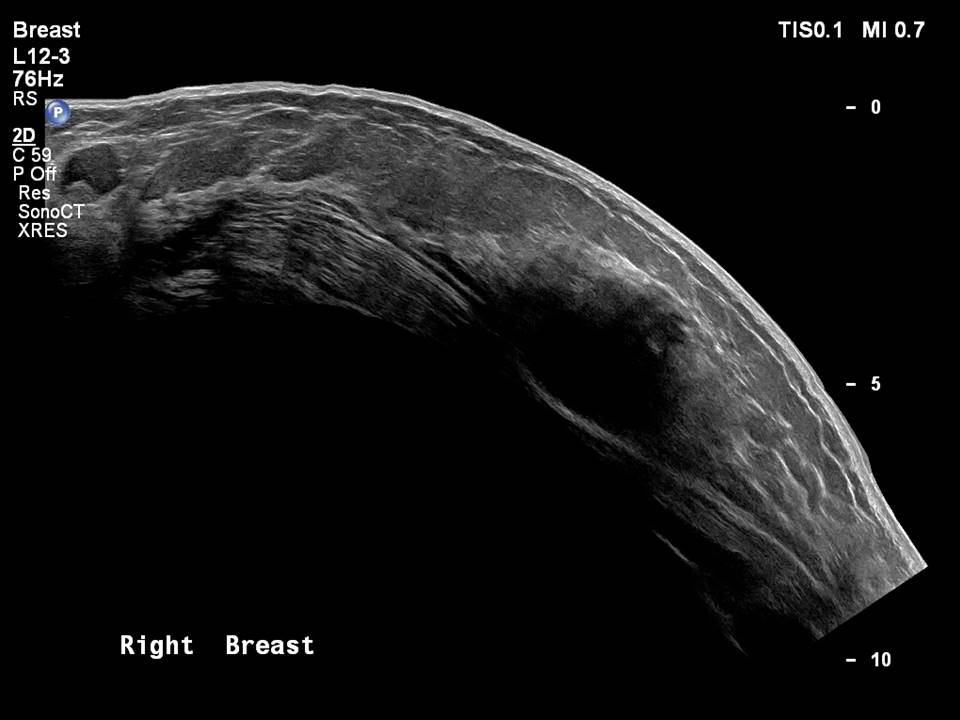
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Right breast, upper inner quadrant at 1–2 o’clock, posterior third with reactive intramammary node at 10 o’clock, middle third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 1, seen partially |
| • Size: | 4.3 × 4.0 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Margins: | Spiculated |
| • Density: | High |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | Enlarged (1.5 × 1.0 cm), with thickened cortex, 0.8 mm thick. Peripherally placed fatty hilum |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Enlarged intramammary node |
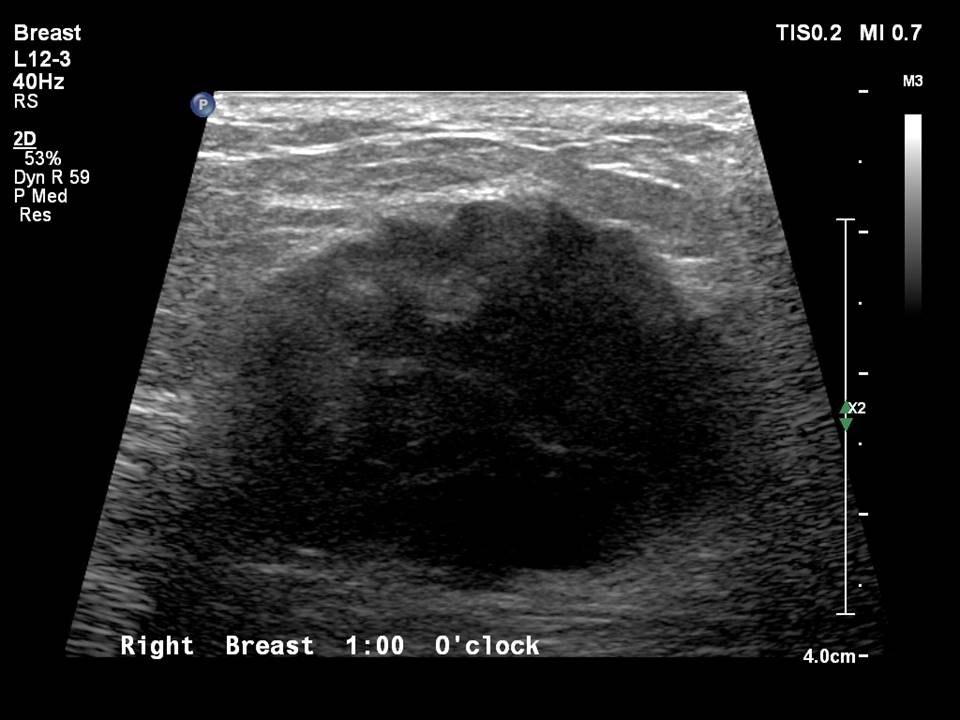
Ultrasound:
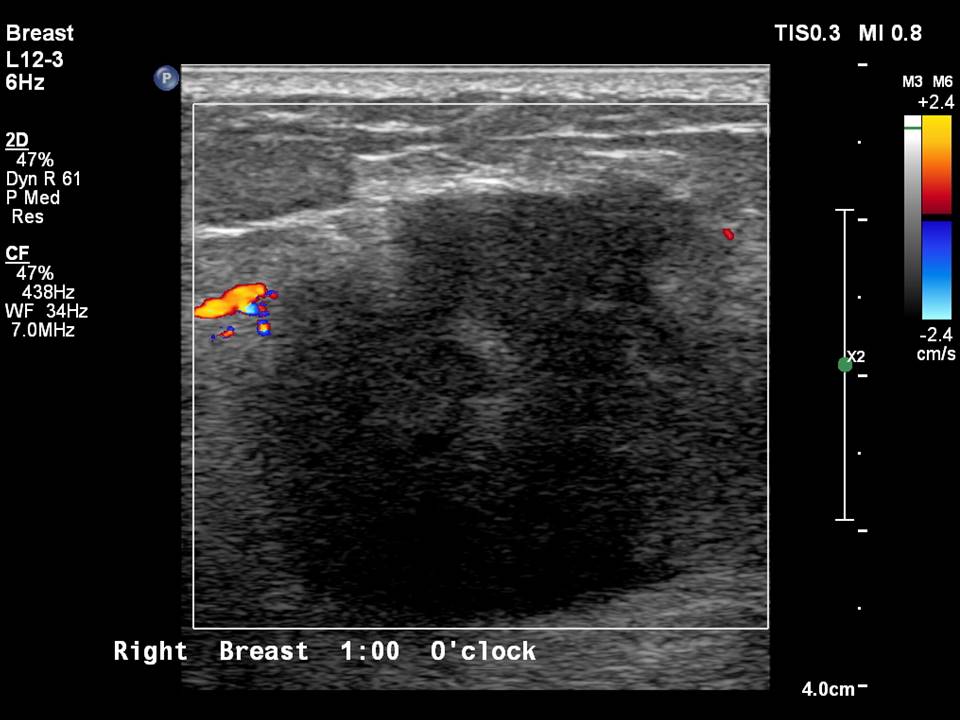
| Ultrasound features: Right breast, upper inner quadrant at 1–2 o’clock, 5.7 cm from the nipple and 2.0 cm skin depth | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Right breast, upper inner quadrant at 1–2 o’clock, 5.7 cm from the nipple and 2.0 cm skin depth |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 2.8 × 2.6 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Orientation: | Not parallel |
| • Margins: | Indistinct |
| • Echo pattern: | Hypoechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Peripheral vascularity in mass on colour flow mapping and enlarged reactive right intramammary node |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: 5 (highly suggestive of malignancy)Further assessment:
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytologyCytology:
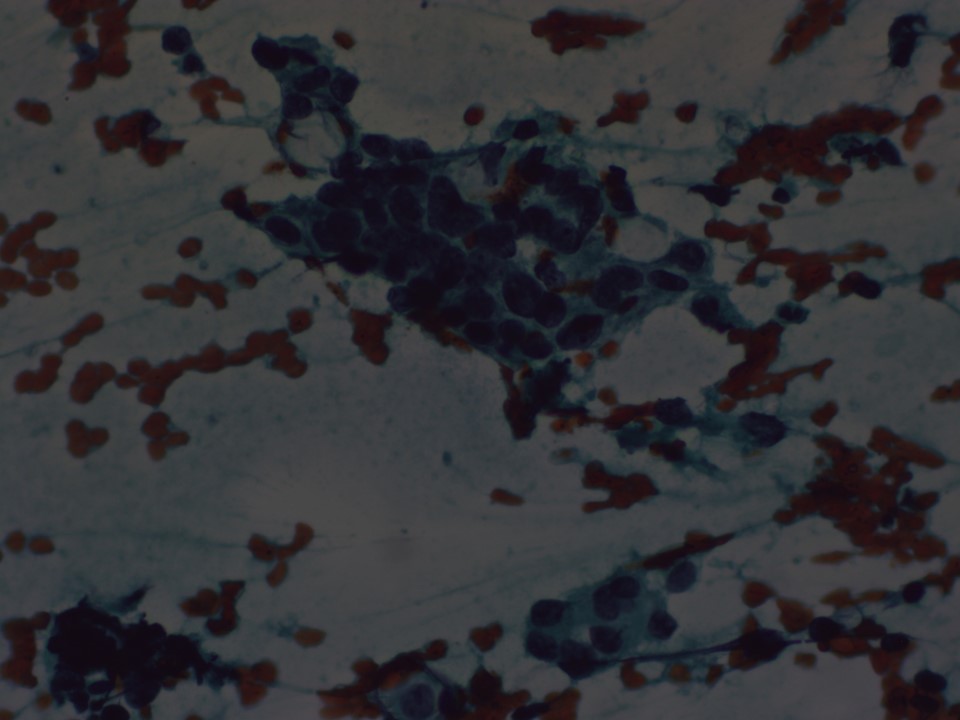
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Right |
| • Quadrant: | Upper inner |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | Whitish |
| ‣ Cytological description: | Smears reveal single isolated and dyscohesive sheets of ductal epithelial cells showing large, hyperchromatic, pleomorphic nuclei with prominent nucleoli. Cytoplasm is moderate to abundant |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Malignant |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Carcinoma breast |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
Histopathology:
MRM
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | MRM |
| ‣ Laterality: | Right |
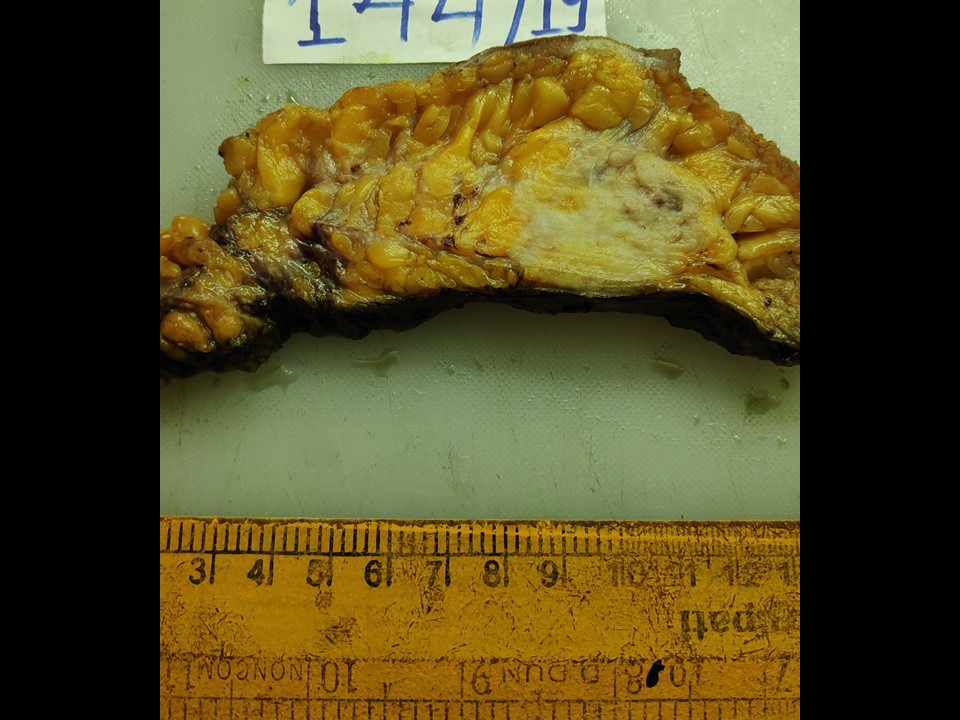
| ‣ Macroscopy: | Right MRM specimen (27 × 18 × 7 cm) with overlying skin flap measuring (12.0 × 5.5 cm). The nipple and areola are unremarkable. On serial sectioning, a well-circumscribed greyish white tumour (4.5 × 4.0 × 3.5 cm) is identified in the upper inner quadrant. It is located 3 cm from the skin and abutting onto the posterior margin of the resection grossly. A second irregular, greyish white, congested area (7.0 × 4.5 × 4.0 cm) was identified. It is 4 cm superolateral from the tumour and shows haemorrhagic and firm whitish areas. A third well-circumscribed nodule (1.5 cm in diameter) is seen lateral to the congested firm area above. The cut surface is greyish white. The attached axillary tail is 5 cm long. Thirteen lymph nodes were identified, the largest of which was 1.0 × 1.0 cm; the others range in size from 0.9 to 0.3 cm. Two apical nodes were also received separately |
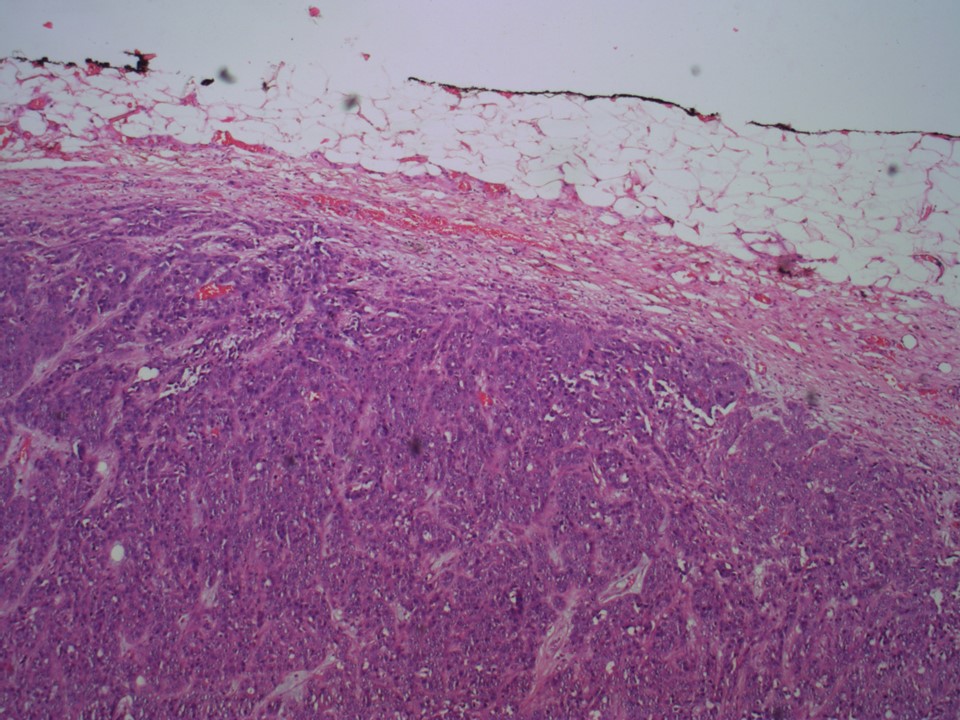
| ‣ Histological type: | Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type |
| ‣ Histological grade: | Grade 3 (3 + 3 + 2 = 8) |
| ‣ Mitosis: | 12 |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | 4.5 cm |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | 0/15 |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | Absent |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | Absent |
| ‣ Margins: | The invasive carcinoma is close to the base; however, the base is technically free microscopically (i.e. tumour is not on the ink and it is within 1 mm from the inked margin) |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | pT2N1 |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | ER negative, PR negative, and HER2 negative |
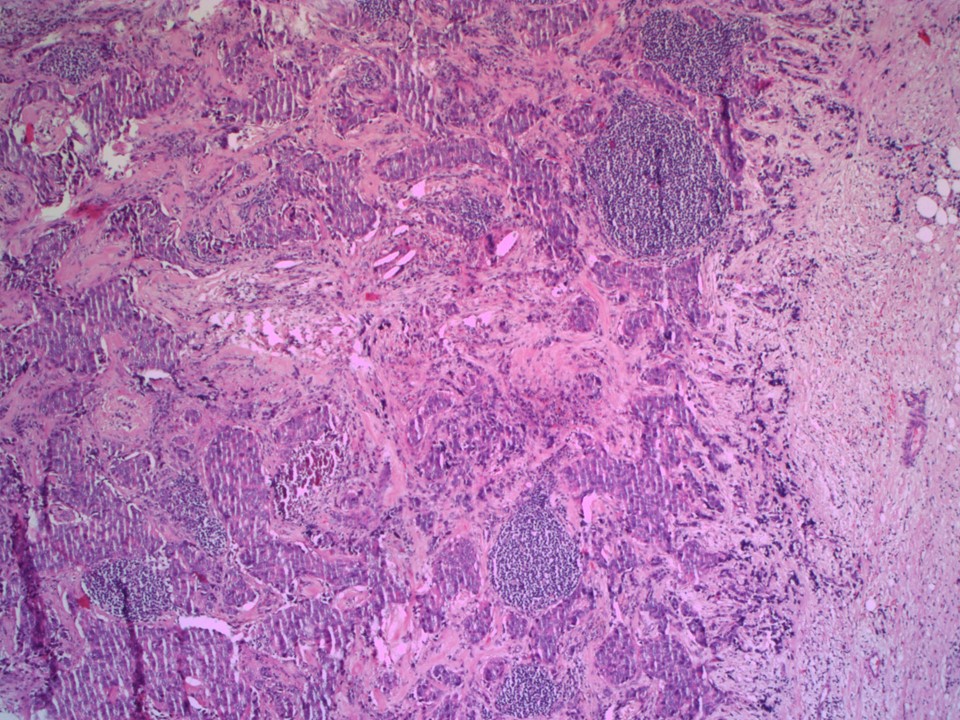
| ‣ Comments: | Because the tumour is close to the base, the pectoral sheath beyond the tumour base was excised for histopathology. Gross: An irregular, yellowish brown, flat flap-like, soft tissue bit (6.0 × 3.0 × 0.8 cm) with two other smaller bits (both 1.5 × 1.0 × 0.8 cm). The cut sections of all show reddish brown areas. Microscopy: Sections showed only fibroadipose and muscle tissue, with no evidence of tumour. Two intramammary nodes show extensive metastases with tumour extending through the nodal capsule into surrounding breast tissue. None of the 15 axillary nodes were involved by metastases. According to the 8th edition of the AJCC Staging Manual, intramammary nodes are included with axillary nodes for staging |
Case summary:
| Premenopausal woman presented with right breast lump. Diagnosed as right breast carcinoma with metastatic intramammary node, BI-RADS 5 on imaging, as right breast carcinoma and axillary metastasis on cytology, and as invasive breast carcinoma of no special type, pT2N1 on histopathology. |
Learning points:
|