Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Filter by language: English / Русский
Go back to the list of case studies
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
| Case number: | 185 |
| Age: | 72 |
| Clinical presentation: | Postmenopausal woman with average risk of developing breast cancer presented with left axillary lump. Clinical examination revealed non tender, mobile lump in the left axilla, no palpable breast lump was detected. |
Mammography:
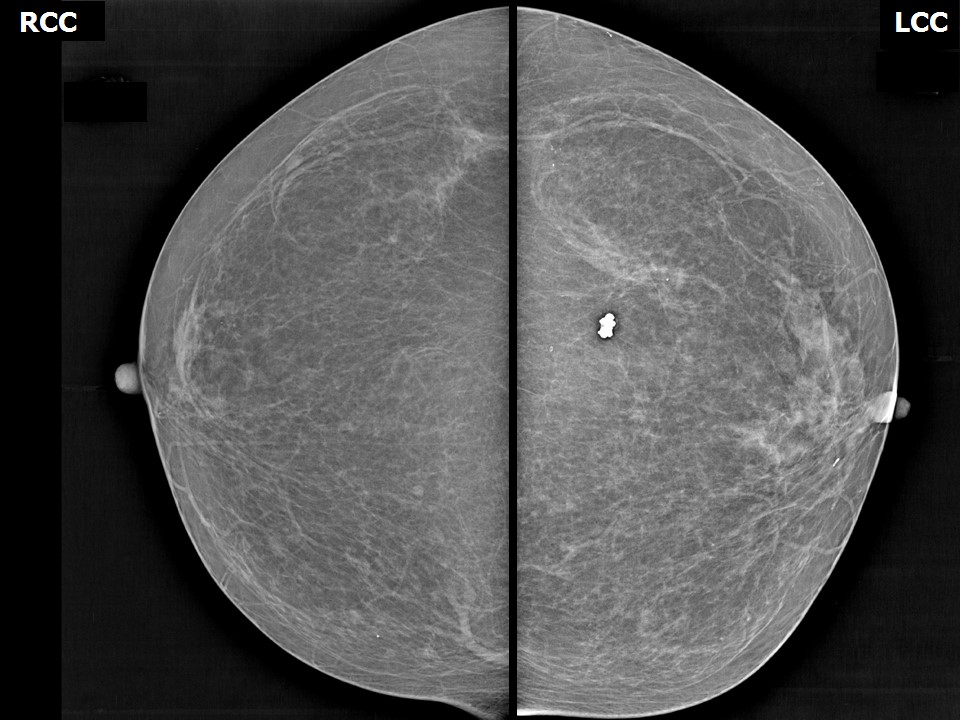
| Breast composition: | ACR category a (the breasts are almost entirely fatty) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Left breast, upper outer quadrant at 2 o’clock, anterior third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 0 |
| • Size: | None |
| • Shape: | None |
| • Margins: | None |
| • Density: | None |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | Pleomorphic |
| • Distribution: | Regional |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
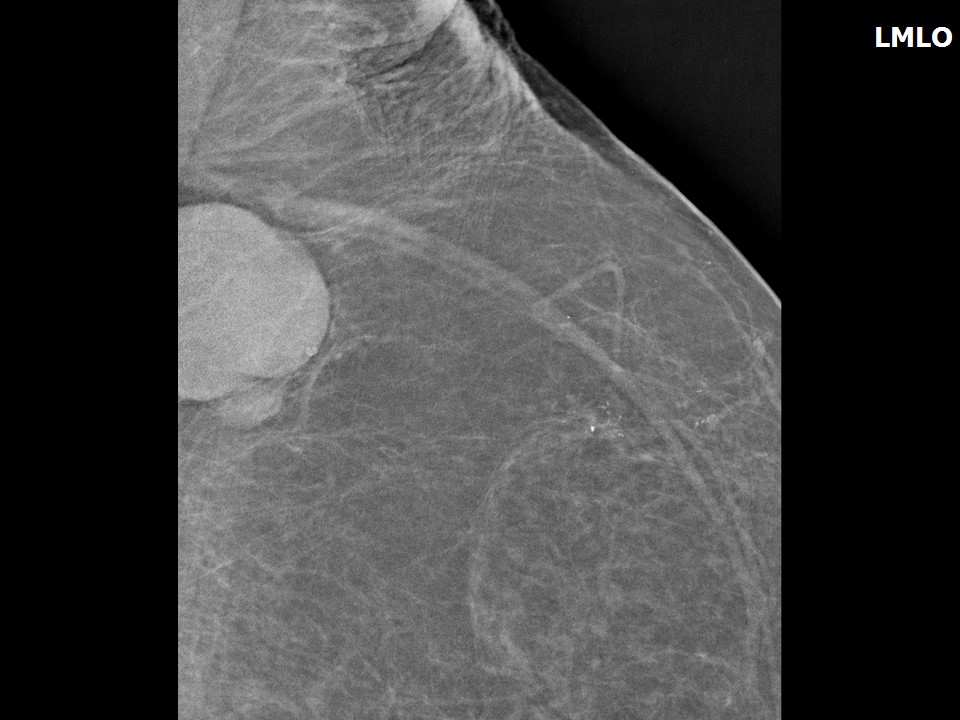
| ‣ Associated features: | Enlarged dysmorphic axillary node |
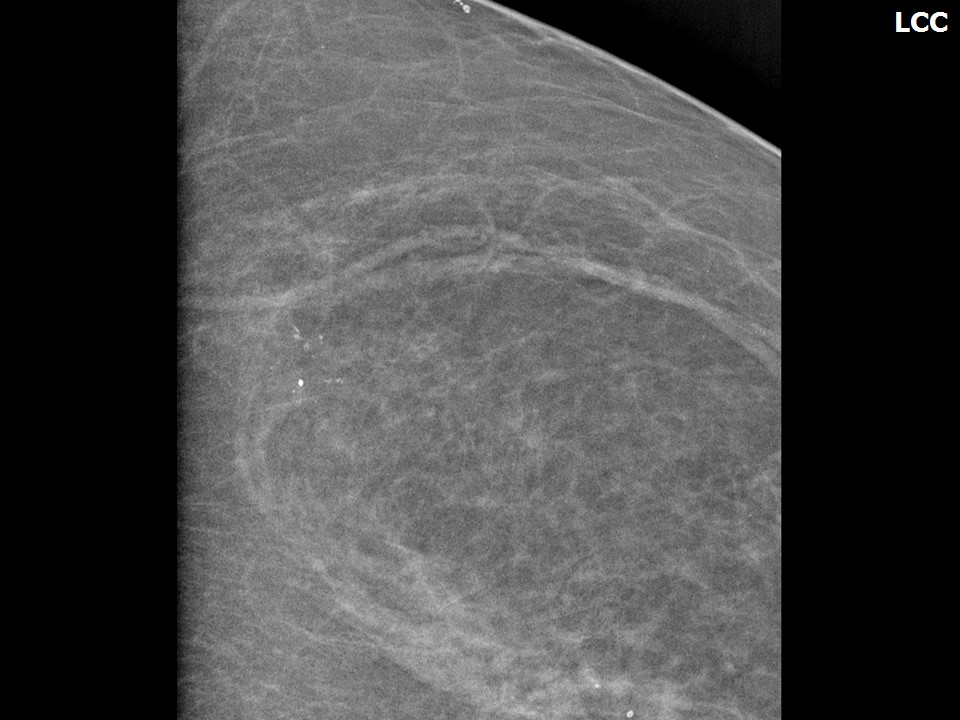
| Breast composition: | ACR category a (the breasts are almost entirely fatty) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Left breast, upper outer quadrant at 1 o’clock, middle third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 0 |
| • Size: | None |
| • Shape: | None |
| • Margins: | None |
| • Density: | None |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | Round, monomorphic |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | Diffuse |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | None |
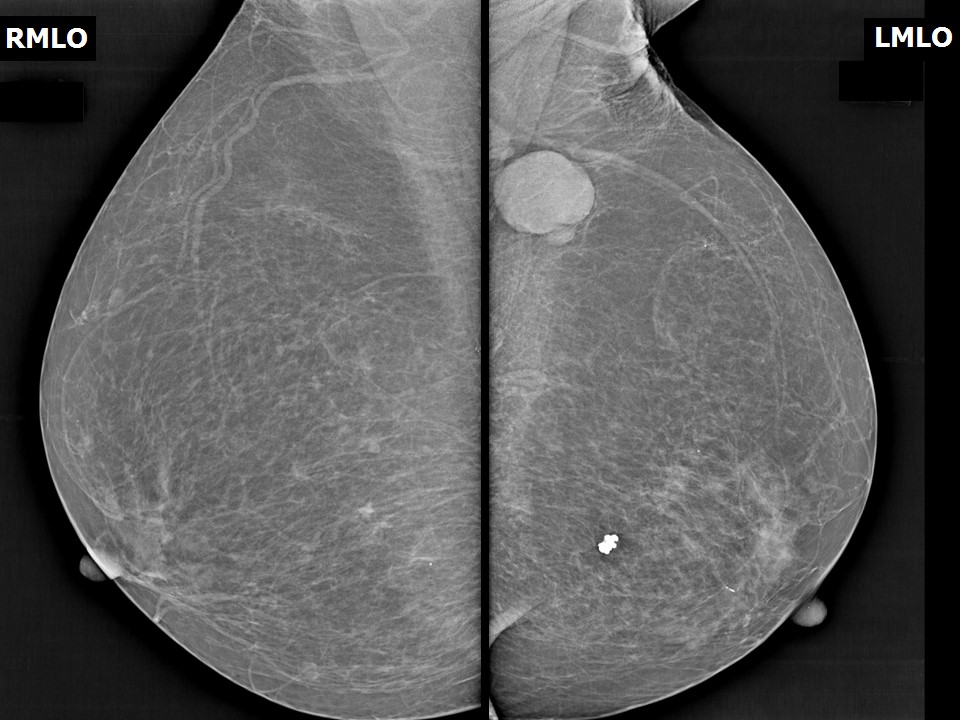
| Breast composition: | ACR category a (the breasts are almost entirely fatty) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Left breast, lower outer quadrant at 5 o’clock, posterior third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 0 |
| • Size: | None |
| • Shape: | None |
| • Margins: | None |
| • Density: | None |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | Popcorn-like macrocalcifications |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | None |
Ultrasound:
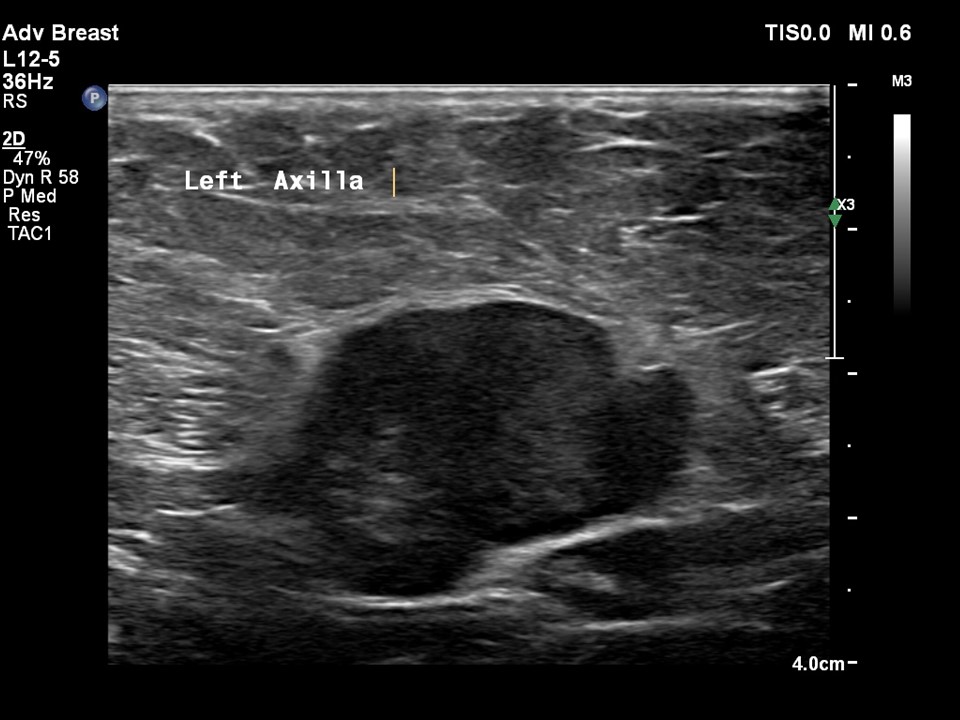
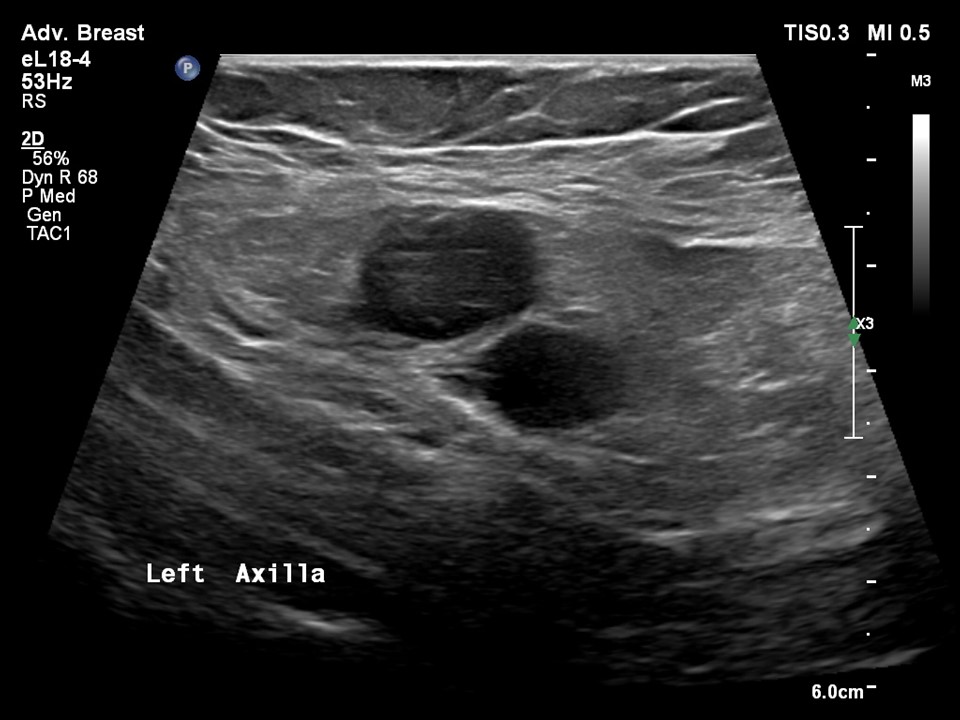
| Ultrasound features: Left axilla | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Left axilla |
| • Number: | Multiple |
| • Size: | 4.0 × 3.0 cm (largest) |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Orientation: | None |
| • Margins: | Indistinct |
| • Echo pattern: | Hypoechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
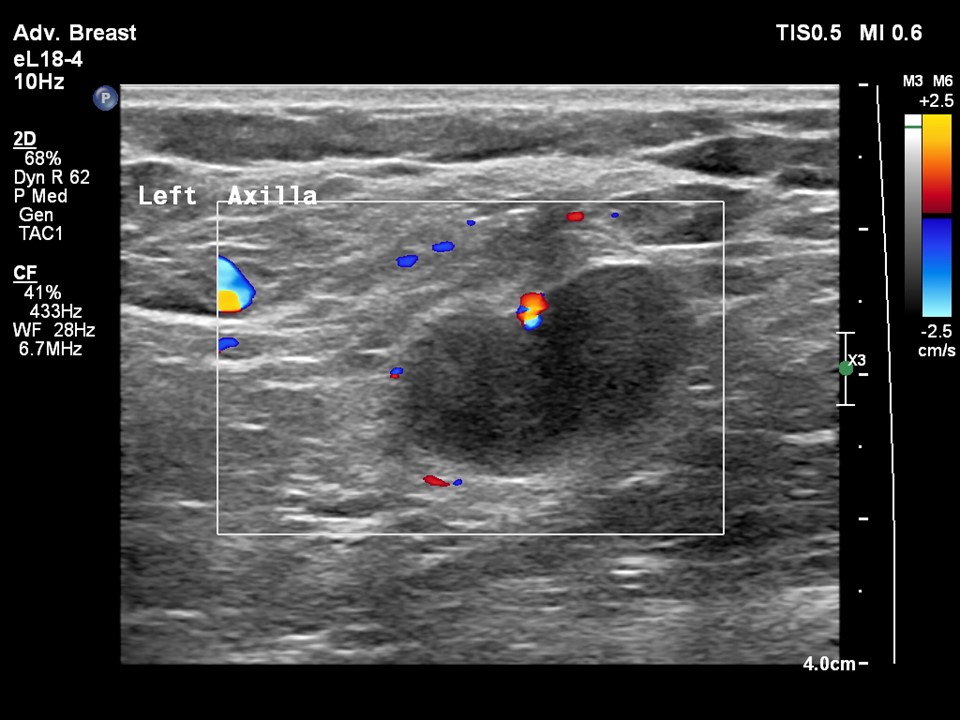
| ‣ Associated features: | Axillary dysmorphic lymphadenopathy with non-hilar vascularity on colour flow mapping |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: 4C (high suspicion for malignancy)Further assessment:
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytology, for core biopsy and further imaging with breast MRICytology:
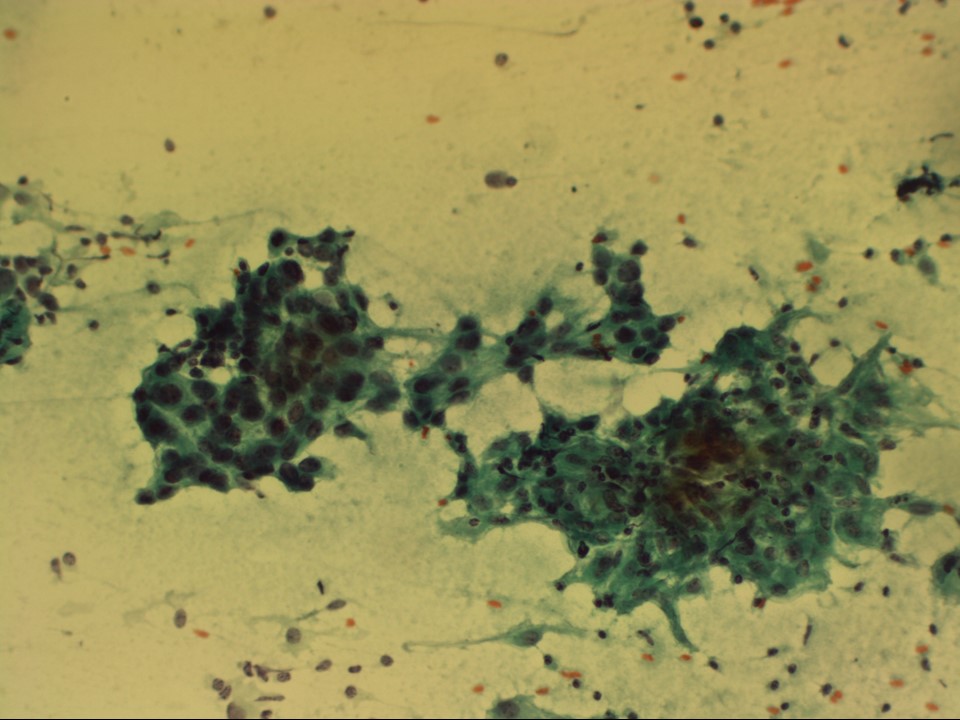
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Left axillary node |
| • Quadrant: | No lump in breast |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | Whitish |
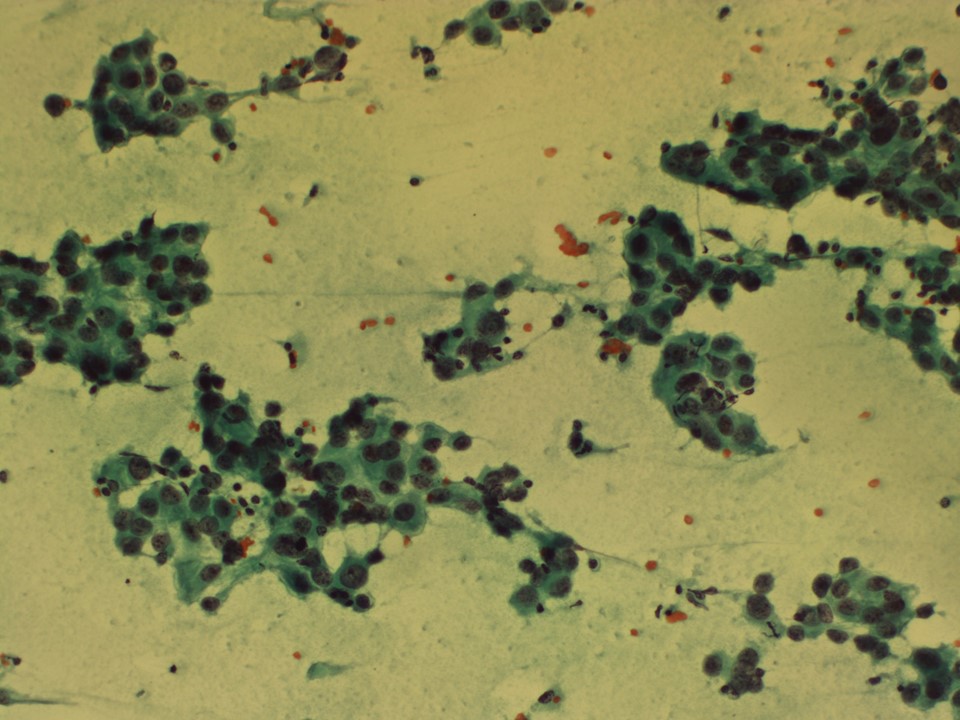
| ‣ Cytological description: | Smears reveal many loosely cohesive clusters and many singly scattered large malignant epithelial cells. These cells have hyperchromatic pleomorphic nuclei and coarse chromatin. Nucleoli are inconspicuous. There is moderate amphophilic cytoplasm. Background shows many lymphocytes and a few epithelioid cell conglomerates. There is no necrosis |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Malignant |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Left axillary lump, metastasis of adenocarcinoma with granulomatous inflammation in the background. Distant metastasis is suggested. Primary should be looked for in the breast, lung, or gastrointestinal tract |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
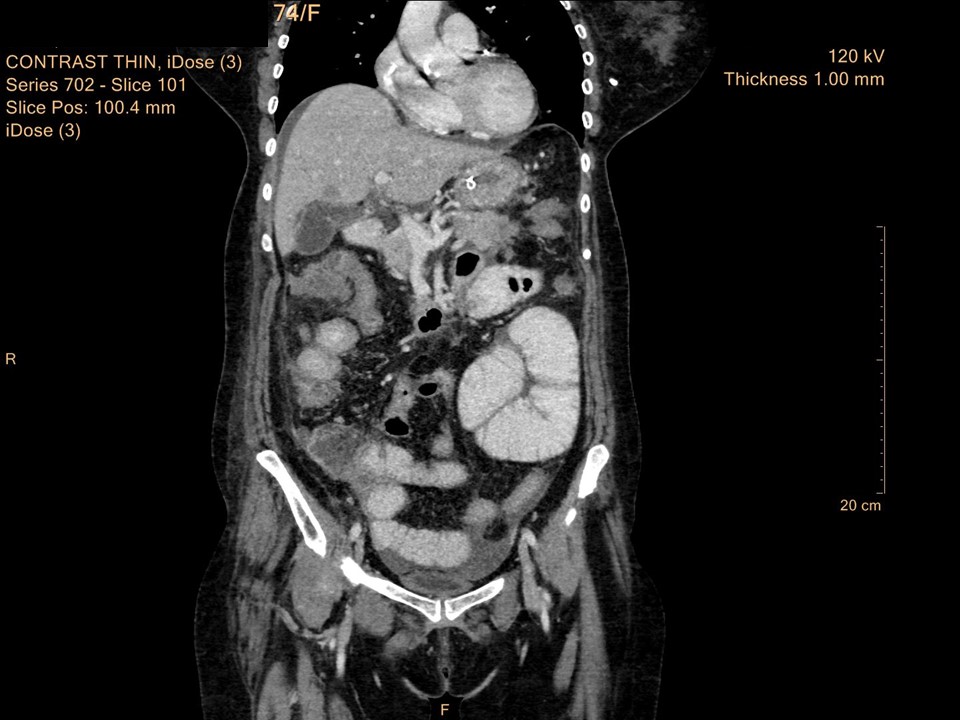
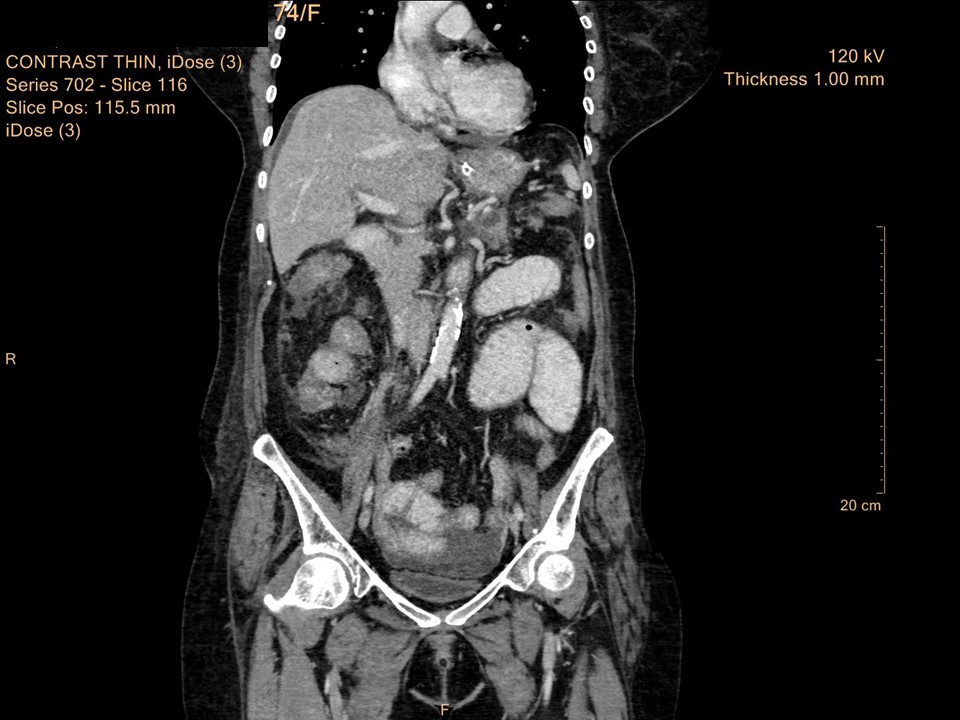
Systemic workup to look for primary: Contrast-enhanced CT scan of abdomen and pelvis was performed:
Case summary:
| Postmenopausal woman presented with lump in left axilla. Mammography and breast ultrasound revealed left breast regional calcifications with enlarged dysmorphic left axillary nodes, likely metastatic nodes. BI-RADS category 4C on imaging. Cytology of left axillary node showed metastasis of adenocarcinoma with granulomatous inflammation in the background and it was advised to look for primary in the breast, lung, or gastrointestinal tract. Further systemic workup on contrast-enhanced CT scan of abdomen and pelvis to look for primary revealed right hepatic flexure colonic mass, features suspicious of malignancy. Final histopathology diagnosis: adenocarcinoma colon pT4. |
Learning points:
|