Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Filter by language: English / Русский
Go back to the list of case studies
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
| Case number: | 177 |
| Age: | 39 |
| Clinical presentation: | Premenopausal woman with average risk of developing breast cancer presented with a left breast areolar nodule. On examination, there was expressible serous discharge from the left nipple. |
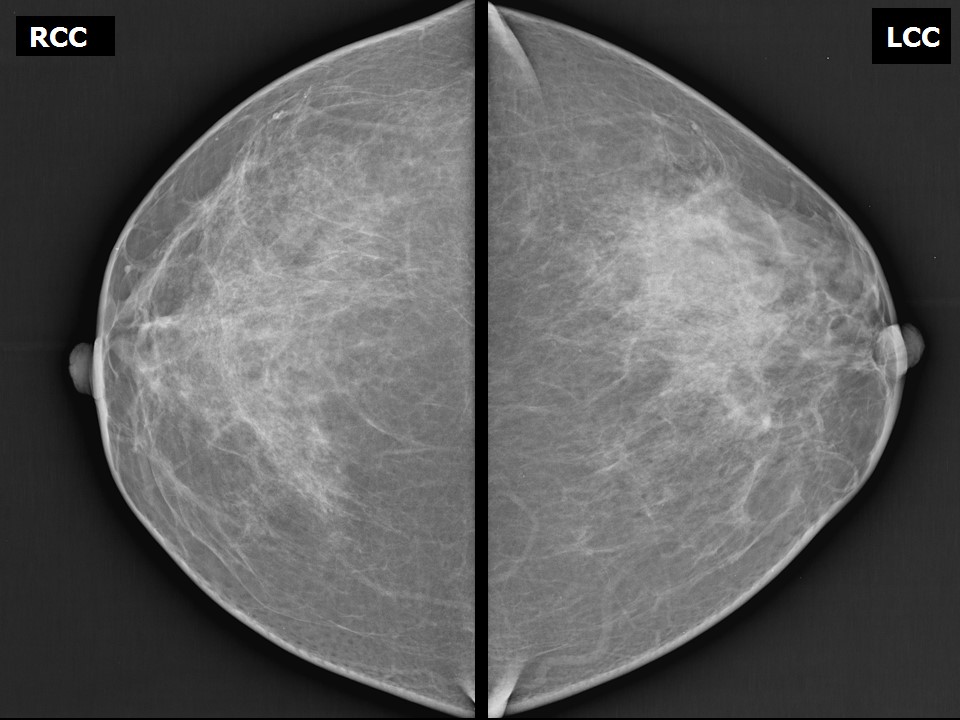
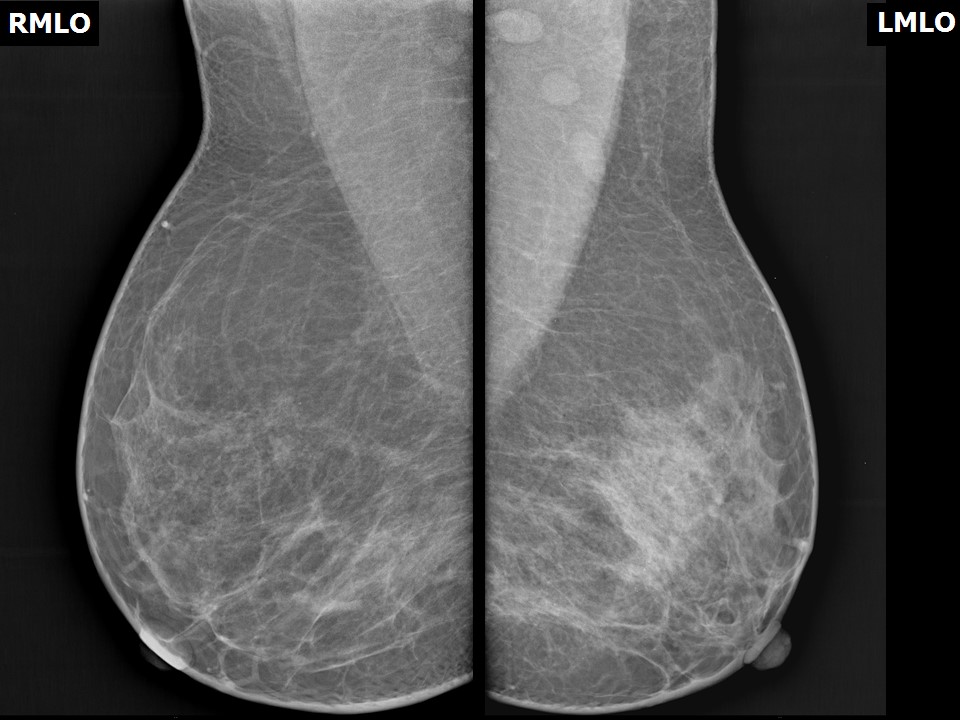
Mammography:
| Breast composition: | ACR category b (there are scattered areas of fibroglandular density) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Left breast, central portion of the breast, anterior third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | No mass |
| • Shape: | None |
| • Margins: | None |
| • Density: | None |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | Focal |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Solitary dilated duct |
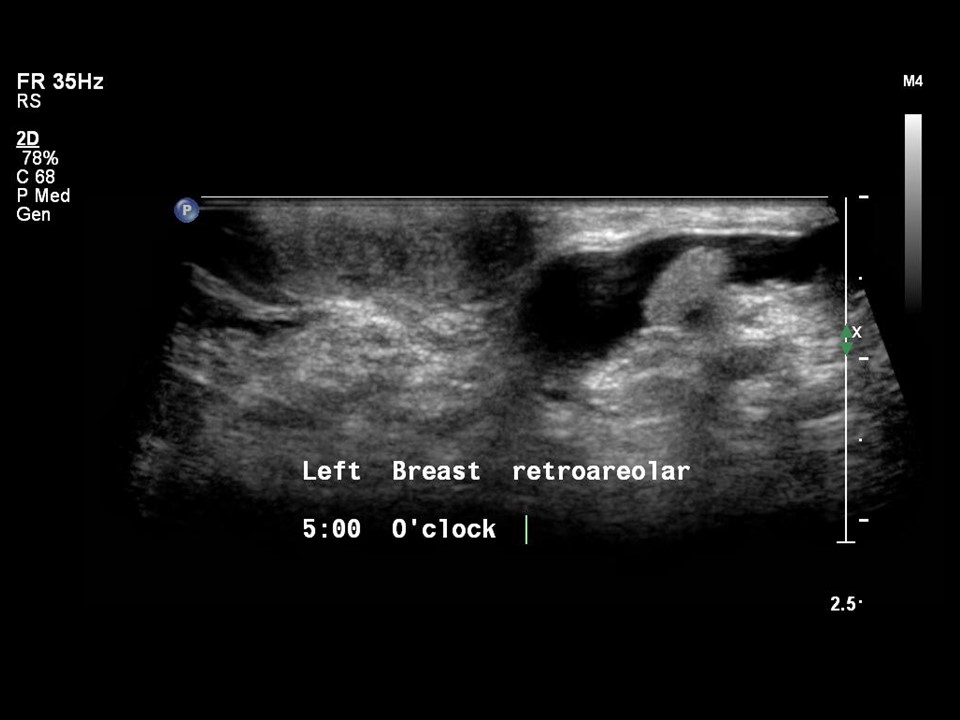
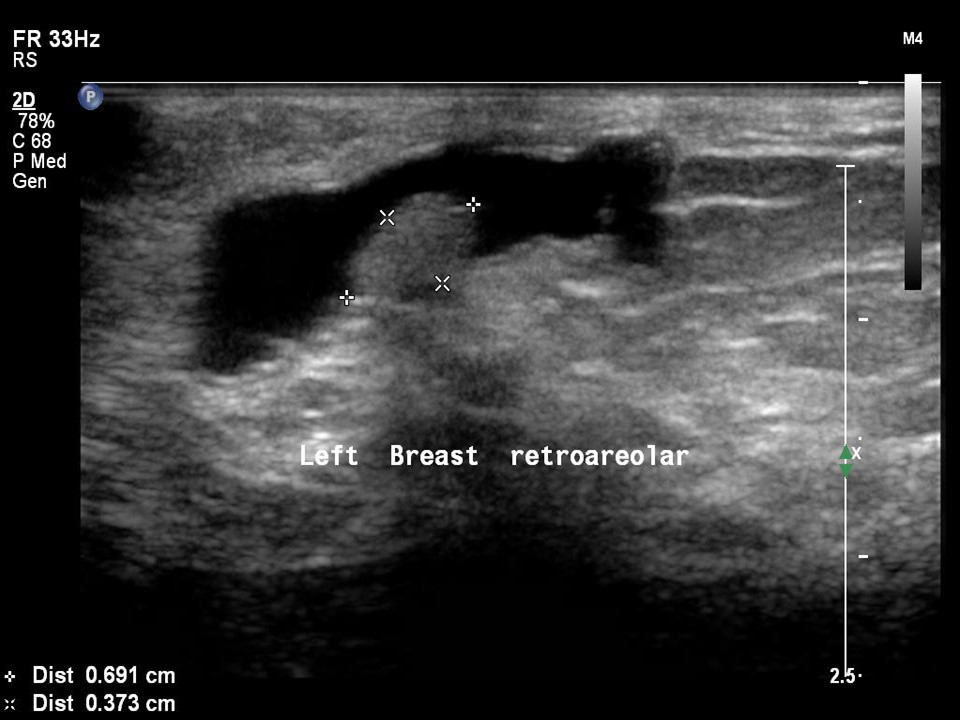
Ultrasound:
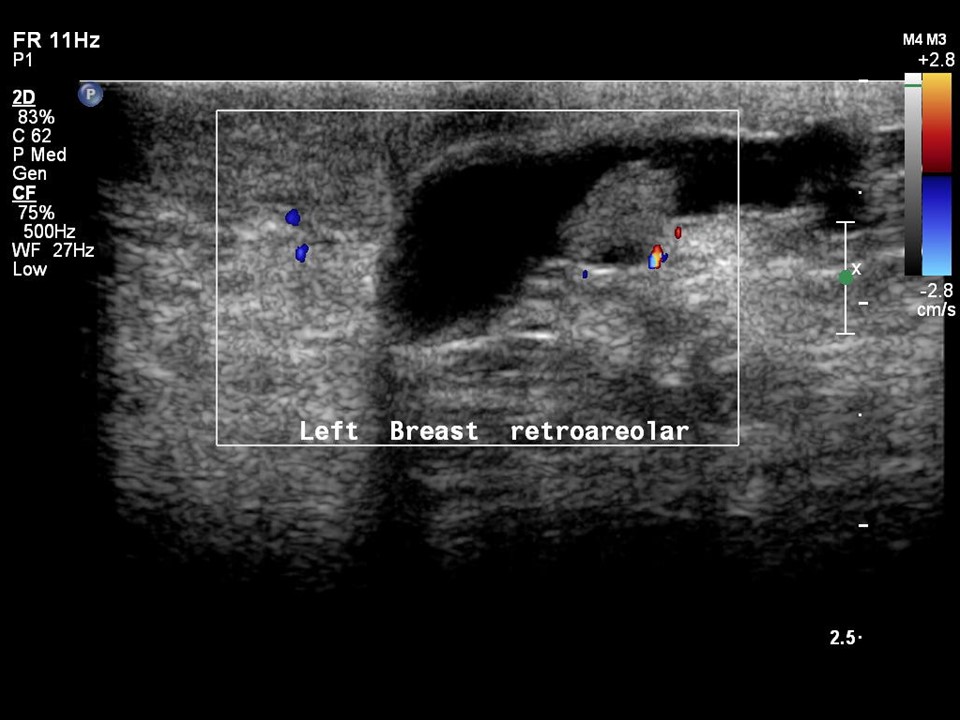
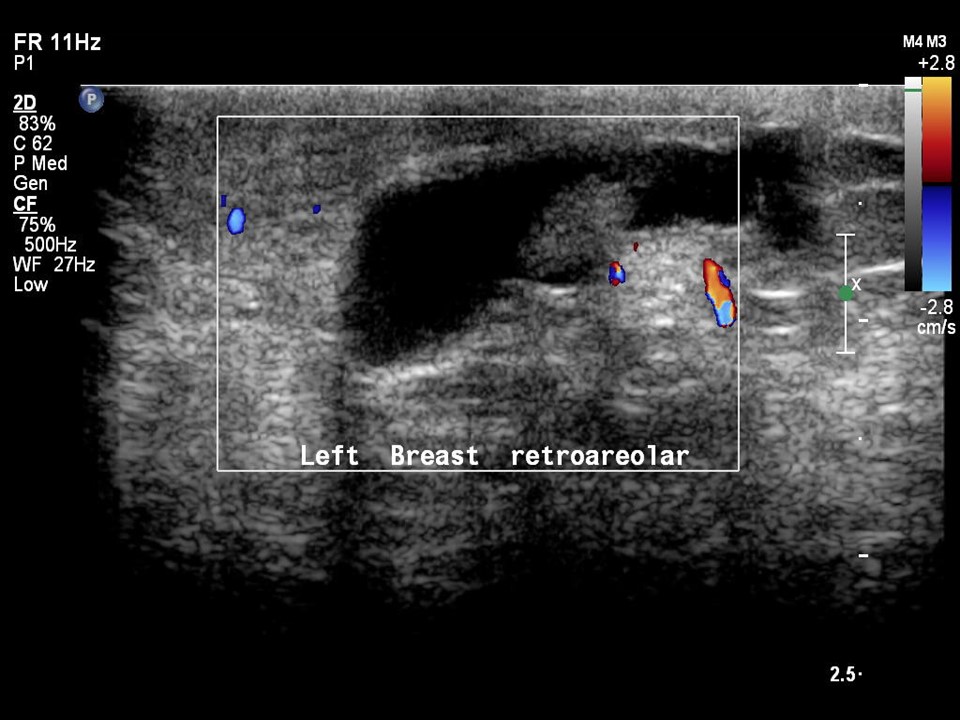
| Ultrasound features: Intraductal lesion in solitary dilated duct in left subareolar region, lower outer quadrant at 5 o’clock | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Intraductal lesion in solitary dilated duct in left subareolar region, lower outer quadrant at 5 o’clock |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 1.0 × 4.0 cm |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Orientation: | Parallel |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed |
| • Echo pattern: | Hypoechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Solitary dilated duct |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: 4A (low level of suspicion for malignancy)Further assessment:
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytologyCytology:
| Cytology features: | |
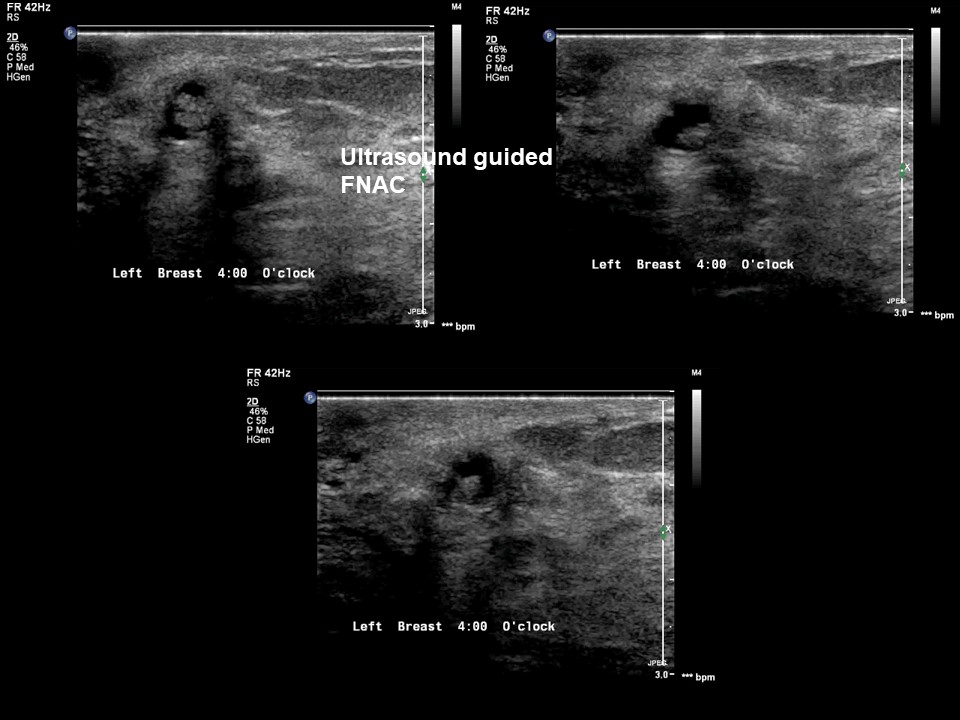
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Left |
| • Quadrant: | Retroareolar lump |
| • Localization technique: | Ultrasound-guided FNAC of intraductal lesion |
| • Nature of aspirate: | Whitish |
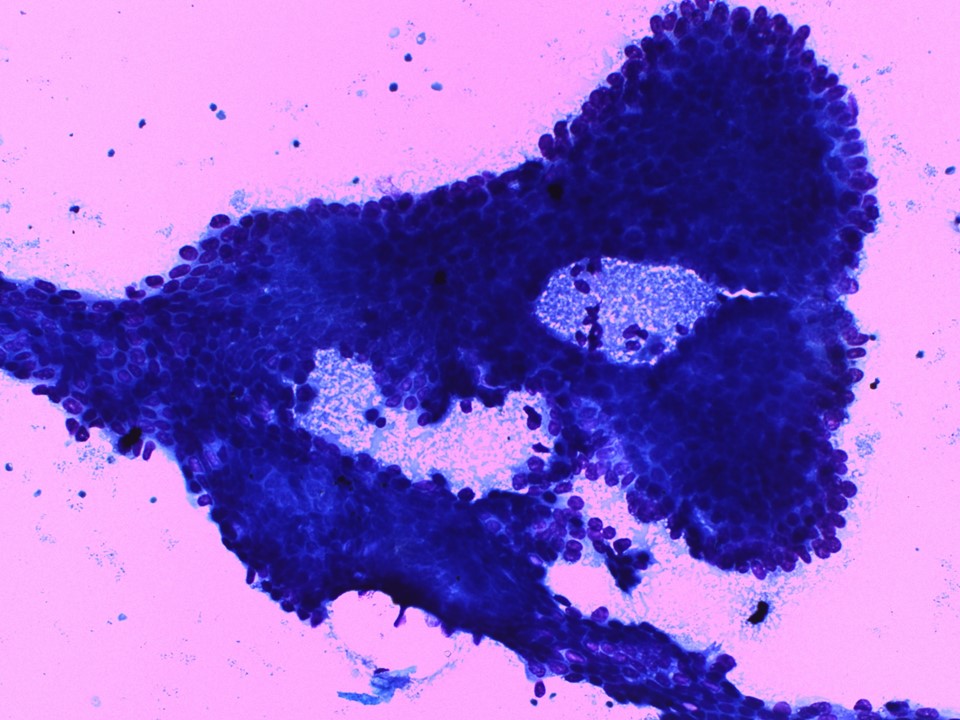
| ‣ Cytological description: | Smears are moderately cellular. Three-dimensional papillary groups with fibrovascular cores are seen. Flat sheets of ductal cells with myoepithelial cells are also present. Background shows foamy macrophages, apocrine metaplasia, and some inflammatory cells |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Atypical, probably benign |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Papillary neoplasm, favour benign |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
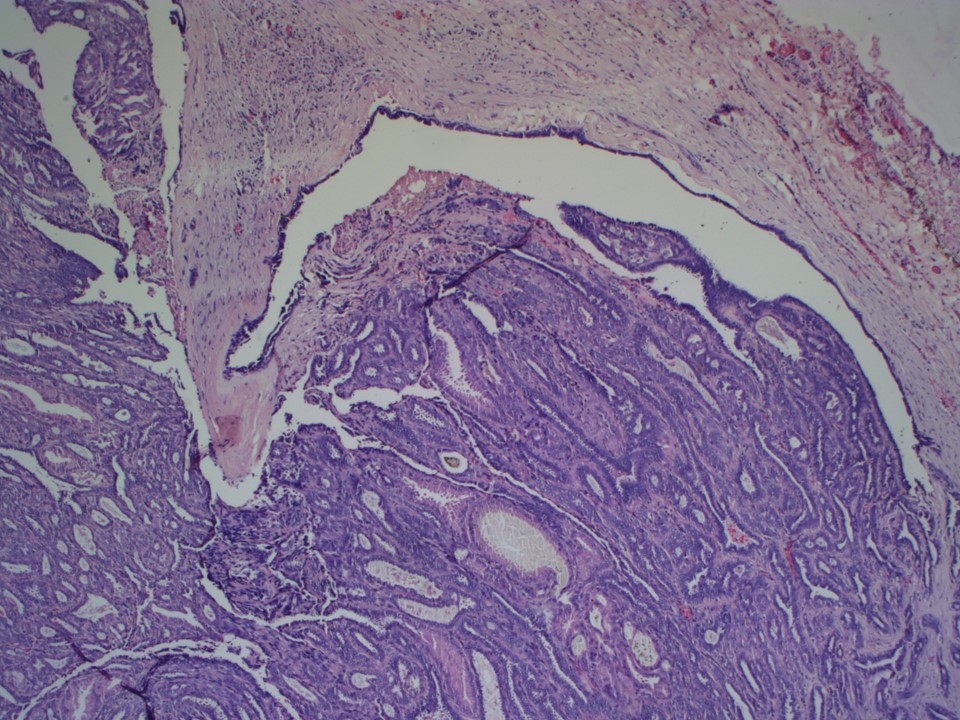
Histopathology:
Microdochectomy
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | Microdochectomy |
| ‣ Laterality: | Left |
| ‣ Macroscopy: | Microdochectomy specimen (2.0 × 2.0 ×1.5 cm) with apex marked with suture. On opening, a dilated duct with a small polypoid nodule (0.8 × 0.7 × 0.4 cm) was seen |
| ‣ Histological type: | Intraductal papilloma |
| ‣ Histological grade: | |
| ‣ Mitosis: | |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | |
| ‣ Margins: | |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | |
| ‣ Comments: |
Case summary:
| Premenopausal woman presented with left breast, expressible serous nipple discharge. Diagnosed as left breast subareolar solitary dilated duct with intraductal lesion, BI-RADS 4A on imaging, as benign proliferative change on cytology, and as papilloma on histopathology. |
Learning points:
|