Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Filter by language: English / Русский
Go back to the list of case studies
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
| Case number: | 019 |
| Age: | 71 |
| Clinical presentation: | Postmenopausal woman with average risk of developing breast cancer presented with left nipple retraction first noticed 2 months ago. |
Mammography:
| Breast composition: | ACR category a (the breasts are almost entirely fatty) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Left breast, central portion of the breast, central zone, middle third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 2.6 × 2.3 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Margins: | Spiculated |
| • Density: | Equal |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | Focal |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Retracted nipple and skin thickening |
Ultrasound:
| Ultrasound features: Left breast, central portion of the breast | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Left breast, central portion of the breast |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 1.7 × 1.5 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Orientation: | Not parallel |
| • Margins: | Angular |
| • Echo pattern: | Hypoechoic |
| • Posterior features: | Posterior shadowing |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Nipple retraction, skin thickening |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: 5 (highly suggestive of malignancy)Further assessment:
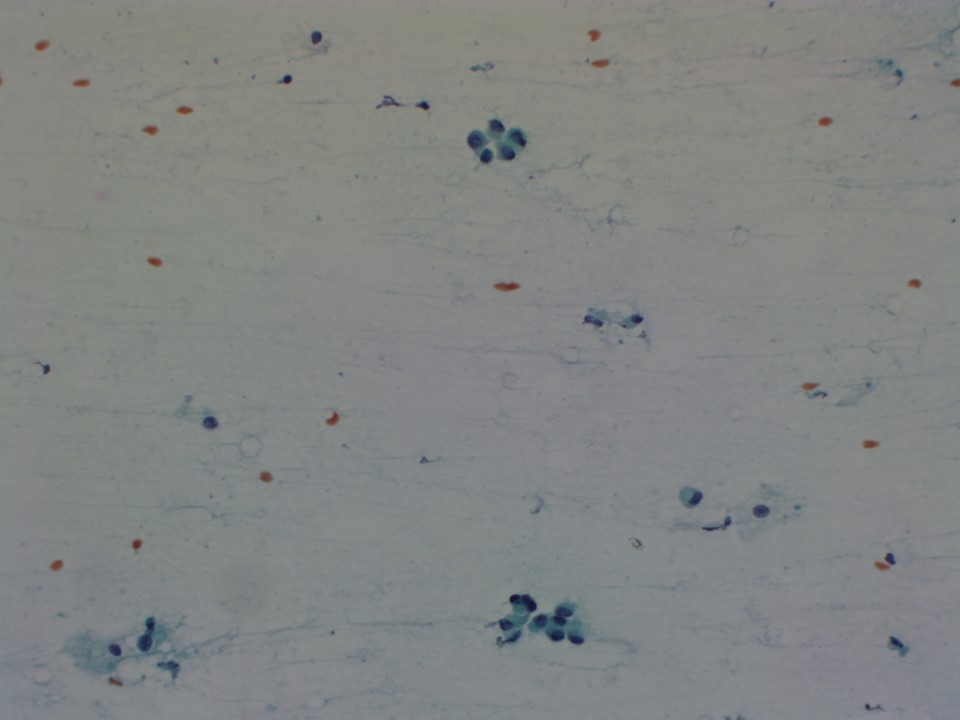
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytologyCytology:
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Left |
| • Quadrant: | Retroareolar lesion |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | 0.2 mL of yellowish greasy fluid |
| ‣ Cytological description: | Cellular smears reveal sheets of benign ductal epithelial cells, occasional cells show anisonucleosis and increased nuclear–cytoplasmic (N:C) ratio. Isolated and loosely cohesive cells are also present showing mild anisonucleosis. Background shows proteinaceous material and foamy macrophages |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Suspicious, probably in situ or invasive carcinoma |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Smears are suspicious for malignancy. Advised repeat ultrasound-guided FNAC or core biopsy to confirm malignancy |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
Histopathology:
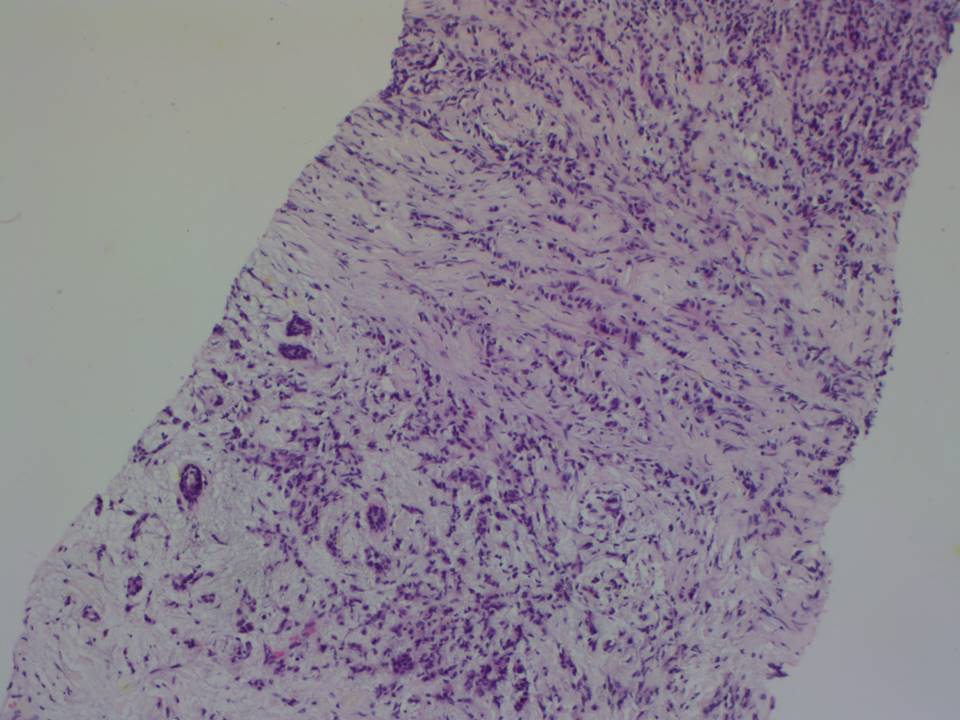
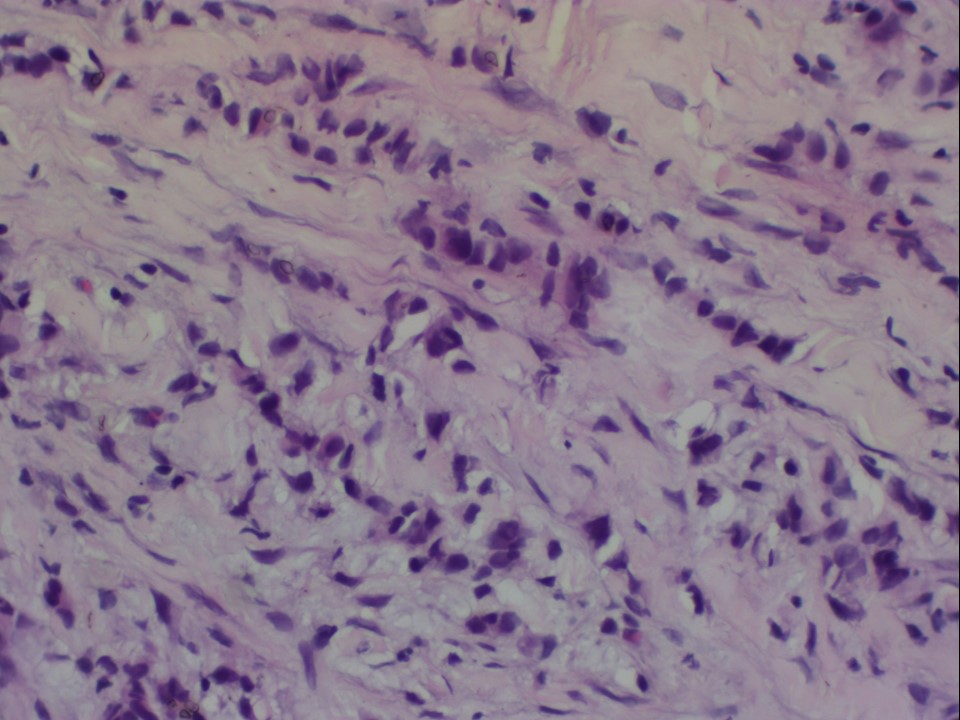
Core needle biopsy
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | Core needle biopsy |
| ‣ Laterality: | Left |
| ‣ Macroscopy: | Five cores: longest is 15 mm in length and smallest is 6 mm in length |
| ‣ Histological type: | Invasive lobular carcinoma |
| ‣ Histological grade: | Grade 2 (3 + 2 + 1 = 6) |
| ‣ Mitosis: | 4 |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | |
| ‣ Margins: | |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | |
| ‣ Comments: |
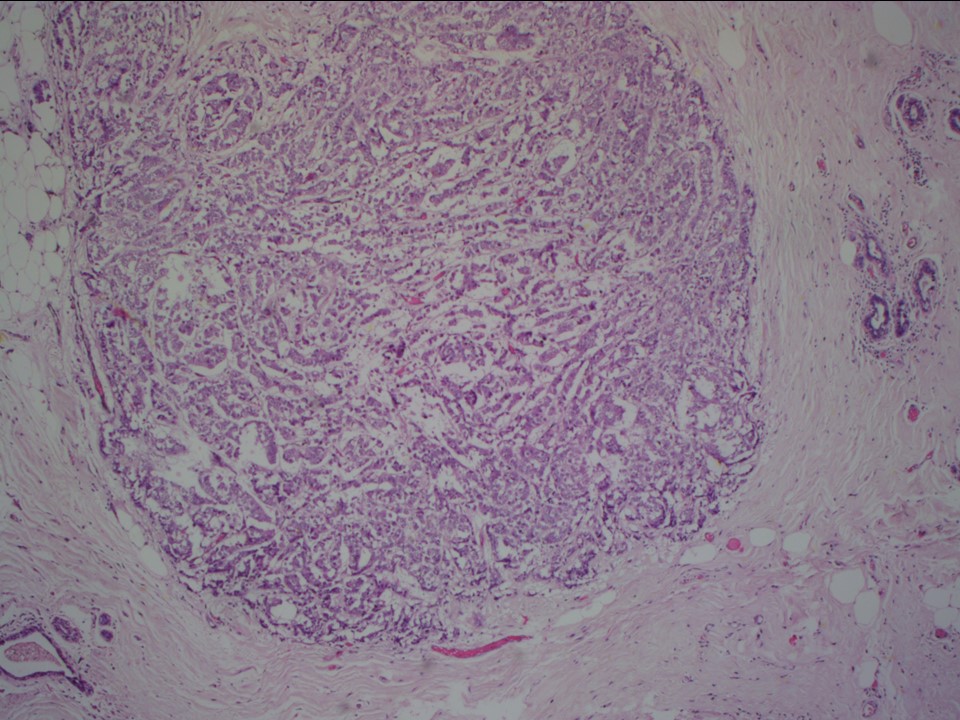
MRM
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | MRM |
| ‣ Laterality: | Left |
| ‣ Macroscopy: | MRM specimen 20.5 × 17.5 × 4.0 cm, with overlying skin flap 10.0 × 3.5 cm. The nipple and areola appear to be mildly retracted. On serial sectioning, a tumour (2.9 × 2.8 × 2.5 cm) is identified, located in the retroareolar region. It is 1.3 cm from the skin and 1.3 cm from the base. Firm whitish fibrous areas (5.0 × 2.0 × 1.0 cm) are seen adjacent to the tumour, located 1.3 cm from the tumour |
| ‣ Histological type: | Invasive lobular carcinoma |
| ‣ Histological grade: | Grade 2 (3 + 2 + 1 = 6) |
| ‣ Mitosis: | 3 |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | 2.9 cm (of the largest tumour) |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | 14/23 involved |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | Absent |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | Not seen. Lobular neoplasia not seen |
| ‣ Margins: | Free of tumour (base, overlying skin, nipple, and areola are free of tumour) |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | pT2(m)N3 |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | |
| ‣ Comments: | Multiple smaller foci of carcinoma are seen in the sections taken from the firm area adjacent to the main tumour with microscopic size ranging from 0.2 mm to 15 mm. Areas with fibrocystic change are also seen |
Case summary:
| Postmenopausal woman presented with left nipple retraction. Diagnosed as left breast carcinoma with left nipple retraction, BI-RADS 5 on imaging, as suspicious for malignancy on cytology, and as invasive lobular carcinoma, pT2(m)N3 on histopathology. |
Learning points:
|