Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Filter by language: English / Русский
Go back to the list of case studies
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
| Case number: | 131 |
| Age: | 67 |
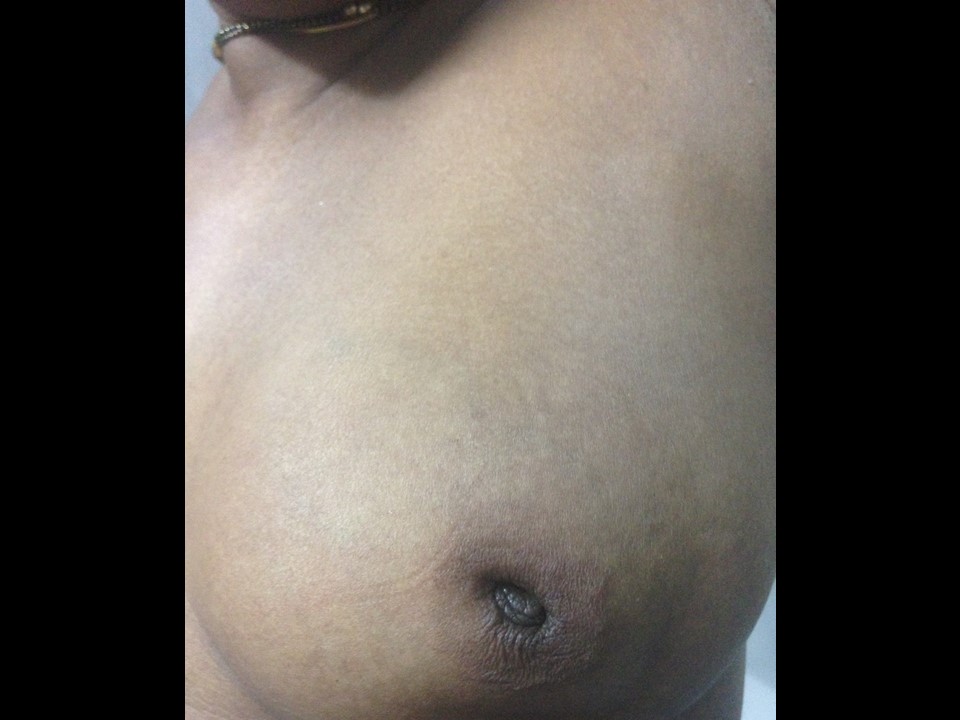
| Clinical presentation: | Postmenopausal woman with average risk of developing breast cancer presented with left breast lump noticed a few weeks ago with mastalgia. |
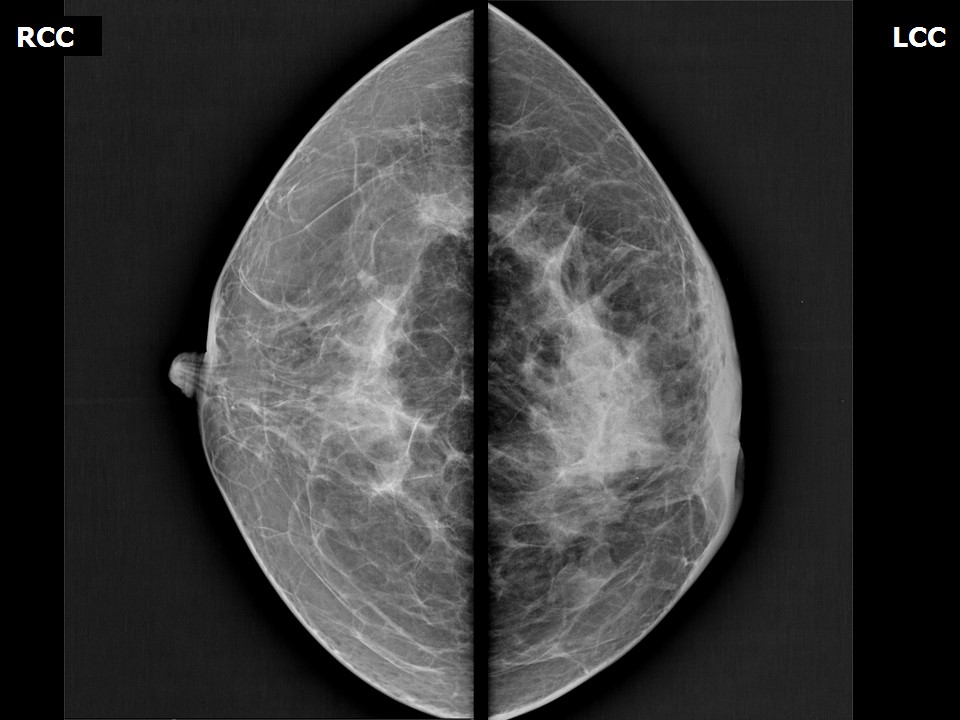
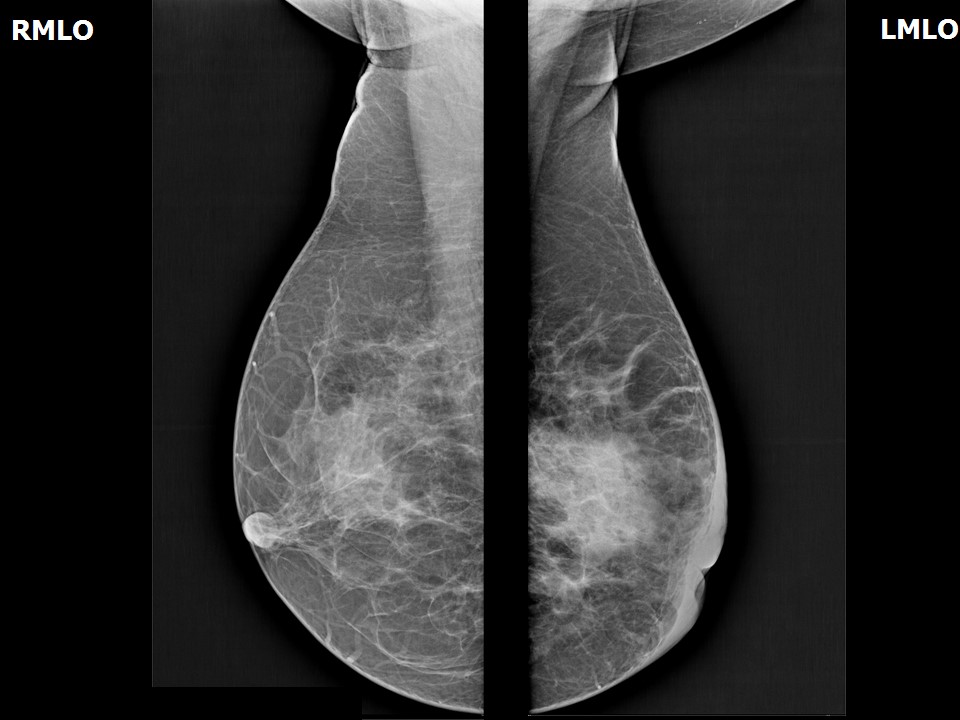
Mammography:
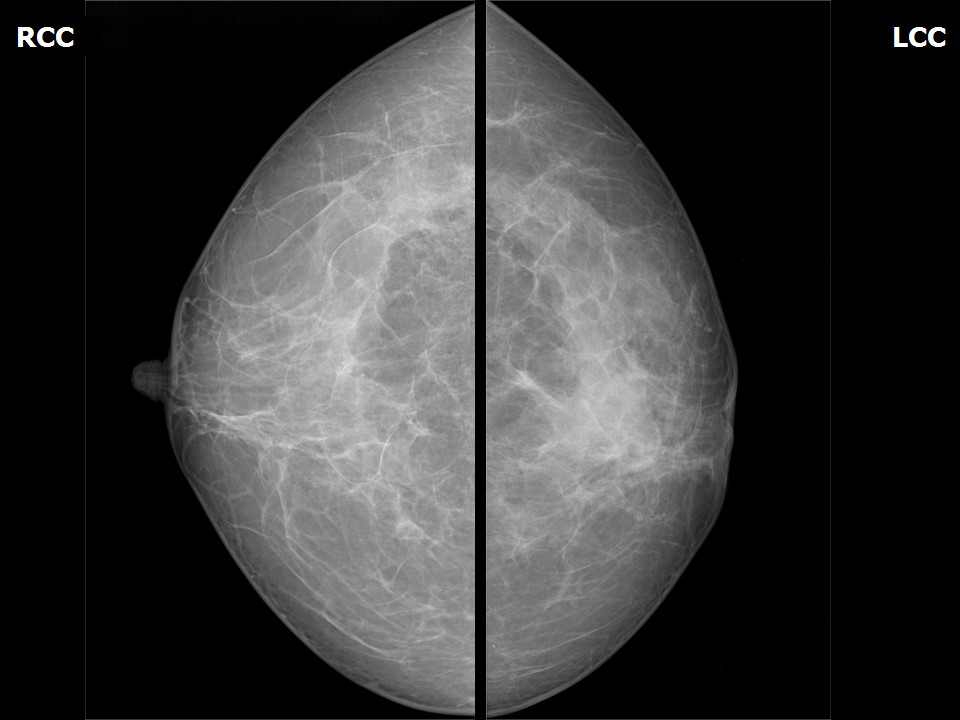
| Breast composition: | ACR category c (the breasts are heterogeneously dense, which may obscure small masses) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Left breast, central portion of the breast at 6 o’clock, middle third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 0 |
| • Size: | None |
| • Shape: | None |
| • Margins: | None |
| • Density: | None |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | Present |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | Present |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
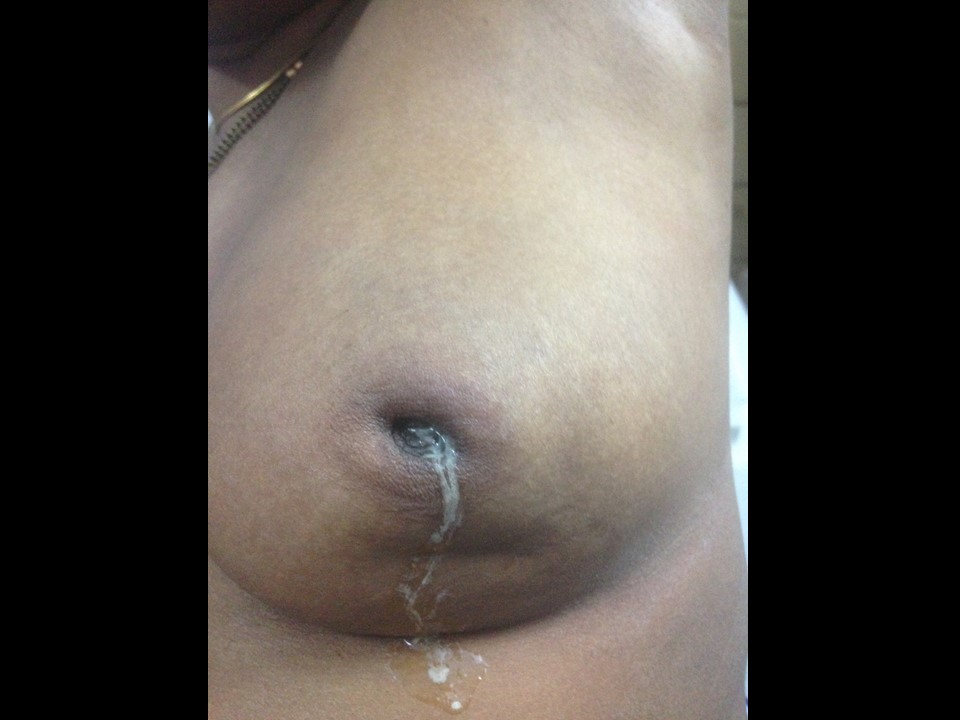
| ‣ Associated features: | Axillary adenopathy and nipple retraction |
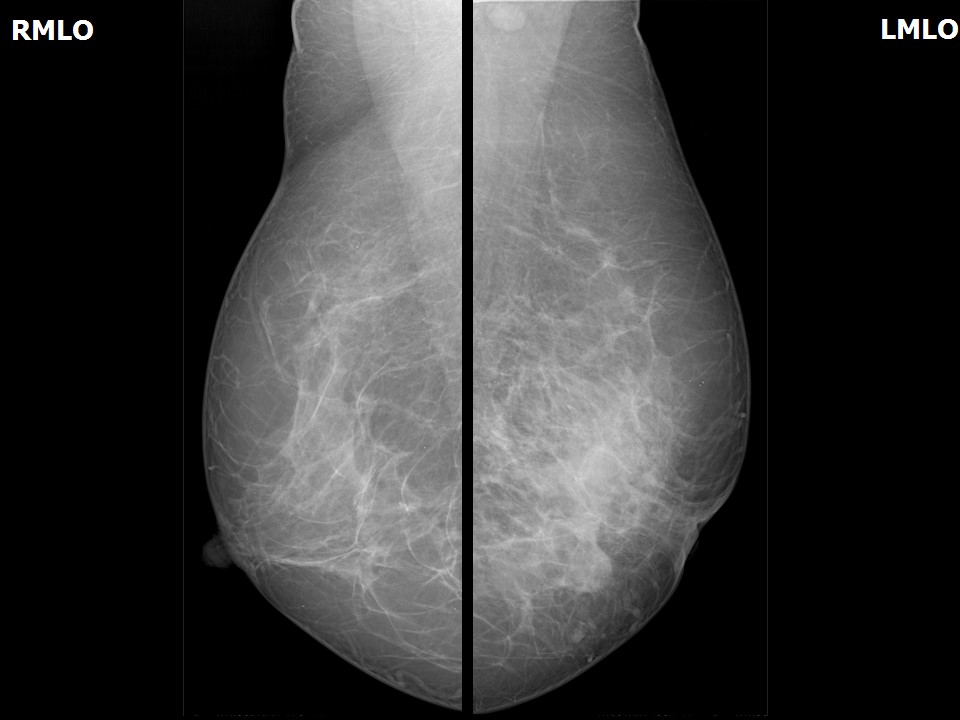
| Breast composition: | ACR category c (the breasts are heterogeneously dense, which may obscure small masses) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Follow-up at 6 months: Left breast, lower inner quadrant at 2–7 o’clock, middle third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 0 |
| • Size: | None |
| • Shape: | None |
| • Margins: | None |
| • Density: | None |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | Present |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | Present |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Skin thickening, trabecular thickening, axillary adenopathy, and nipple retraction |
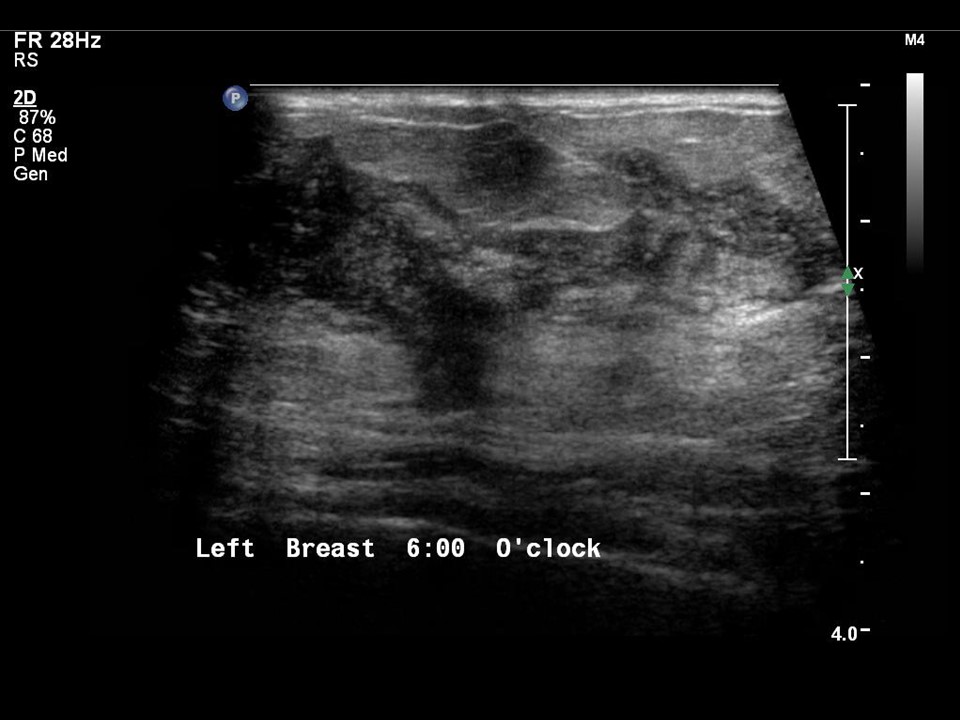
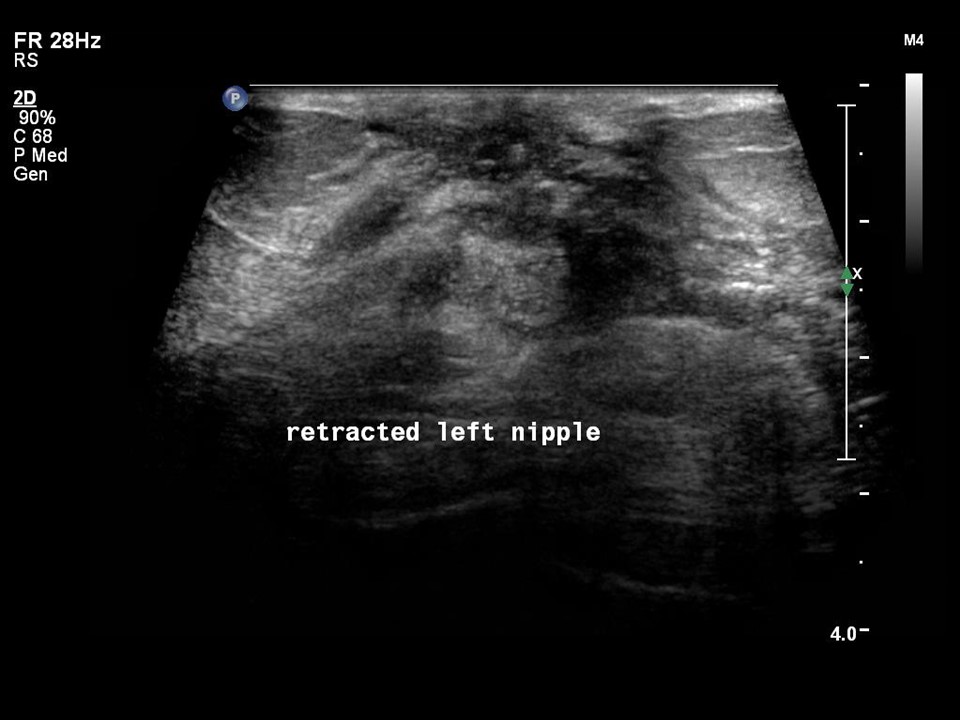
Ultrasound:
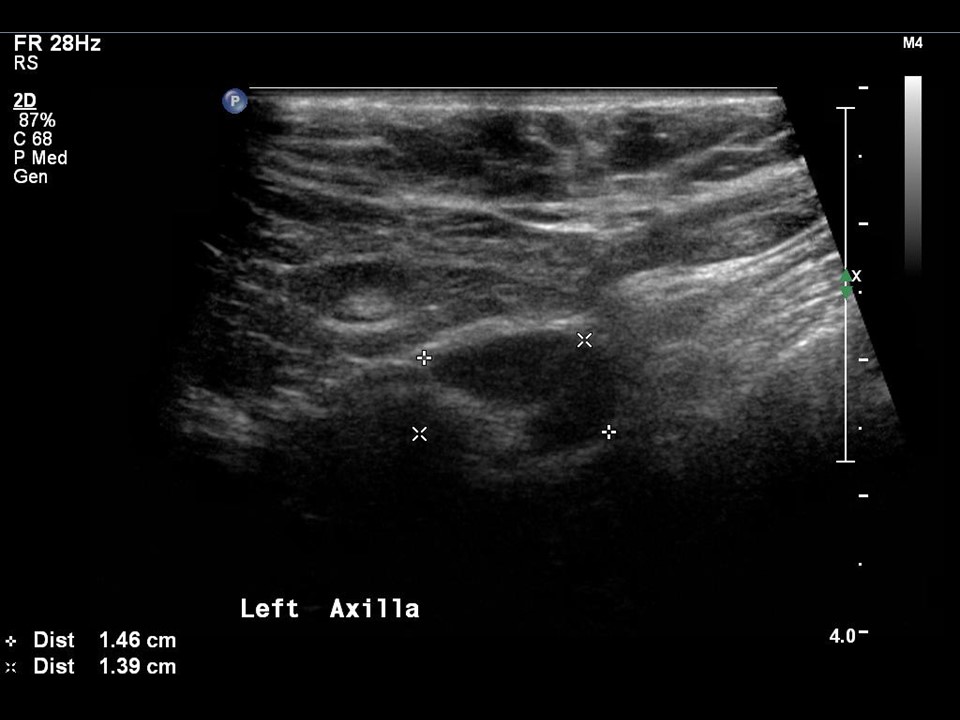
| Ultrasound features: Left breast, central portion of the breast | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Left breast, central portion of the breast |
| • Number: | 0 |
| • Size: | 5.0 × 2.5 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Orientation: | Not parallel |
| • Margins: | Indistinct |
| • Echo pattern: | Heteroechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
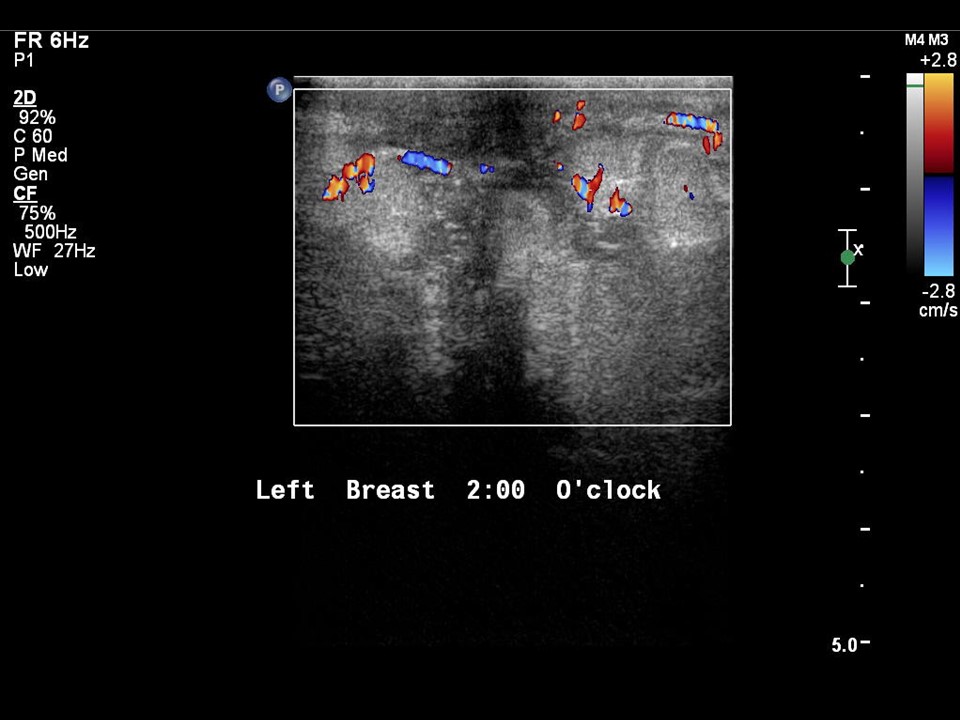
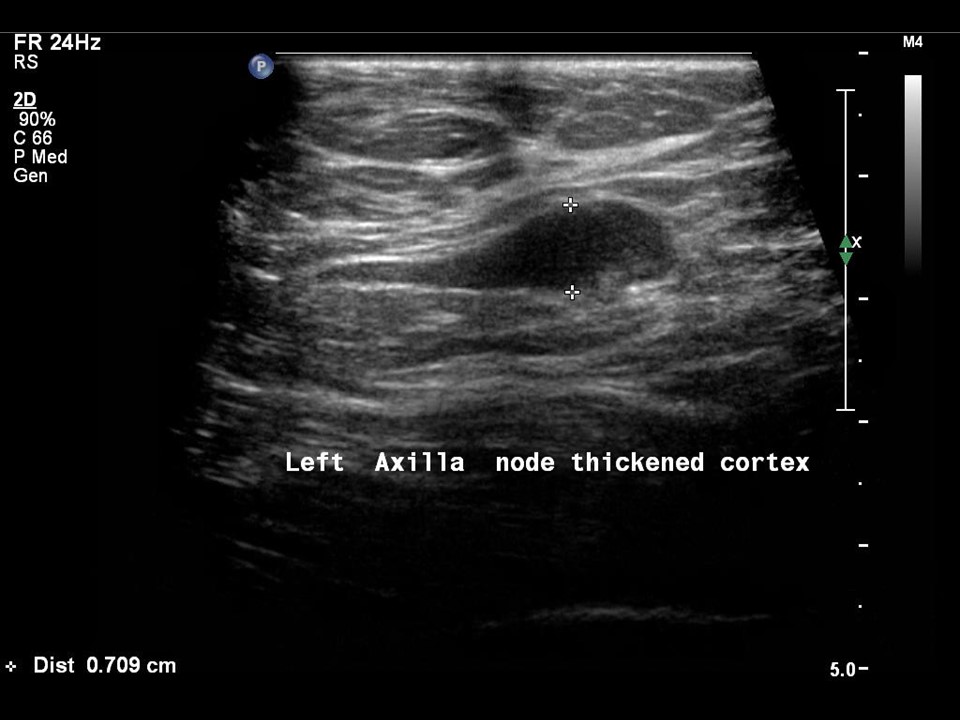
| ‣ Associated features: | Nipple retraction, vascularity in mass, and axillary lymphadenopathy |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
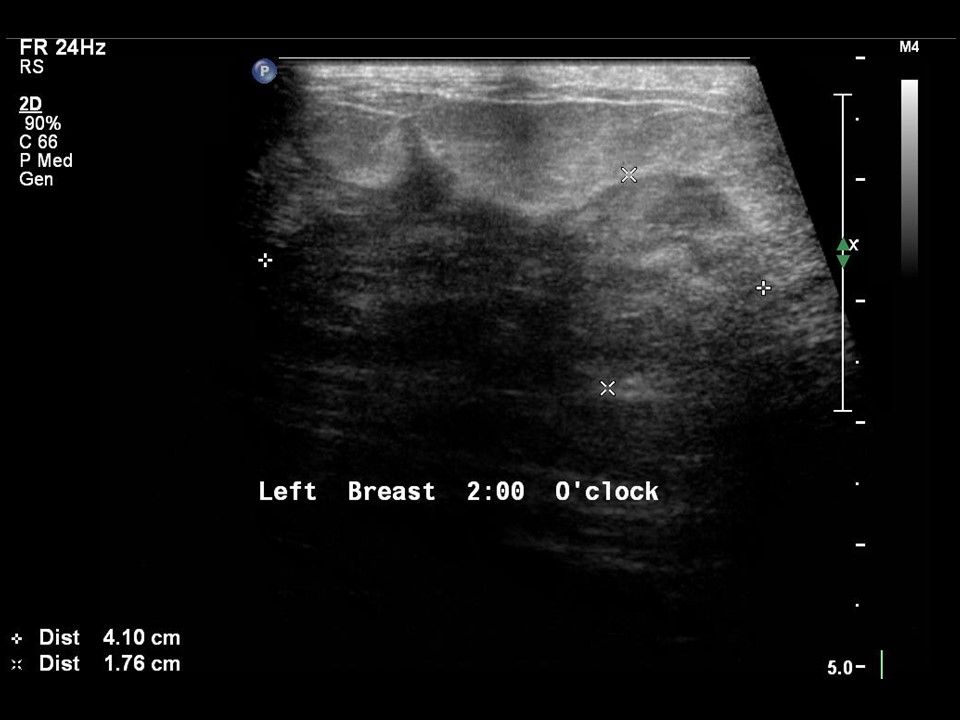
| Ultrasound features: Follow-up at 6 months: Left breast, outer quadrants at 2–6 o’clock | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Follow-up at 6 months: Left breast, outer quadrants at 2–6 o’clock |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 4.0 × 2.0 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Orientation: | Not parallel |
| • Margins: | Indistinct |
| • Echo pattern: | Heteroechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Nipple retraction, vascularity in mass, and axillary lymphadenopathy |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: 4A (low level of suspicion for malignancy)Further assessment:
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytologyCytology:
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Left |
| • Quadrant: | Three nodules at 2, 3, and 6 o’clock positions |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | 0.2–0.5 mL of thick whitish pus-like material |
| ‣ Cytological description: | Smears from all three areas showed a florid acute inflammatory infiltrate admixed with lymphocytes and many histiocytes. A few of the histiocytes have an epithelioid appearance with giant cells |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Benign |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | An acute suppuration inflammation with granulomatous mastitis. PCR test of the aspirated material was negative for Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
Histopathology:
Simple Mastectomy
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | Simple Mastectomy |
| ‣ Laterality: | Left |
| ‣ Macroscopy: | Specimen (16.0 × 14.0 × 5.5 cm) with overlying skin flap with nipple and areola (12.0 × 5.5 cm). On serial sectioning, a diffuse, firm, whitish area (11.0 × 6.0 cm) is identified. Soft multiple necrotic foci are seen within the firm areas |
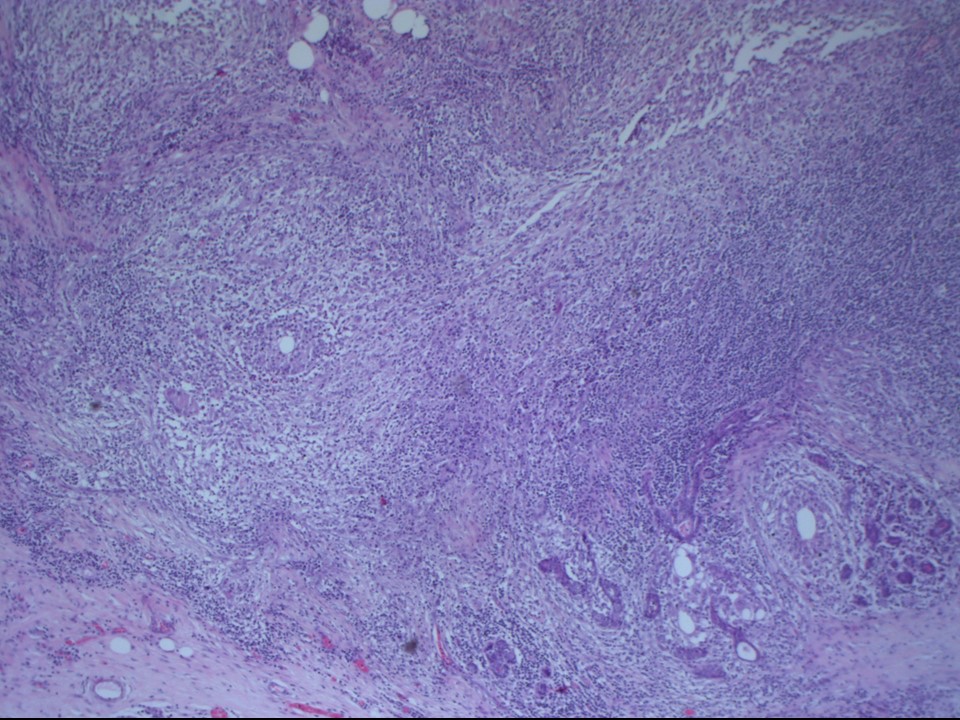
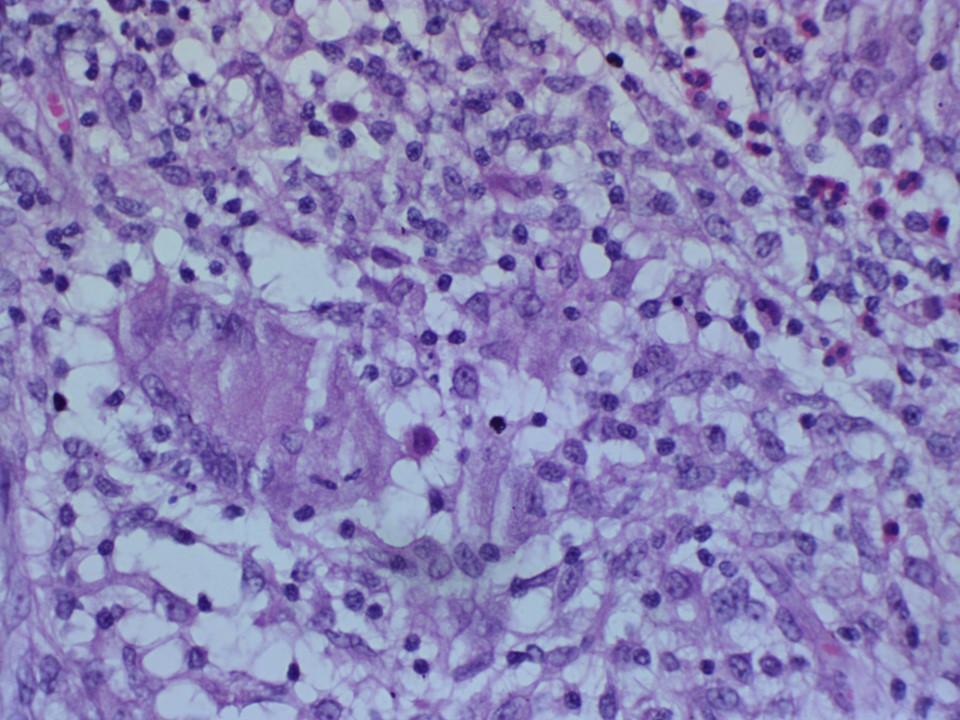
| ‣ Histological type: | Sections from the diffuse firm areas in the breast reveal multiple granulomas showing foci of necrosis and acute suppuration replacing the mammary lobules. The granulomas are composed of epithelioid cells, giant cells, some of which are of the Langhans type, and lymphocytes. Many microabscesses are seen |
| ‣ Histological grade: | |
| ‣ Mitosis: | |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | |
| ‣ Margins: | |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | |
| ‣ Comments: | Ziehl–Neelsen stain was negative for acid-fast bacilli |
Case summary:
| Postmenopausal woman presented with left breast lump with mastalgia. Diagnosed as BI-RADS 4A on imaging and as granulomatous mastitis on cytology and histopathology. |
Learning points:
|