Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Filter by language: English / Русский
Go back to the list of case studies
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
| Case number: | 032 |
| Age: | 65 |
| Clinical presentation: | Postmenopausal woman with average risk of developing breast cancer presented with a painful lump in the left breast. She had a history of excision of a benign breast lump in the right breast. Examination revealed a 2 cm lump in the inner lower quadrant of the left breast. |
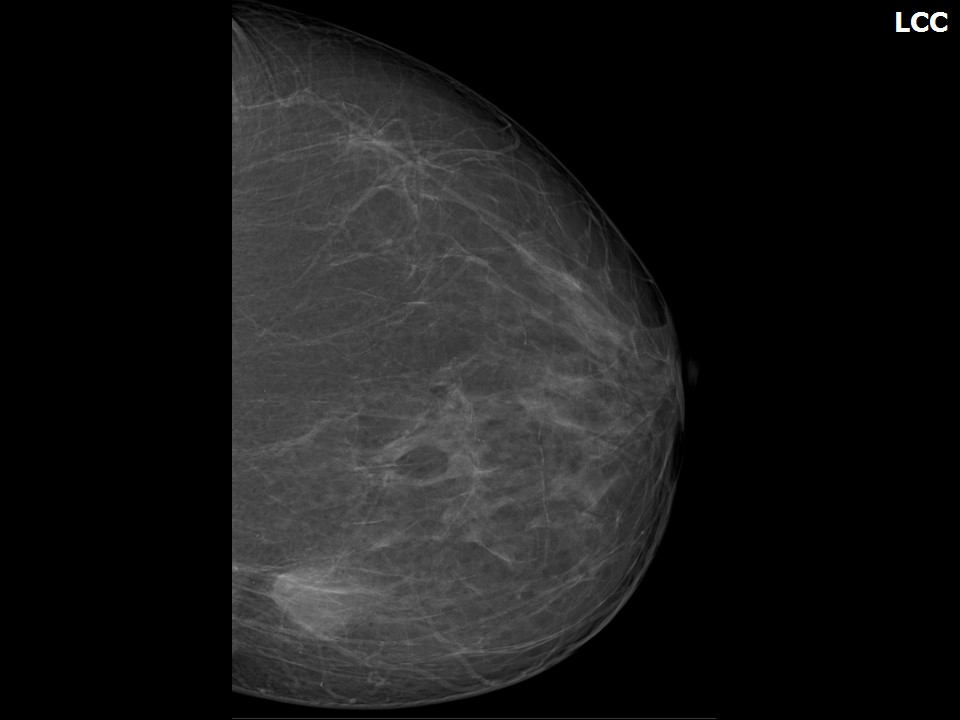
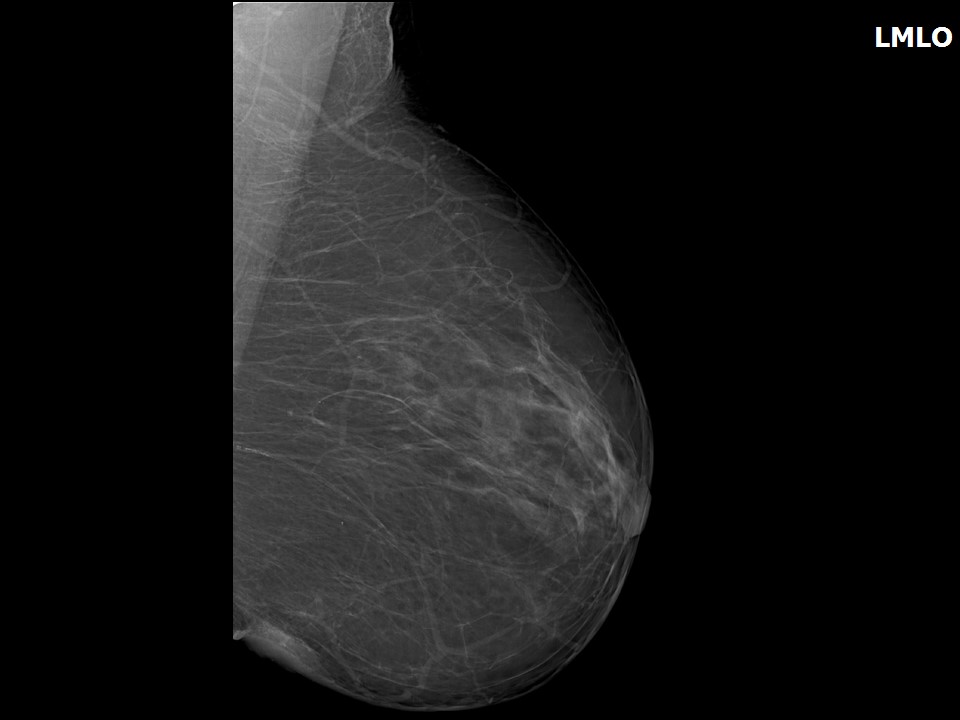
Mammography:
| Breast composition: | ACR category a (the breasts are almost entirely fatty) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Left breast, lower inner quadrant at 8 o’clock, hypodermis, posterior third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 2.0 × 1.0 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Margins: | Indistinct |
| • Density: | Equal |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | Vascular calcification |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Skin thickening |
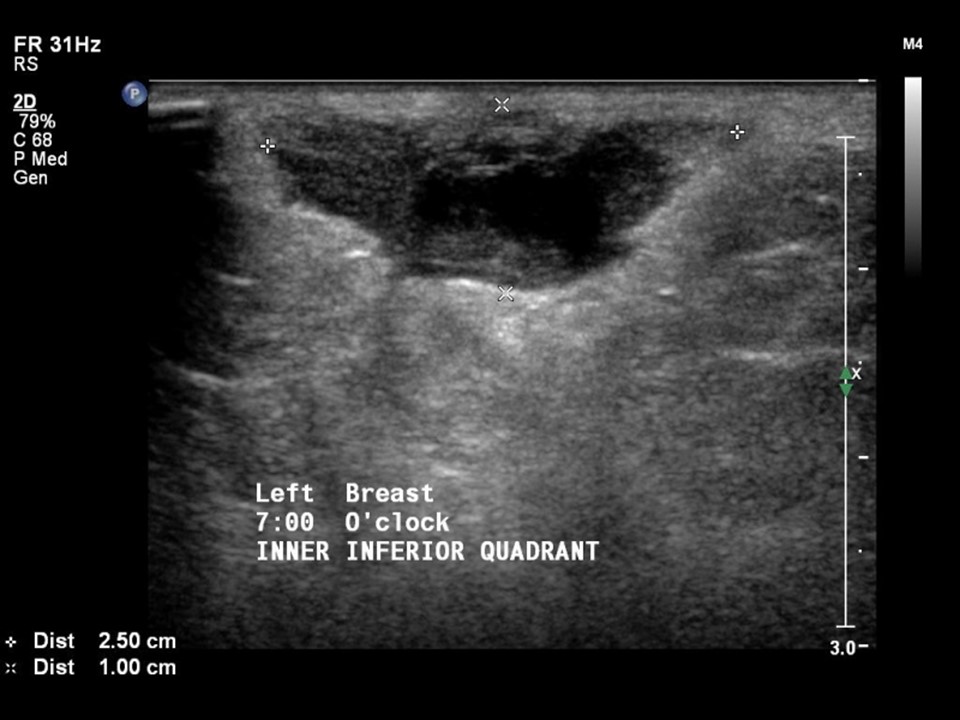
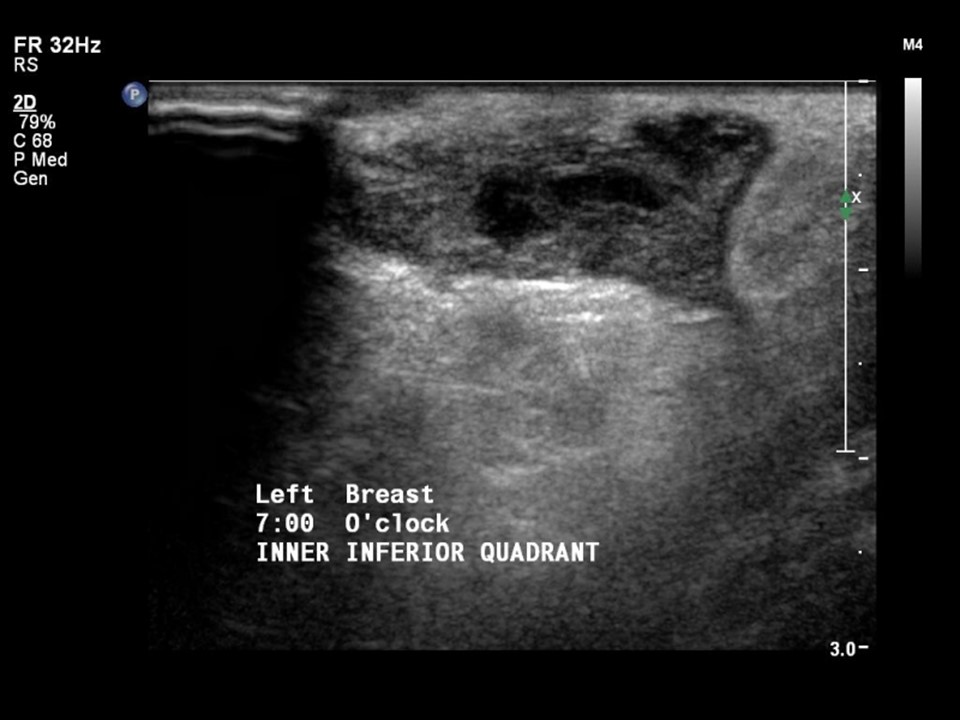
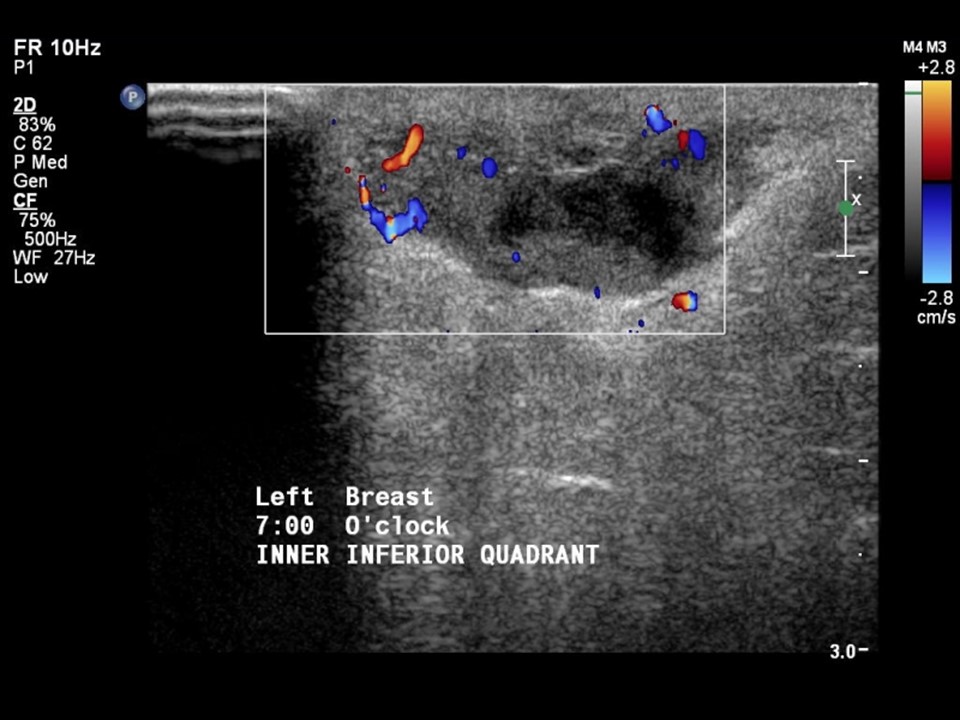
Ultrasound:
| Ultrasound features: Left breast, lower inner quadrant at 7–8 o’clock | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Left breast, lower inner quadrant at 7–8 o’clock |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 2.5 × 1.0 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Orientation: | Parallel |
| • Margins: | Indistinct |
| • Echo pattern: | Heterogeneous |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Vascularity – vessels in rim and internal vascularity. Skin thickening |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: 2 (benign)Further assessment:
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytologyCytology:
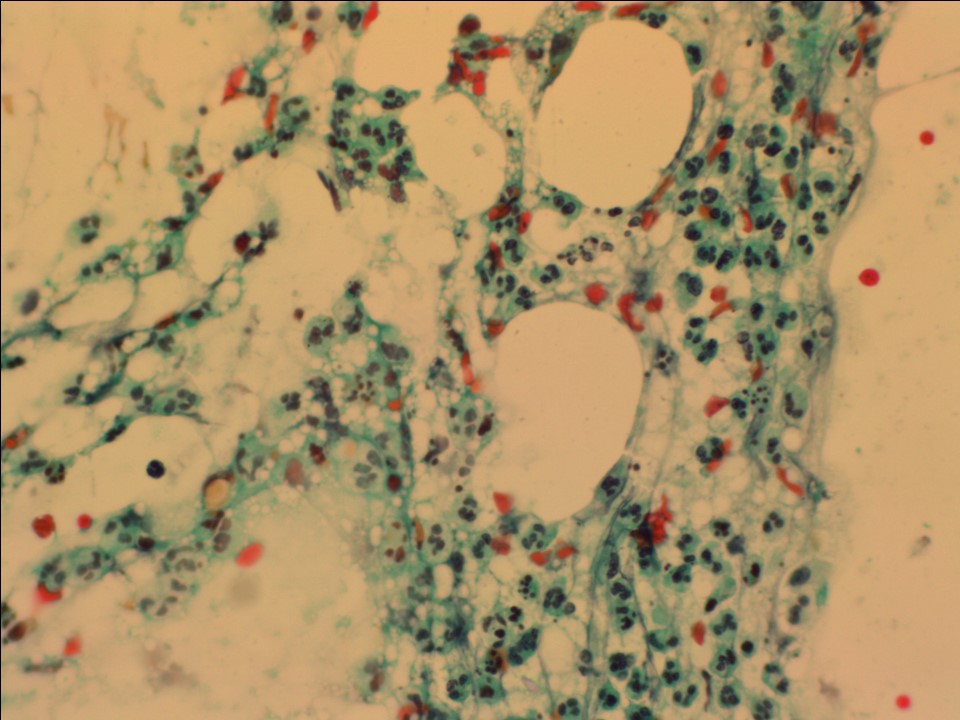
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Left |
| • Quadrant: | Lower inner |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | 0.5 mL of purulent yellowish material |
| ‣ Cytological description: | Smears reveal mainly neutrophils and numerous macrophages, tingible body macrophages, giant cells, and isolated and small groups of ductal epithelial cells showing reparative changes. Background is necrotic with red blood cells (RBCs) |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Benign |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Breast abscess |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
Histopathology:
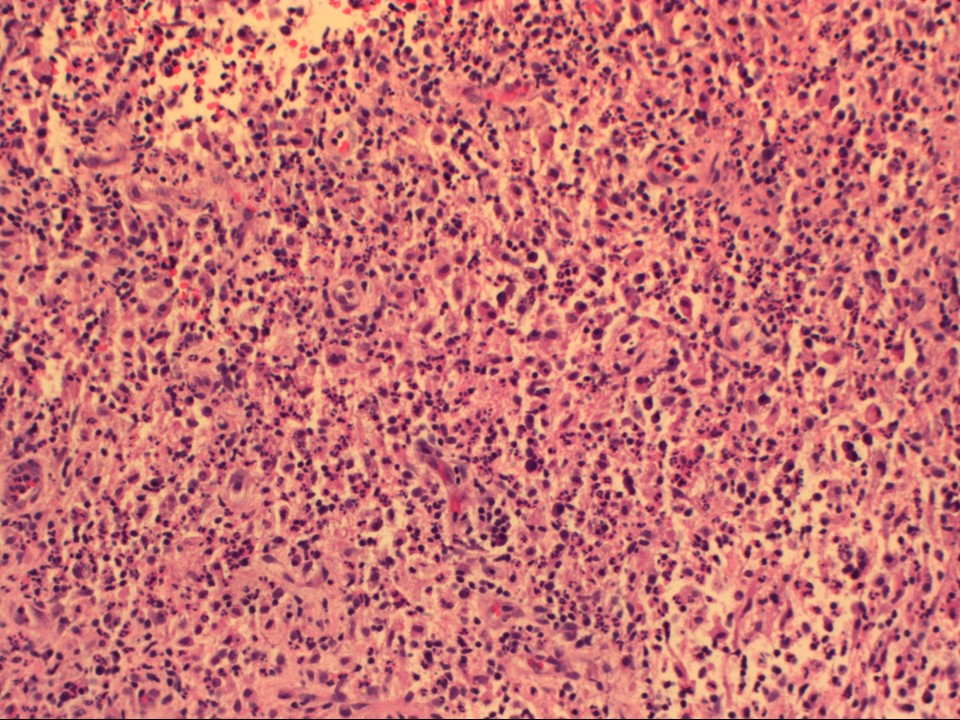
Excision biopsy
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | Excision biopsy |
| ‣ Laterality: | Left |
| ‣ Macroscopy: | Single fibrofatty bit (3.5 × 2.5 × 2.0 cm). External surface partially covered with skin. Cut surface is soft and yellowish with a single pus-filled cavity 1.0 cm in diameter |
| ‣ Histological type: | Sections through the tissue labelled as antibioma reveal skin-covered tissue with an underlying well-circumscribed area showing necrosis, granulation tissue, chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate, and numerous foreign body giant cells with a central area showing many neutrophils |
| ‣ Histological grade: | |
| ‣ Mitosis: | |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | |
| ‣ Margins: | |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | |
| ‣ Comments: | Consistent with acute-on-chronic inflammation with organization |
Case summary:
| Postmenopausal woman presented with painful left breast lump. Diagnosed as inflammation in left breast, BI-RADS 2 on imaging, as breast abscess on cytology, and as acute-on-chronic inflammation on histopathology. |
Learning points:
|