Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Filter by language: English / Русский
Go back to the list of case studies
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
| Case number: | 114 |
| Age: | 65 |
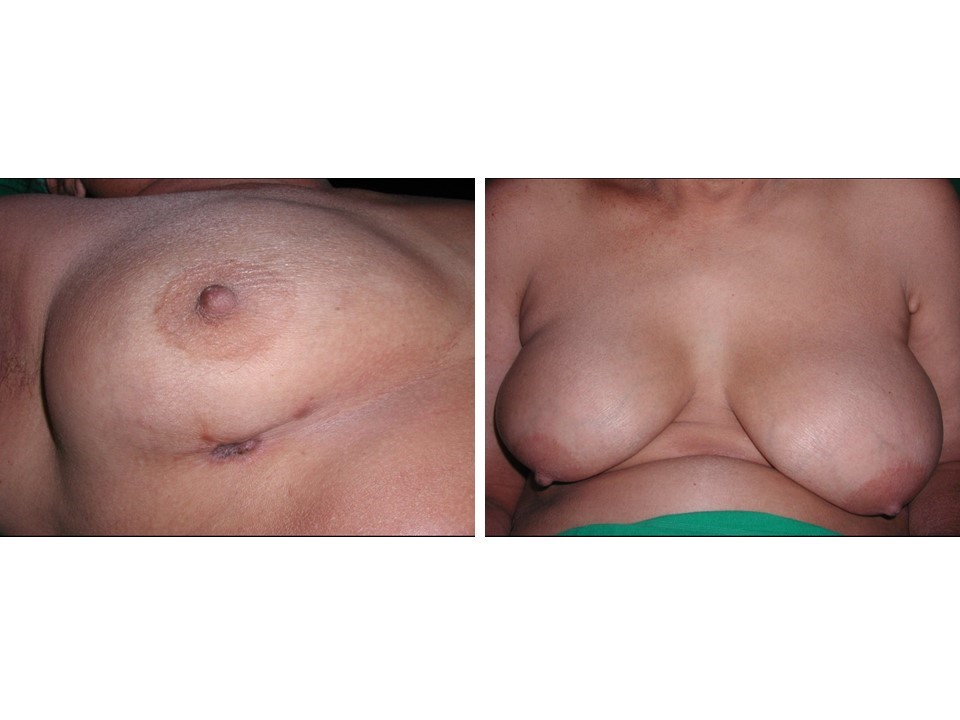
| Clinical presentation: | Postmenopausal woman with average risk of developing breast cancer presented with pain and lump in the left breast. Examination revealed a hard lump, 2 cm in diameter, at the 6 o’clock position, which was fixed to the chest wall. Axillary nodes were not palpable. |
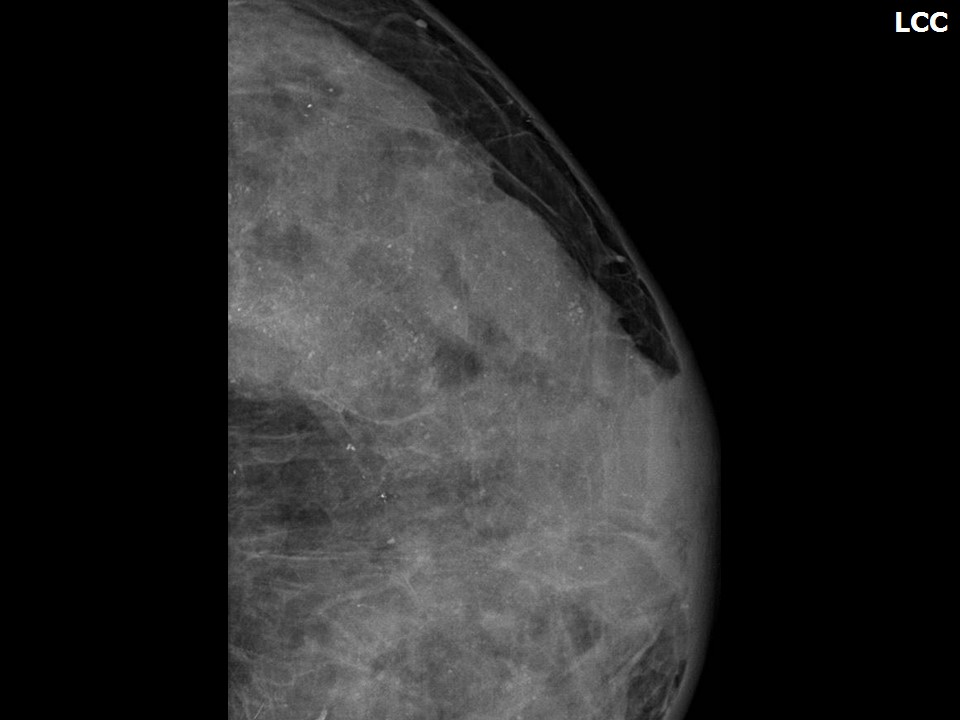
Mammography:
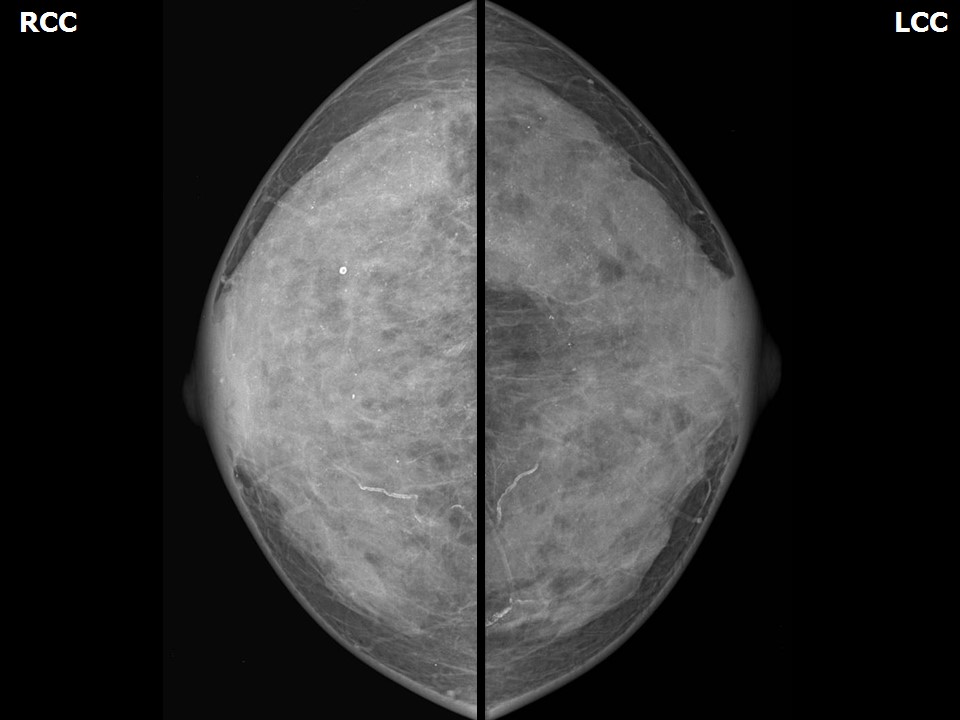
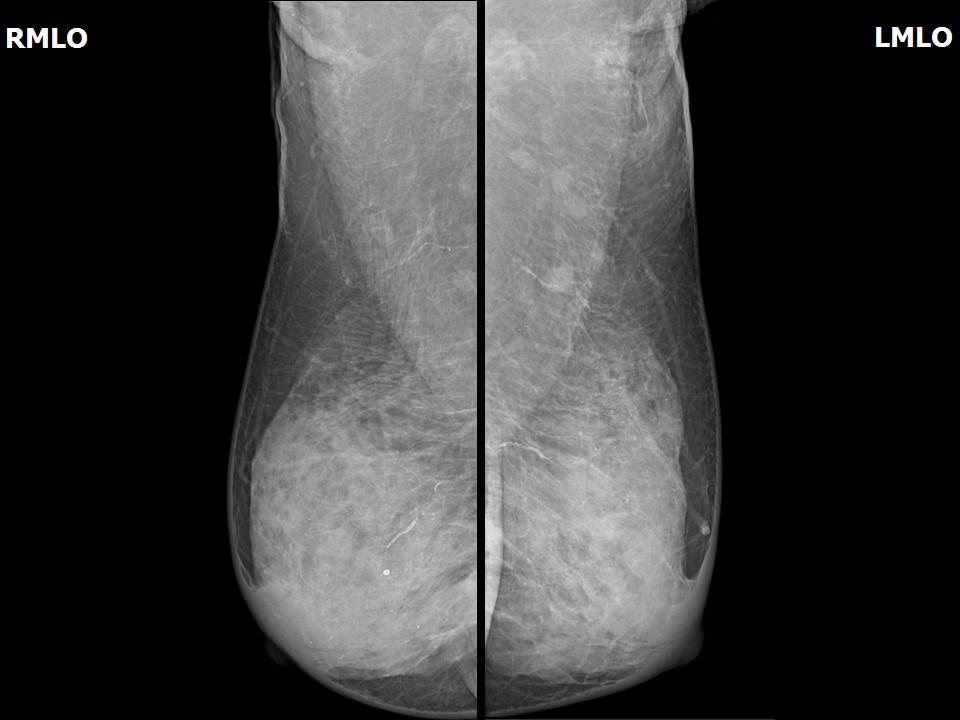
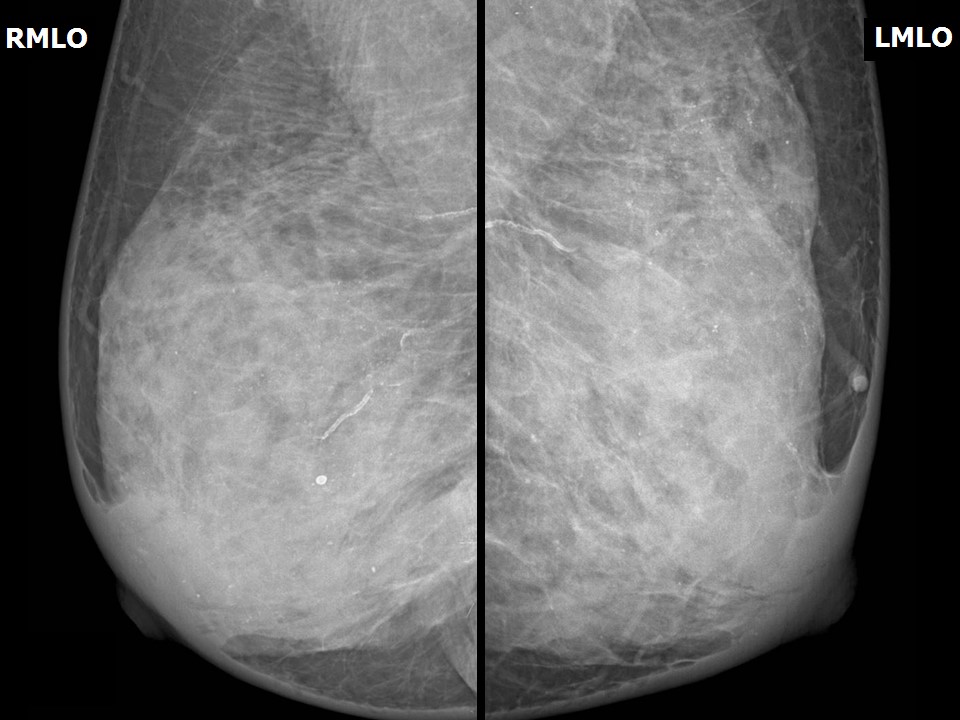
| Breast composition: | ACR category d (the breasts are extremely dense, which lowers the sensitivity of mammography) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Left breast, mass is not visible in the extremely dense breast parenchyma |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 0 |
| • Size: | No |
| • Shape: | None |
| • Margins: | None |
| • Density: | None |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | Round, diffuse in both breasts, vessel calcification also seen |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Skin retraction and calcification |
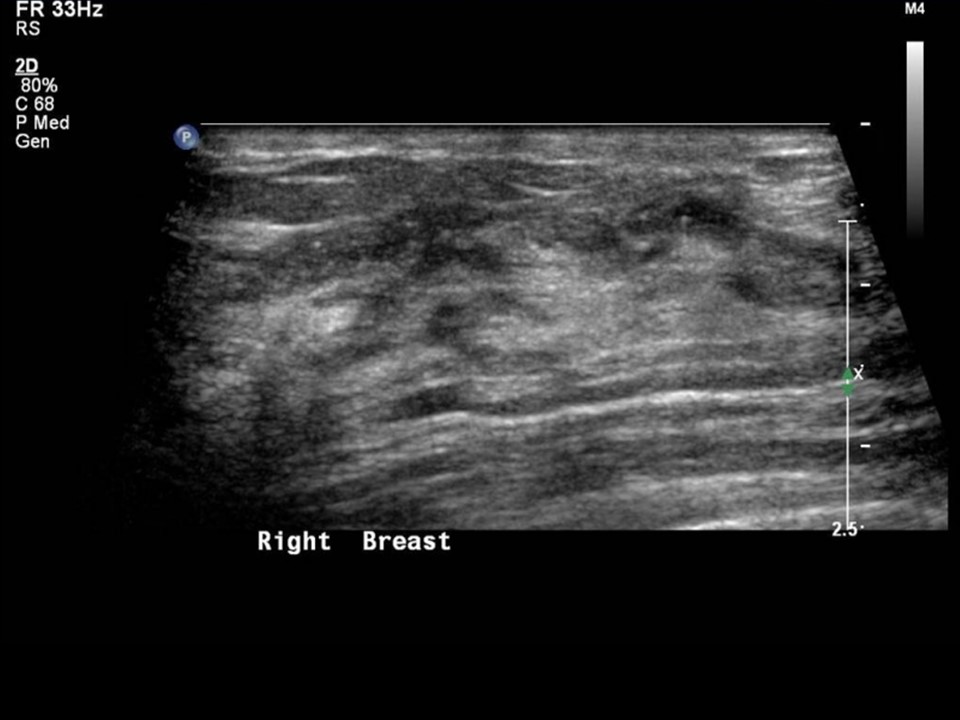
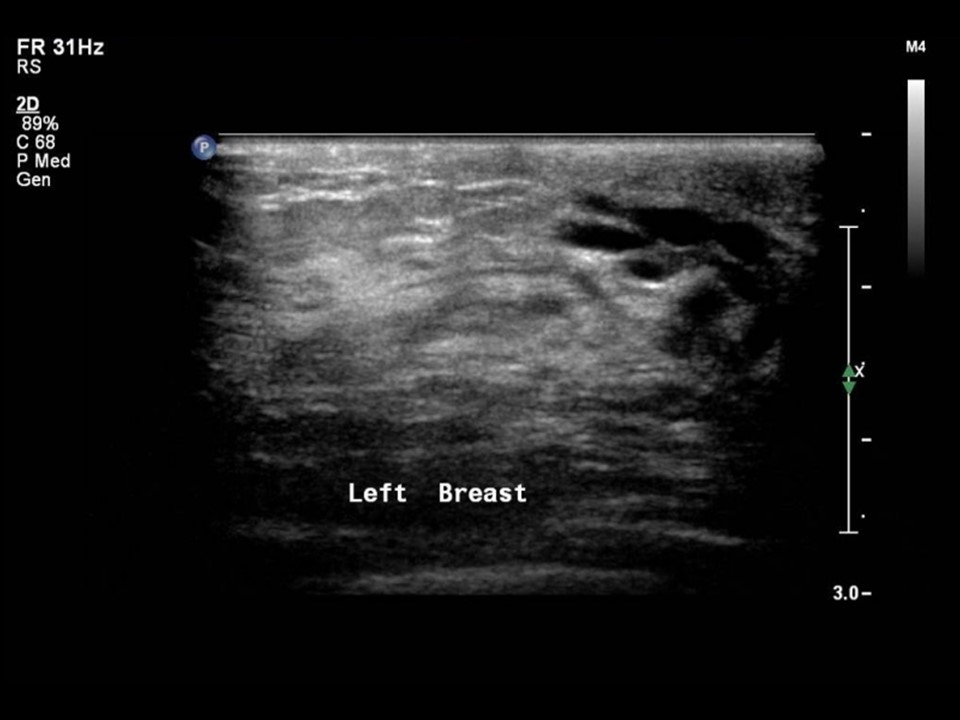
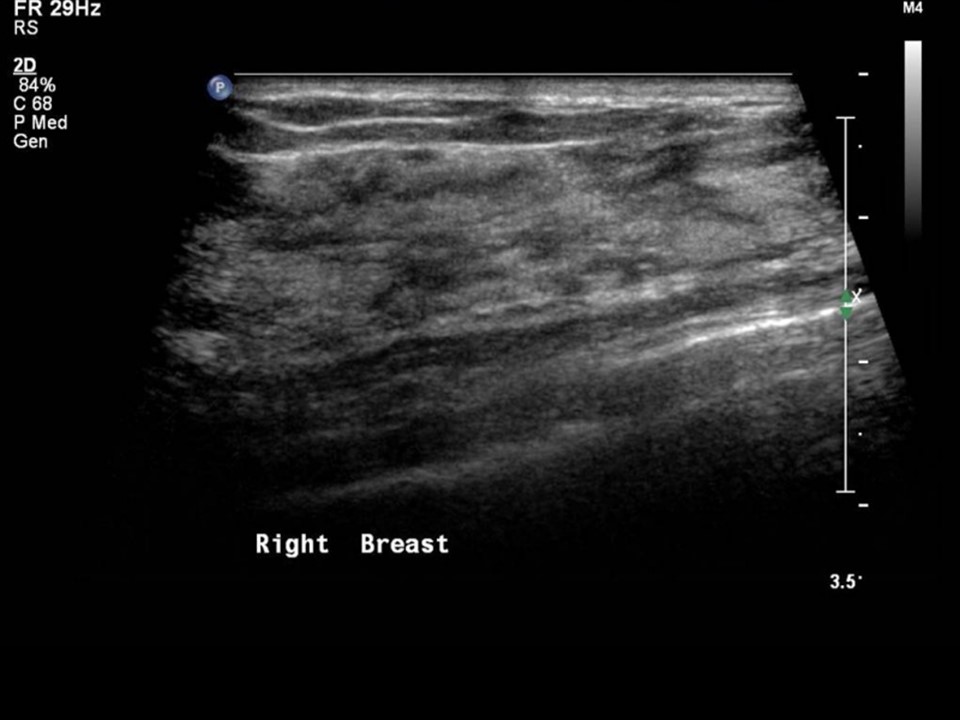
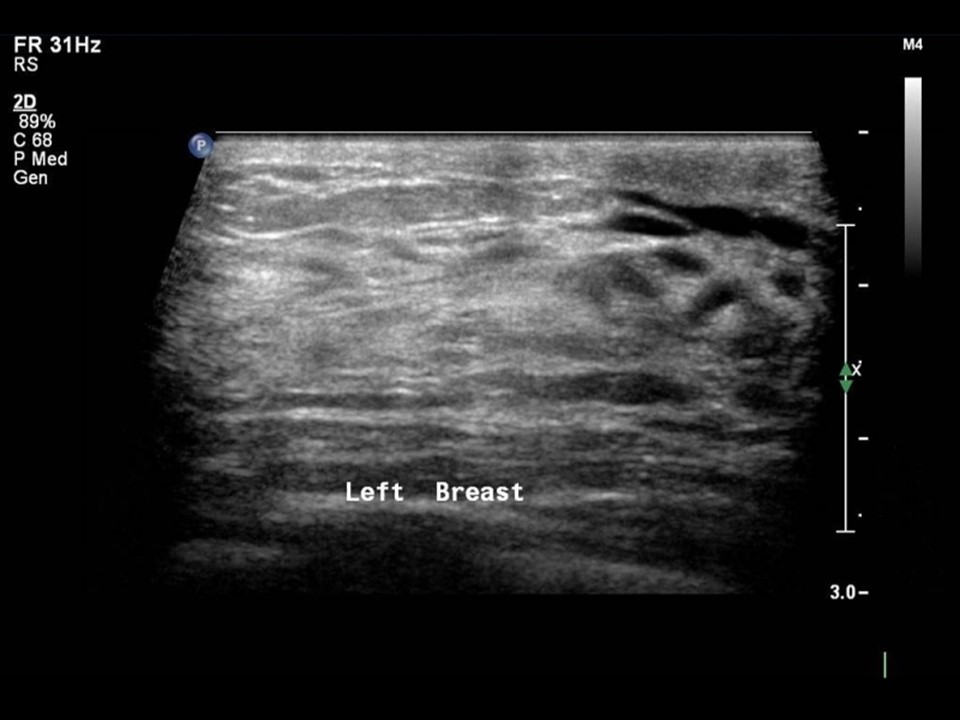
Ultrasound:
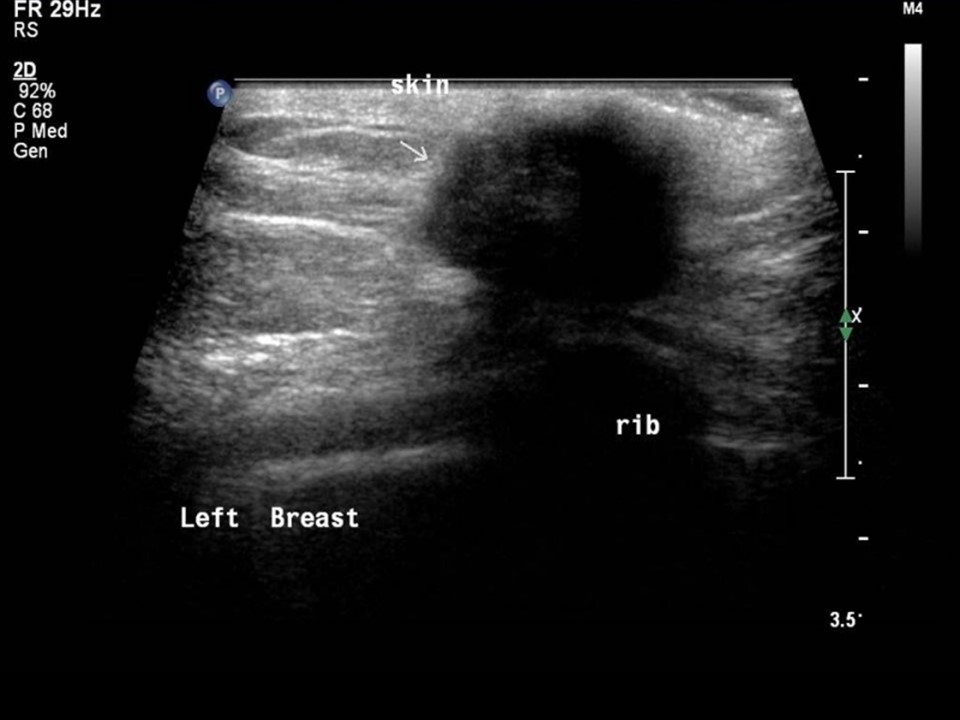
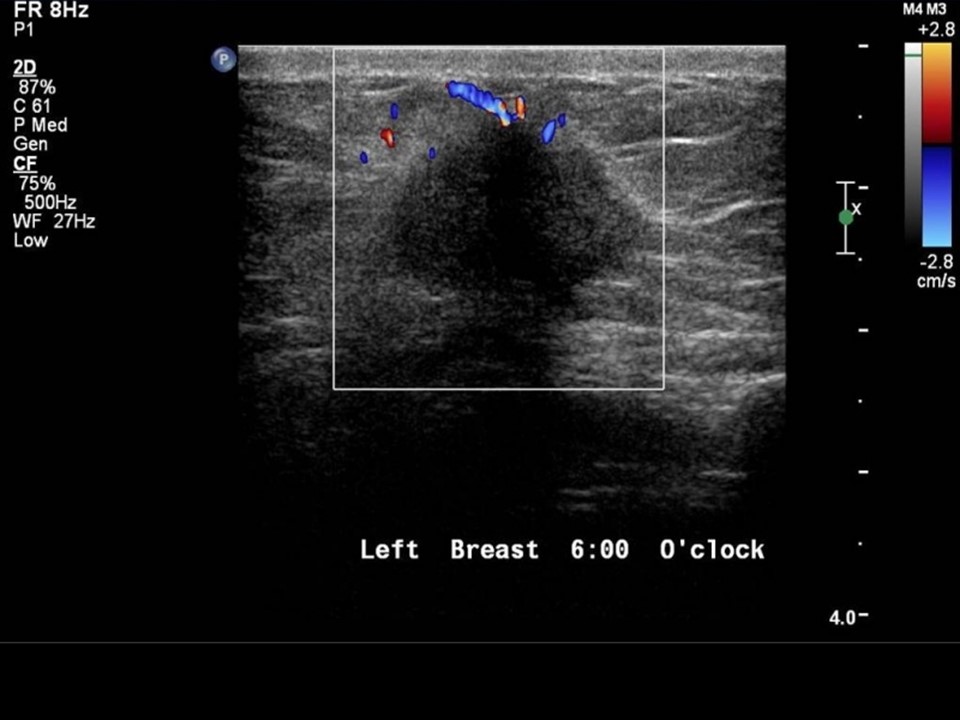
| Ultrasound features: Left breast, lower quadrants at 6 o‘clock | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Left breast, lower quadrants at 6 o‘clock |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 2.0 × 1.1 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Orientation: | Not parallel |
| • Margins: | Spiculated |
| • Echo pattern: | Hypoechoic |
| • Posterior features: | Posterior shadowing |
| ‣ Calcifications: | Outside the mass, in bilateral breast in the dense echogenic glandular tissue |
| ‣ Associated features: | Skin thickening and retraction |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: Right: 2 (benign), Left: 5 (highly suggestive of malignancy)Further assessment:
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytology and for core biopsyCytology:
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Left |
| • Quadrant: | Lower inner |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | Whitish |
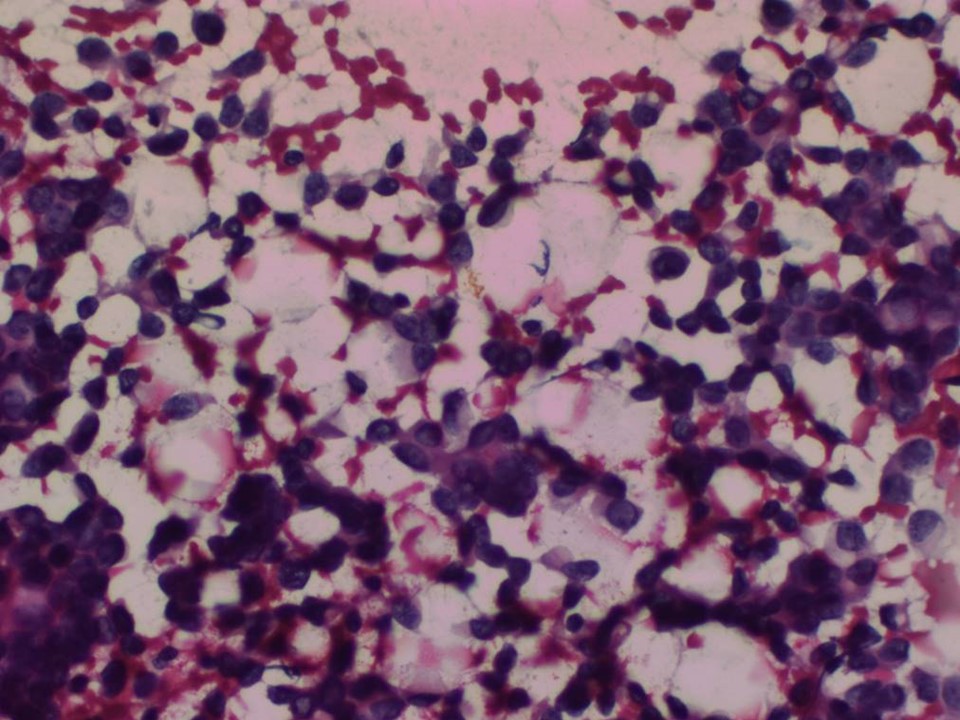
| ‣ Cytological description: | Cellular smear showing loosely cohesive sheets and isolated malignant cells. Cells have high N:C ratio, coarse chromatin, and a few show prominent nucleoli |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Malignant |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Carcinoma |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
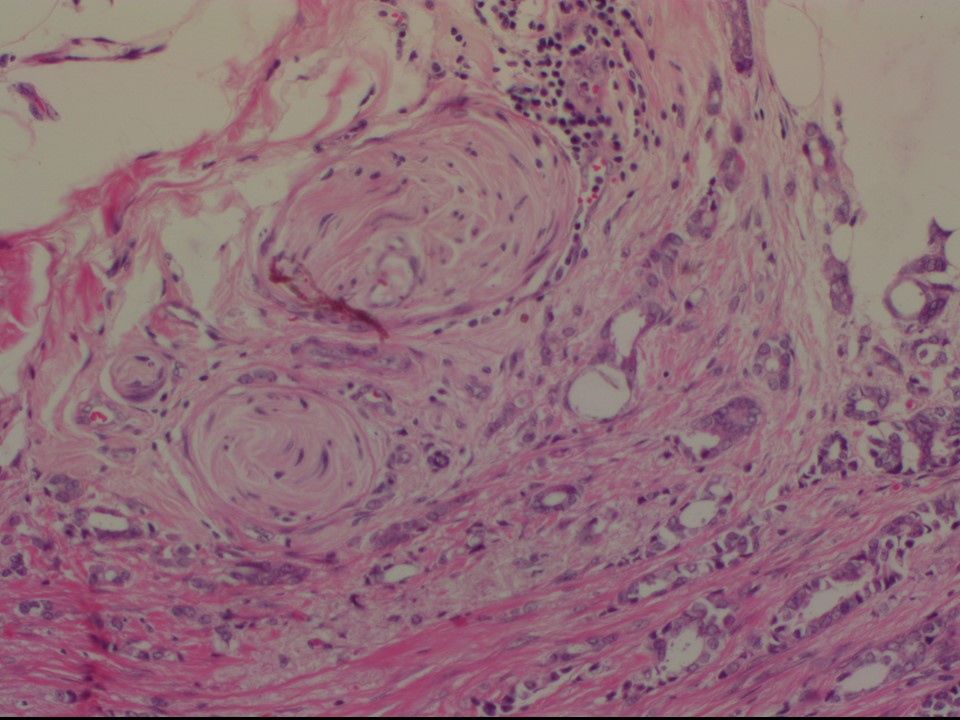
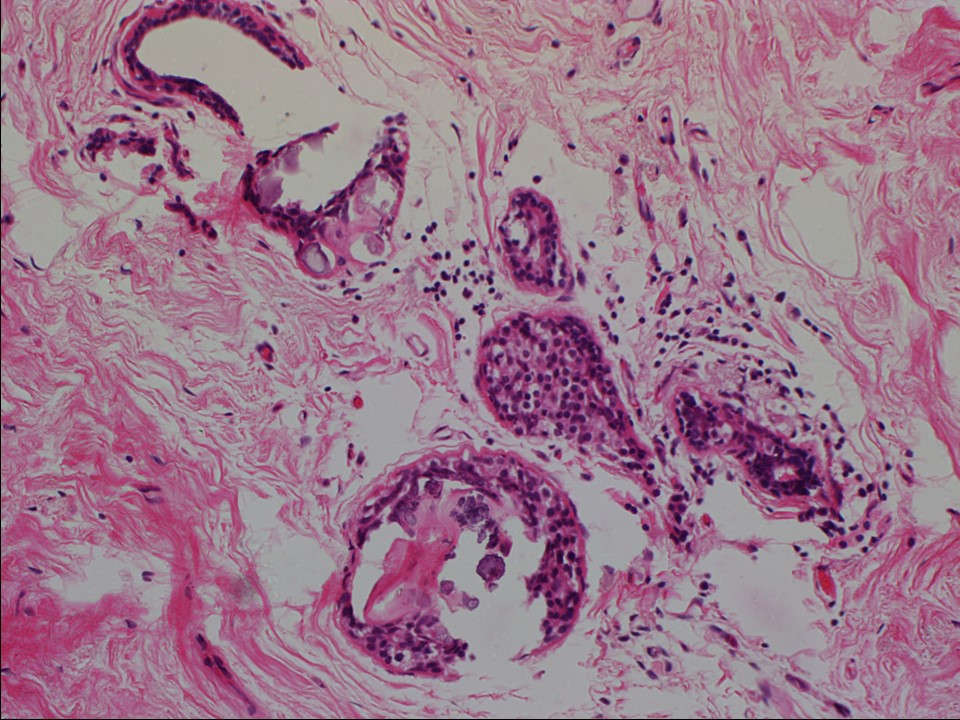
Histopathology:
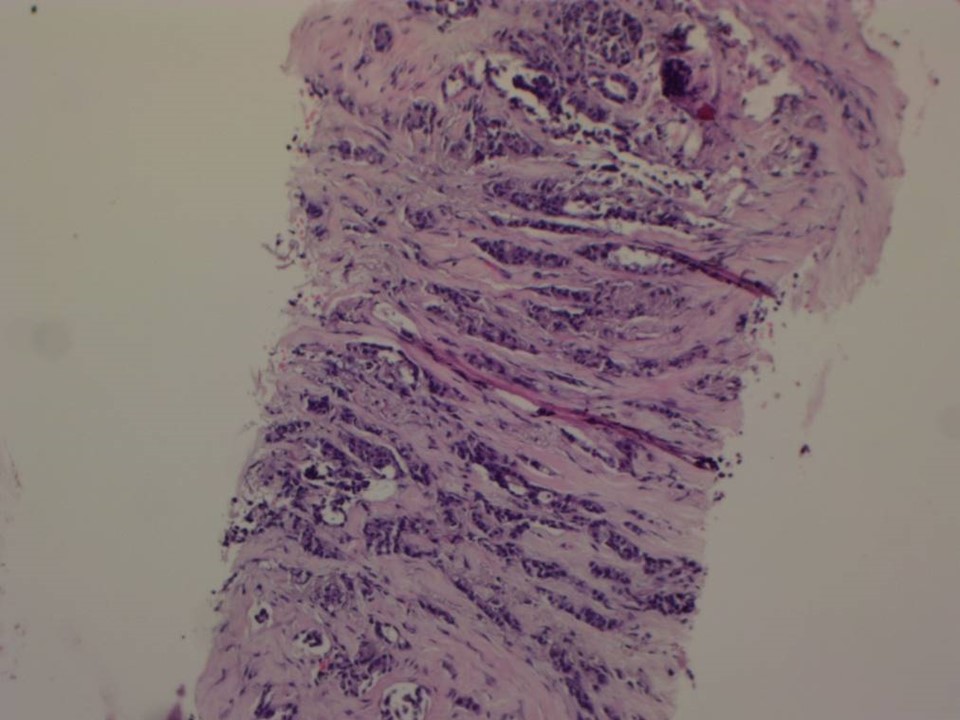
Core needle biopsy
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | Core needle biopsy |
| ‣ Laterality: | Left breast, 6 o’clock |
| ‣ Macroscopy: | 11 cores |
| ‣ Histological type: | Invasive carcinoma of no special type |
| ‣ Histological grade: | Grade 2 (3 + 3 + 1 = 7) |
| ‣ Mitosis: | 6 |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | |
| ‣ Margins: | |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | |
| ‣ Comments: |
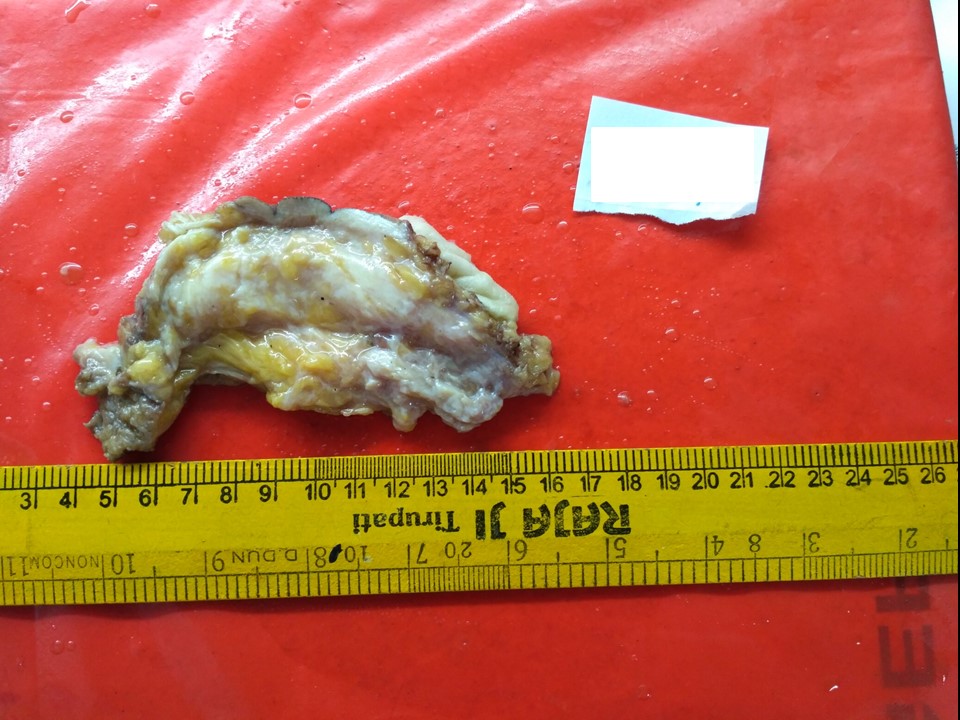
MRM
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | MRM |
| ‣ Laterality: | Left |
| ‣ Macroscopy: | MRM specimen (24.0 × 22.0 × 4.0 cm) with overlying skin flap (16.5 × 5.5 cm). The nipple and areola are intact. Skin appears puckered towards the inferomedial part of the flap and there is a firm area (2.2 × 1.0 × 1.5 cm) below it. This area is 0.5 cm from the posterior margin of resection (base). On serial sectioning, a firm whitish area of fibrosis is identified (10.0 × 3.0 × 5.0 cm) in the subareolar region, central quadrant extending into the superior and inferior quadrants. It is located 1.0 cm from the skin, 2.3 cm from the base. |
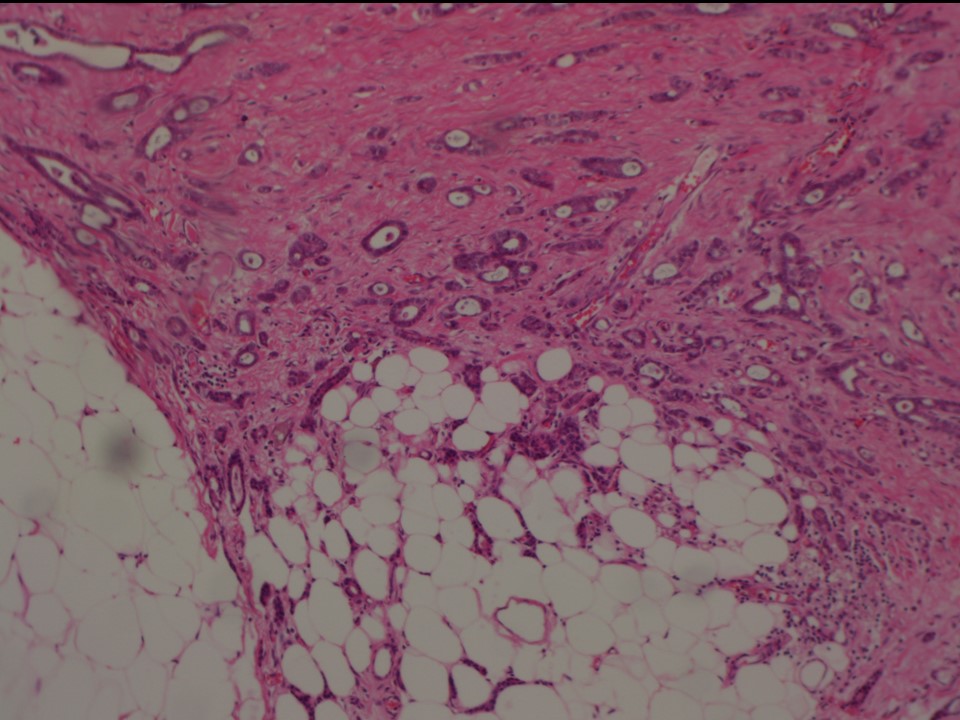
| ‣ Histological type: | Invasive carcinoma of no special type |
| ‣ Histological grade: | Grade 2 (2 + 3 + 1 = 6) |
| ‣ Mitosis: | 7 |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | 2.2 cm in greatest dimension |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | 0/16 |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | Not identified |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | Not identified |
| ‣ Margins: | Free of tumour, but the tumour is seen infiltrating close to the base |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | pT2N0 |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | |
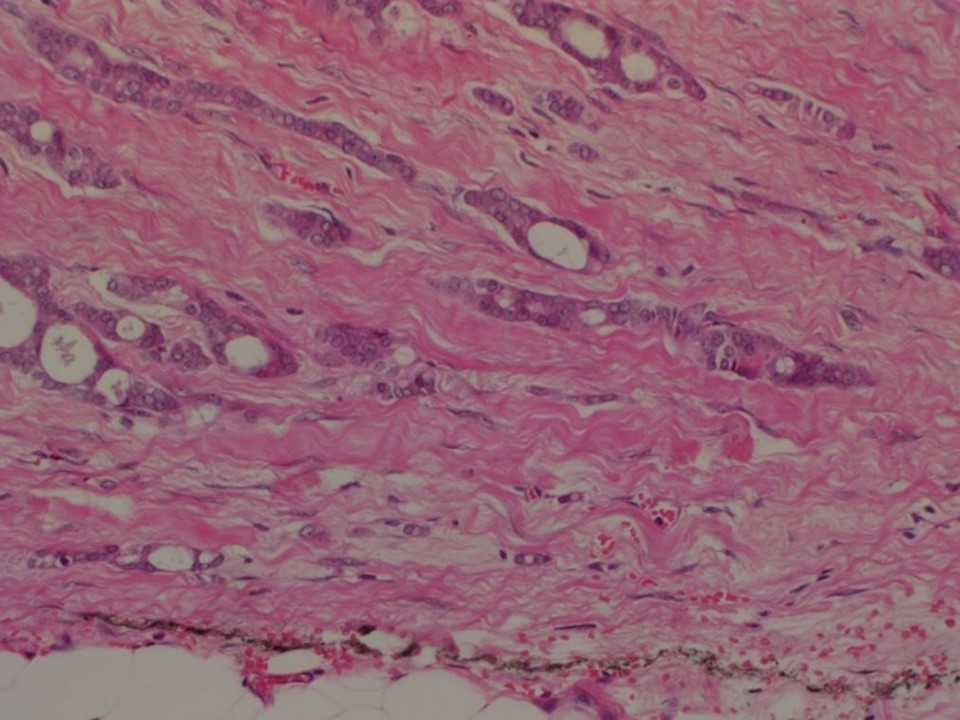
| ‣ Comments: | Perineural invasion is seen. Dense sclerosis is seen in sections from the remaining firm areas in the breast. Calcification is seen in many sections |
Case summary:
| Postmenopausal woman presented with left breast inframammary lump and pain. Diagnosed as BI-RADS 5 on imaging and as invasive carcinoma on cytology and histopathology. Typically benign round acinar calcifications in diffuse distribution, fat necrosis, and vascular calcifications are seen in both breasts on imaging and dense sclerosis with calcifications are seen in many sections on cytology and histopathology. |
Learning points:
|