Go back to the list of case studies .png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends| Case number: | 109 |
| Age: | 63 |
| Clinical presentation: | Postmenopausal woman with average risk of developing breast cancer presented with a lump in the right breast associated with pain. Examination revealed two lumps larger 5 cm in diameter in the upper outer quadrant of the right breast. |
Mammography:
| Breast composition: | ACR category a (the breasts are almost entirely fatty) |
Mammography features: | |
|
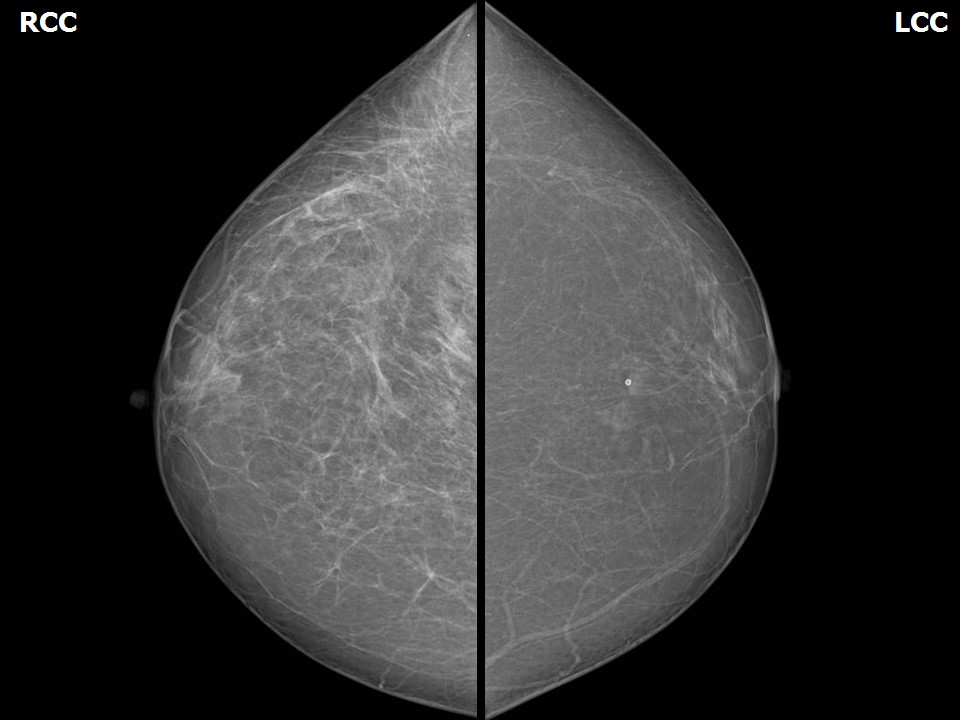
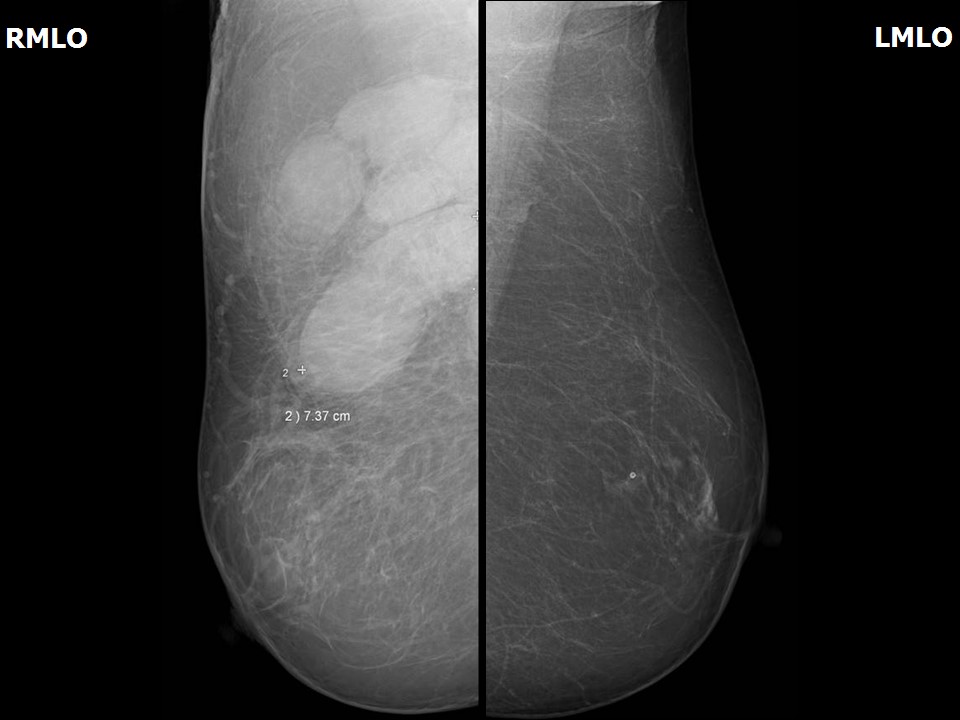
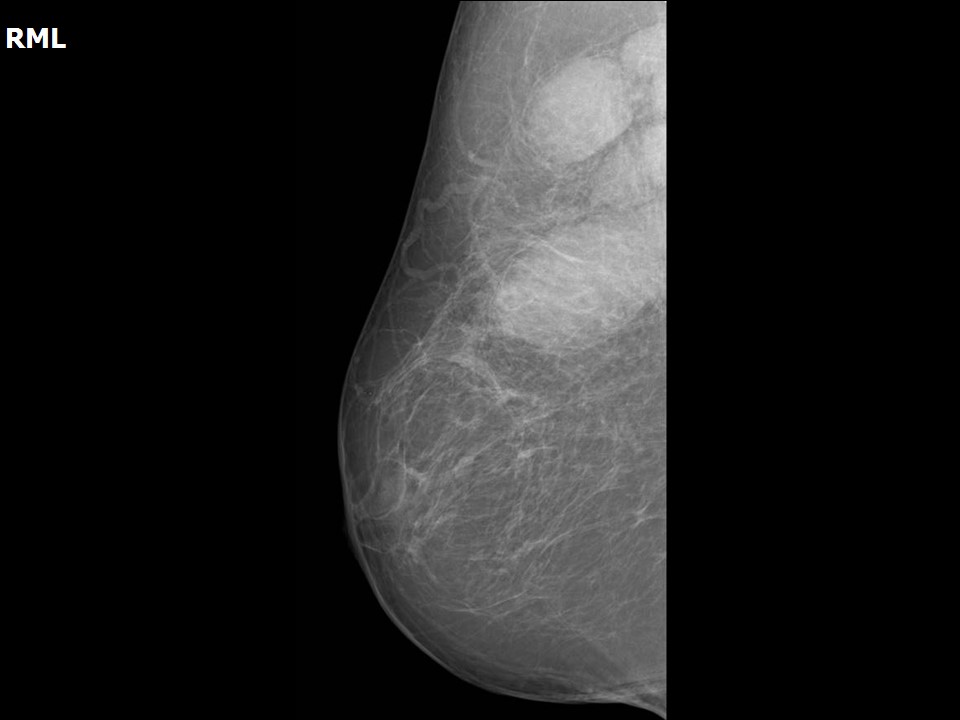
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Right breast, axillary tail and axilla |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | Multiple |
| • Size: | Largest 7.4 cm in greatest dimension |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed |
| • Density: | Equal |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | Present |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | Focal |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Trabecular thickening and axillary lymphadenopathy |
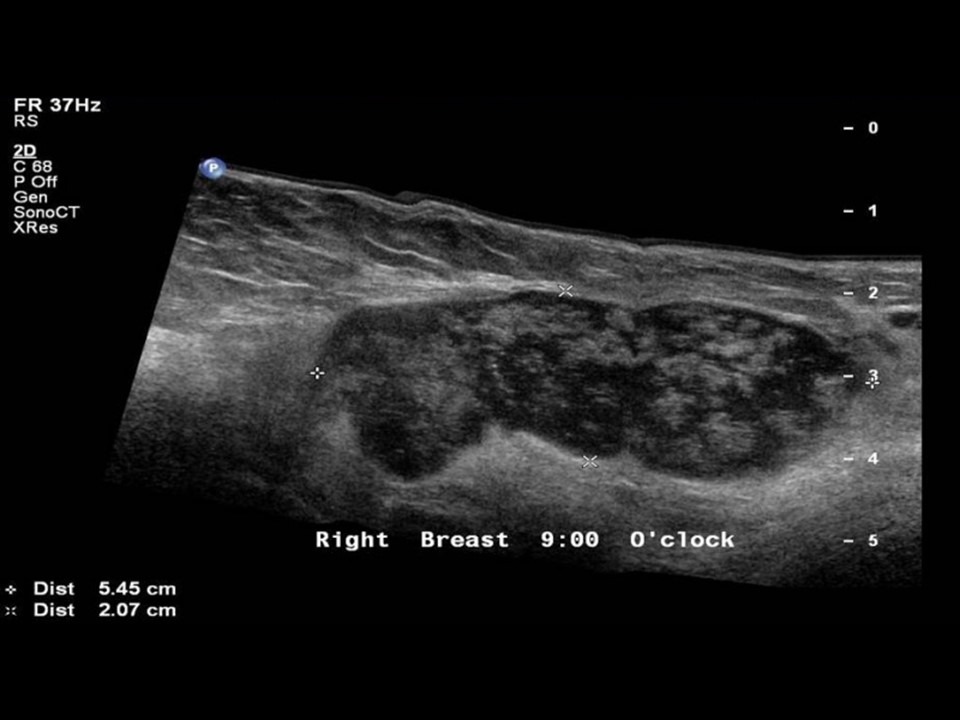
Ultrasound:
| Ultrasound features: Right axilla |
|
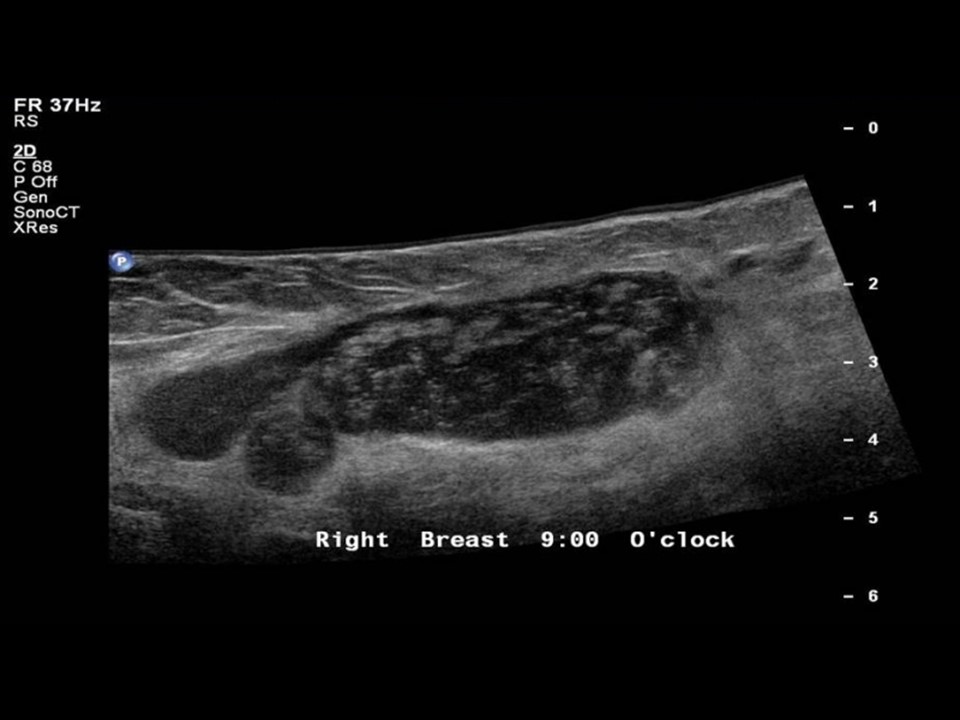
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Right axilla |
| • Number: | Multiple |
| • Size: | 5.5 × 2.0 cm (largest) |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Orientation: | Parallel |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed |
| • Echo pattern: | Heteroechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
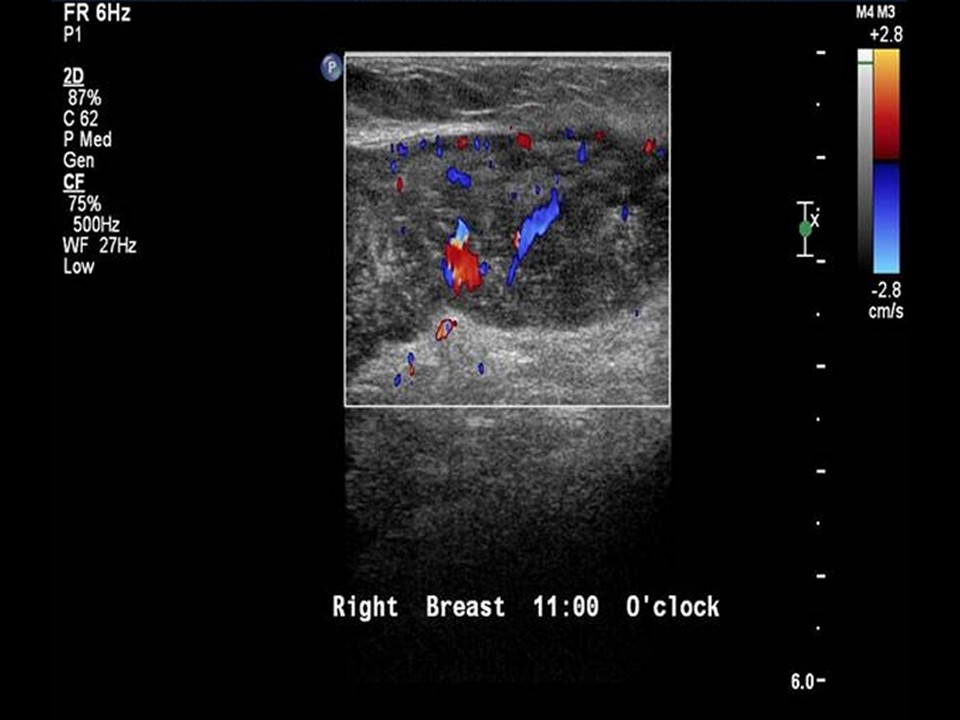
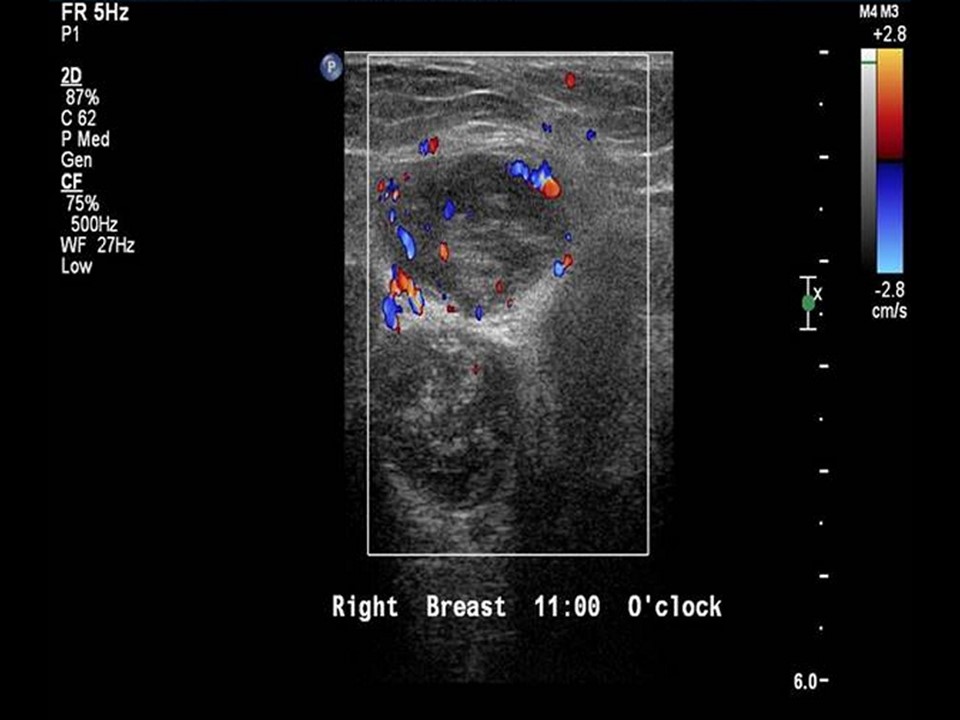
| ‣ Associated features: | Axillary lymphadenopathy with increased vascularity on colour flow mapping |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: 4A (low level of suspicion for malignancy)
Further assessment:
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytology and for excision biopsy
Cytology:
| Cytology features: | |
|
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Right |
| • Quadrant: | Upper outer |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | Whitish |
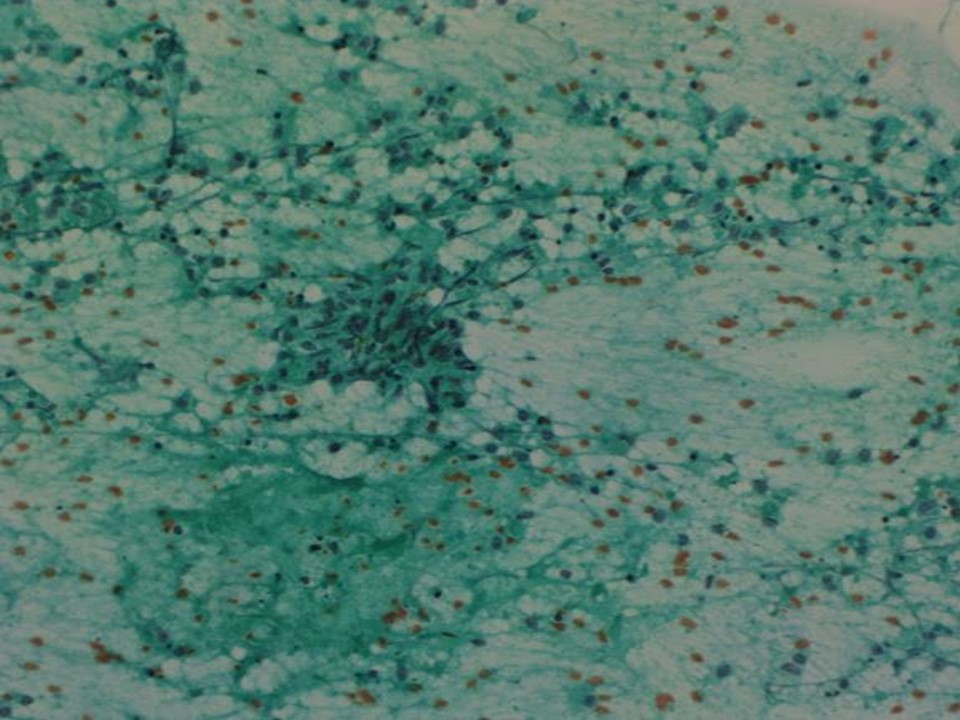
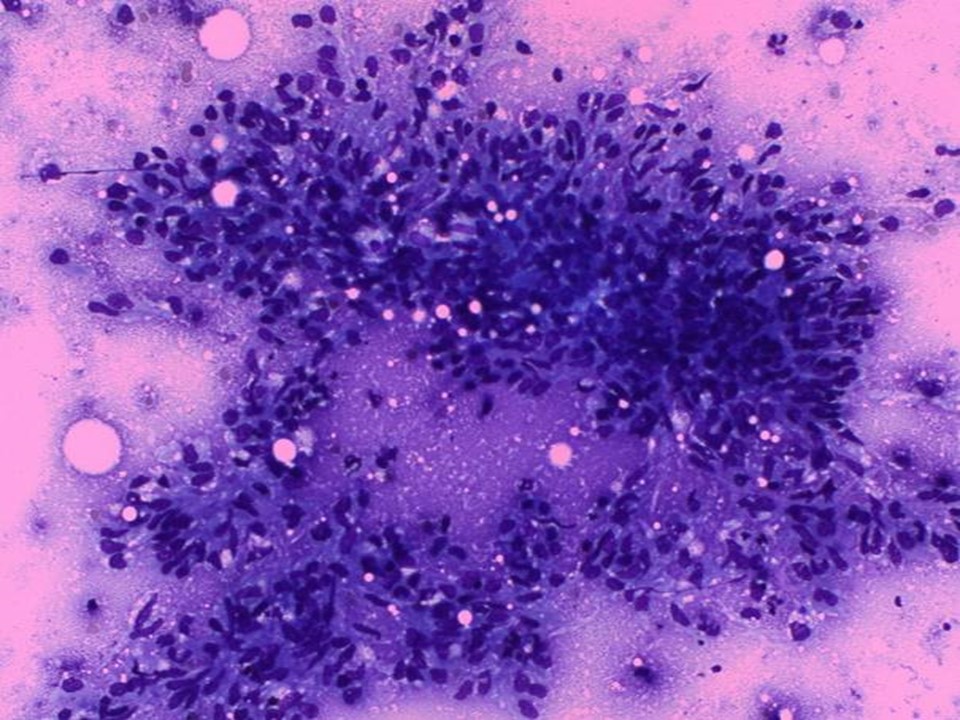
| ‣ Cytological description: | Smears show epithelioid cell conglomerates and mature lymphocytes. Ductal epithelial cells of breast origin not seen |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Benign |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Granulomatous lymphadenitis |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
Histopathology:
Lumpectomy
| Histopathology features: | |
|
| ‣ Specimen type: | Lumpectomy |
| ‣ Laterality: | Right |
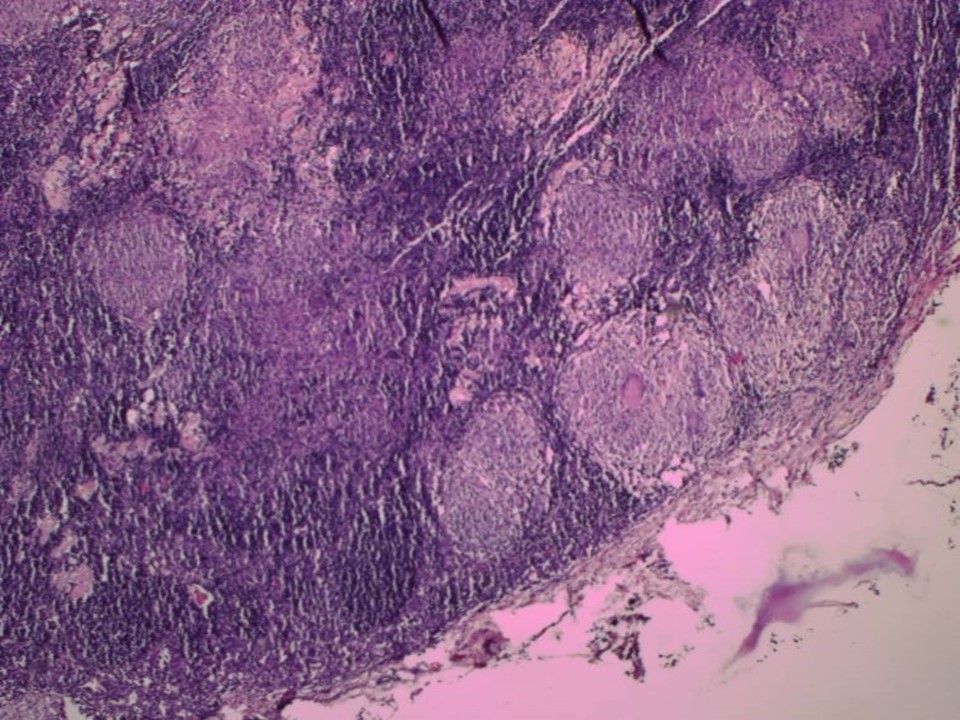
| ‣ Macroscopy: | Capsulated mass (7.0 × 3.0 × 3.0 cm). Cut surface showed whitish areas of caseous necrosis |
| ‣ Histological type: | Sections show lymph node with extensive granulomatous inflammatory reaction with caseous necrosis. Breast ductules and lobules are not seen in the sections. Impression: Tuberculous lymphadenitis |
| ‣ Histological grade: | |
| ‣ Mitosis: | |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | |
| ‣ Margins: | |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | |
| ‣ Comments: | |
Case summary:
| Postmenopausal woman presented with painful right breast lump. Diagnosed as right breast infective aetiology with right axillary reactive lymphadenopathy, BI-RADS 4A on imaging, as granulomatous lymphadenitis on cytology, and as tuberculous lymphadenitis on histopathology. |
Learning points:
- Isolated axillary node tuberculosis is rare. Tuberculosis involving the axillary nodes may present clinically as a mass in the axillary tail or upper quadrant. Biopsy confirms the diagnosis of granulomatous inflammation. In tuberculosis, breast parenchyma can show mastitis of varying degree, from architectural distortion with trabecular thickening to cold abscess formation with caseous necrosis or a discharging sinus.
|
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends