Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Filter by language: English / Русский
Go back to the list of case studies
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
| Case number: | 101 |
| Age: | 74 |
| Clinical presentation: | Postmenopausal woman with increased risk of developing breast cancer was on close clinical as well as mammography follow-up because of a history of cancers of the breast, larynx, colon, and uterus. She presented with a lump in the right breast. Examination revealed an irregular lump in the upper outer quadrant of the right breast. |
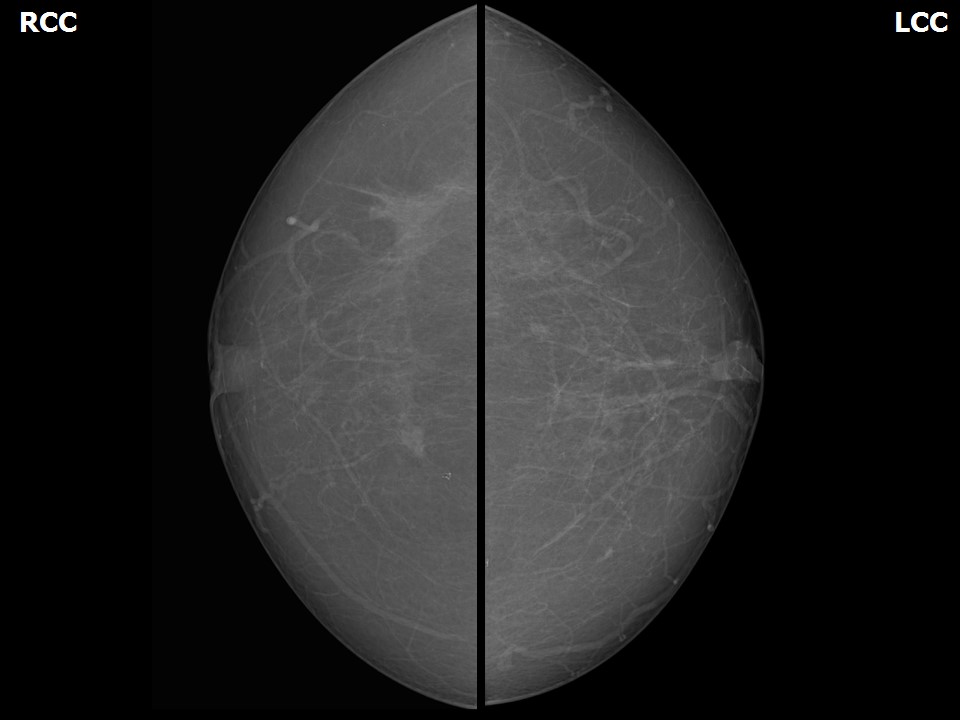
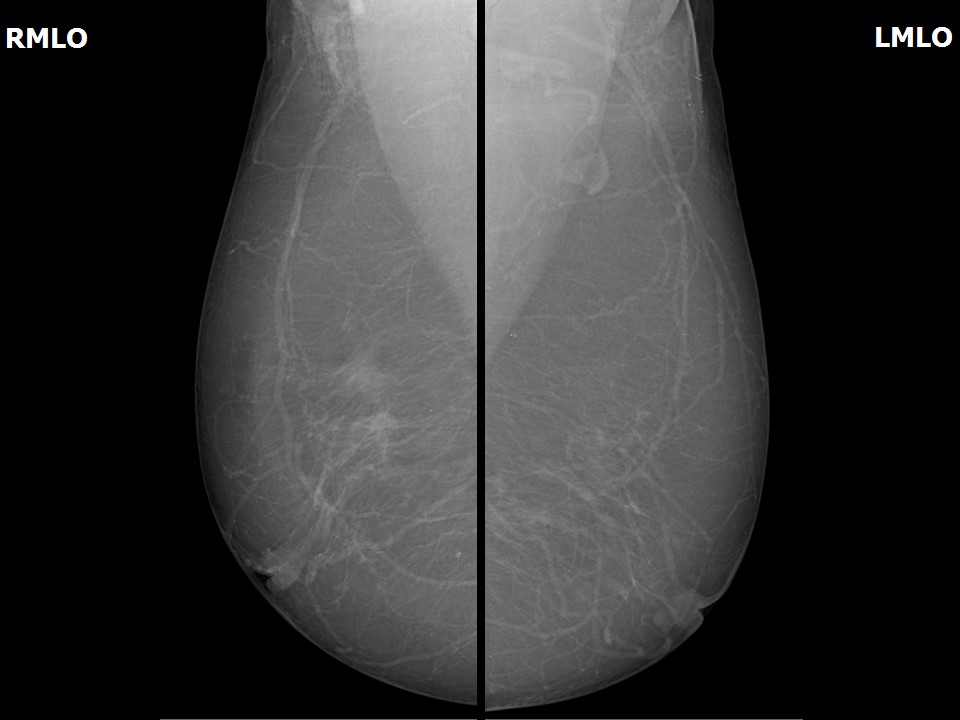
Mammography:
| Breast composition: | ACR category a (the breasts are almost entirely fatty) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: |
|
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 2 |
| • Size: |
|
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Margins: | Spiculated |
| • Density: | High |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | Present |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | Focal |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | None |
Ultrasound:
| Ultrasound features: Right breast, upper outer quadrant at 10 o’clock | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Right breast, upper outer quadrant at 10 o’clock |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 2.0 × 1.0 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Orientation: | Not parallel |
| • Margins: | Spiculated |
| • Echo pattern: | Hypoechoic |
| • Posterior features: | Posterior shadowing |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | None |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: 5 (highly suggestive of malignancy)Further assessment:
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytologyCytology:
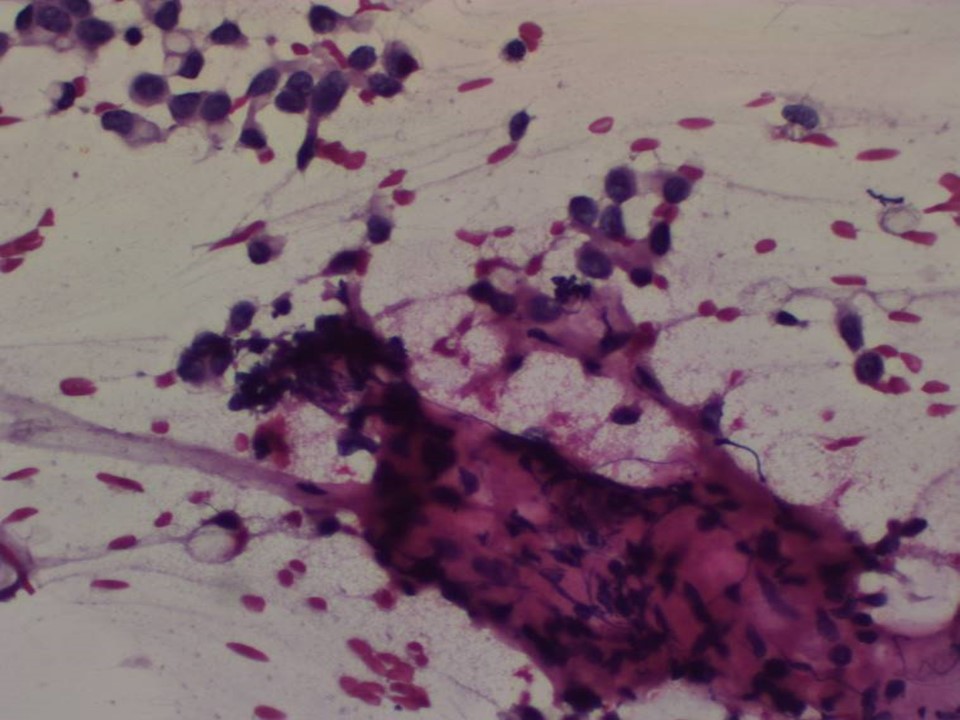
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Right |
| • Quadrant: | Upper outer |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | Whitish |
| ‣ Cytological description: | Paucicellular smears. Smears reveal fibroadipose stromal fragments with scattered malignant cells, single and in very small clusters. The malignant cells have small hyperchromatic nuclei of relatively uniform size with intracytoplasmic lumina/vacuoles |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Malignant |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Carcinoma |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
Histopathology:
Breast-conserving surgery
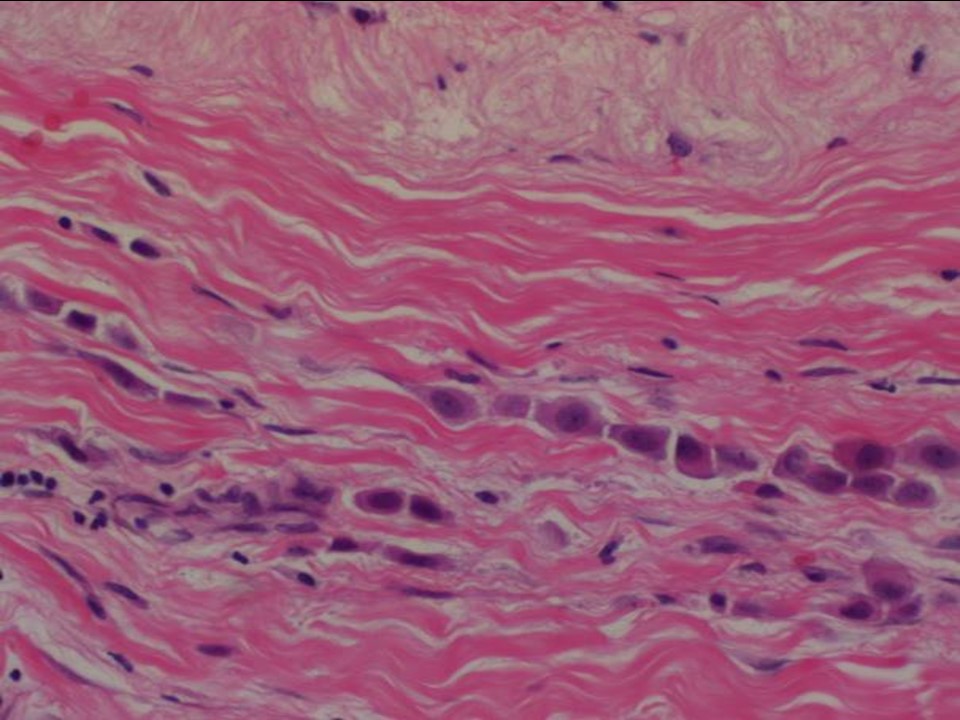
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | Breast-conserving surgery |
| ‣ Laterality: | Right |
| ‣ Macroscopy: | On serial sectioning, a firm greyish white, poorly delimited tumour (1.8 × 1.5 × 1.5 cm) is seen grossly. It is located 2.0 cm from the anterior margin, 1.0 cm from the posterior margin, 2.0 cm from the superior margin, 2.5 cm from the inferior margin, 4.5 cm from the medial margin, and 4.0 cm from the lateral margin. Another firm greyish area (0.8 × 0.7 × 0.5 cm) is flush with the lateral margin and 3.5 cm from the larger tumour |
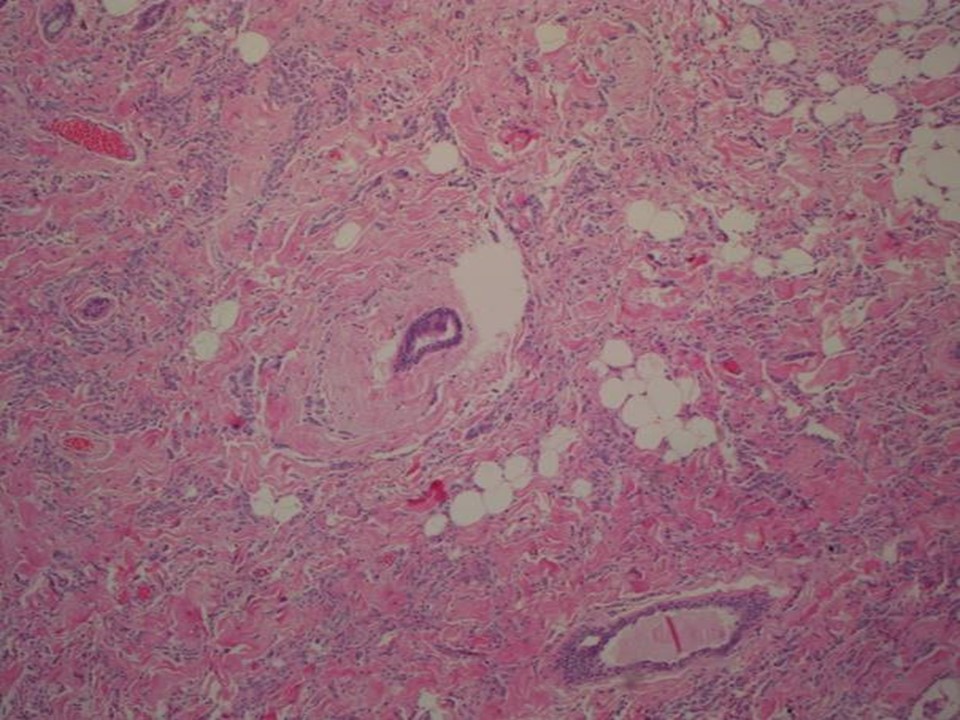
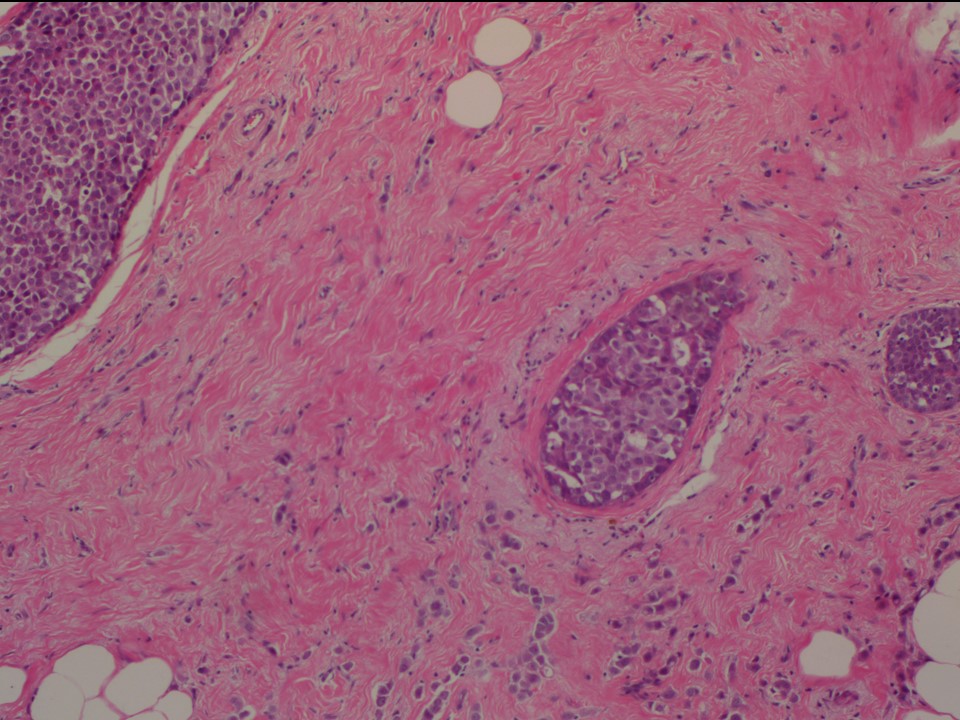
| ‣ Histological type: | Invasive lobular carcinoma |
| ‣ Histological grade: | Grade 2 (3 + 2 + 1 = 6) |
| ‣ Mitosis: | 6 |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | 2.0 cm (another area, 0.5 × 0.5 cm, is 3.5 cm lateral to the larger tumour) |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | 14/22 with extensive extranodal spread |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | Present |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | Cribriform and solid DCIS – low grade |
| ‣ Margins: | Lateral and base (posterior margin are involved by tumour) |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | pT2(2)N3 |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | E-cadherin negative, ER positive (100% tumour cells show strong nuclear staining – Allred score 8/8), PR positive (30% tumour cells show strong nuclear staining – Allred score 8/8), HER2/neu negative (score 0) |
| ‣ Comments: |
Case summary:
| Postmenopausal woman presented with lump in the right breast. Diagnosed as right breast carcinoma (multifocal), BI-RADS 5 on imaging, as breast carcinoma on cytology, and as invasive lobular carcinoma, pT2(2)N3 on histopathology. |
Learning points:
|