Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Filter by language: English / Русский
Go back to the list of case studies
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
| Case number: | 089 |
| Age: | 43 |
| Clinical presentation: | Premenopausal, nulliparous woman with increased risk of developing breast cancer because of family history of breast cancer presented with lumps in the right breast of duration 18 months. She also had occasional cyclical mastalgia. Examination revealed a lump in the right retroareolar region at the 6 o’clock position. The lump was hard with limited mobility within breast. Smaller lumps were noted in the upper and lower outer quadrants of the right breast. The right axilla was normal. Central group of nodes were palpable in the left axilla. |
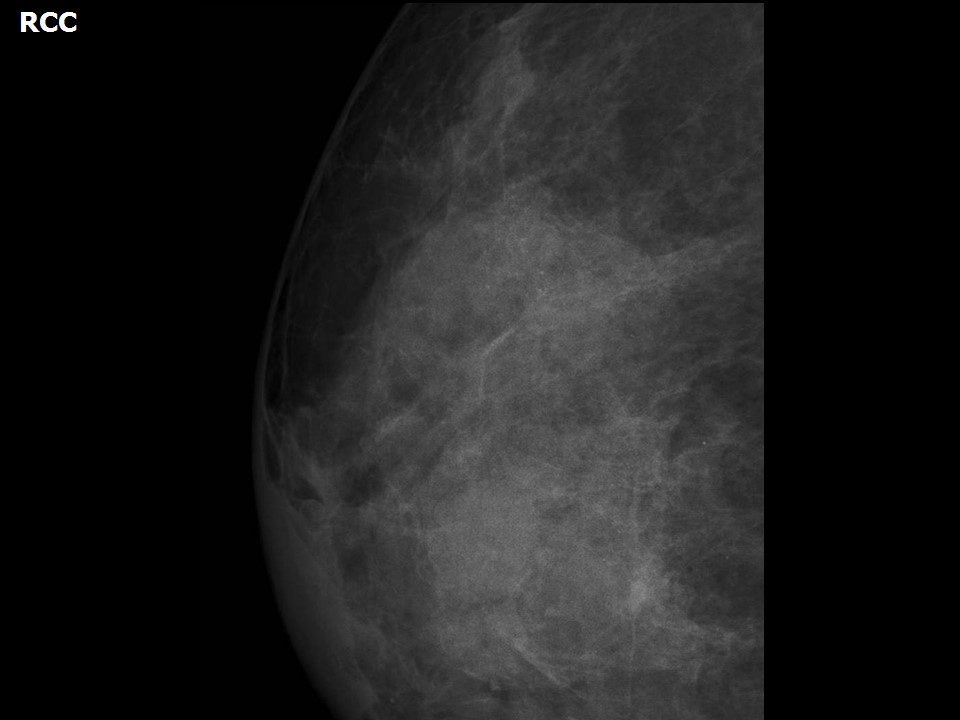
Mammography:
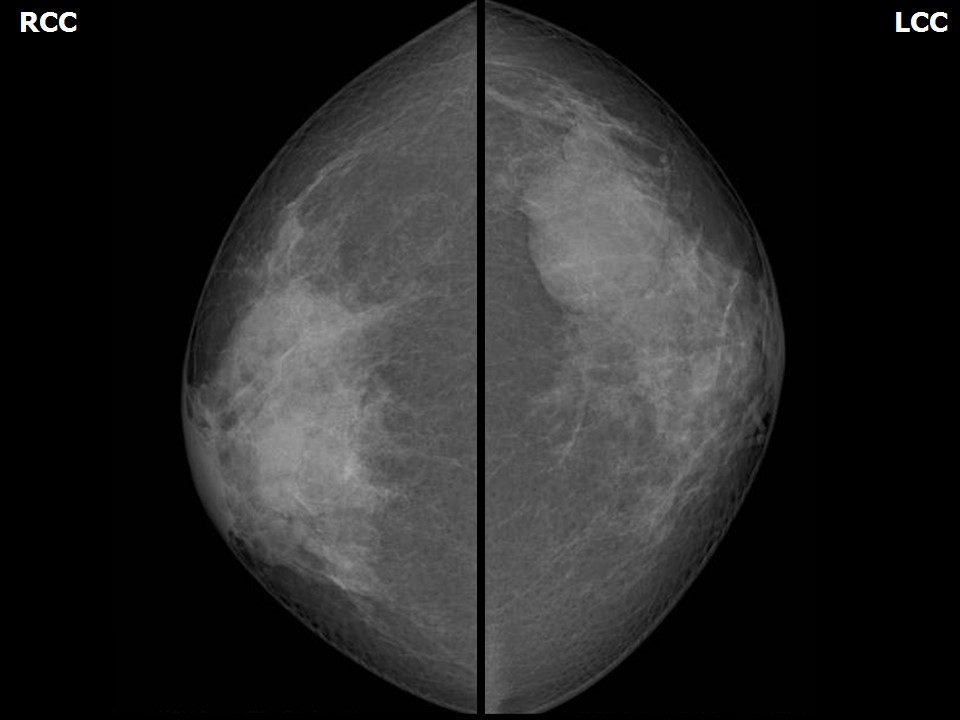
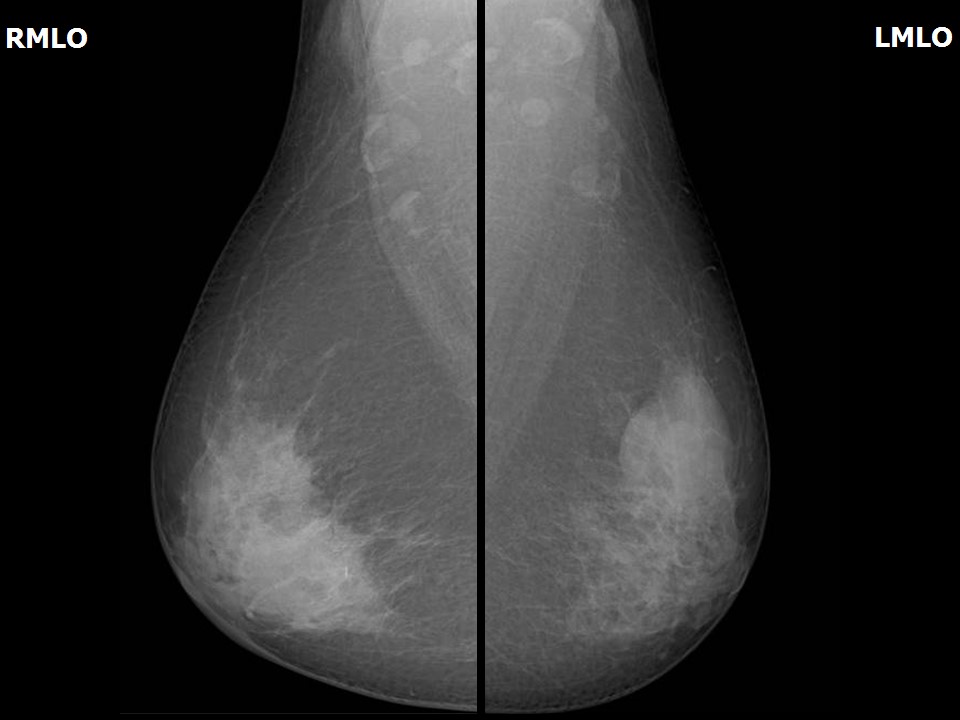
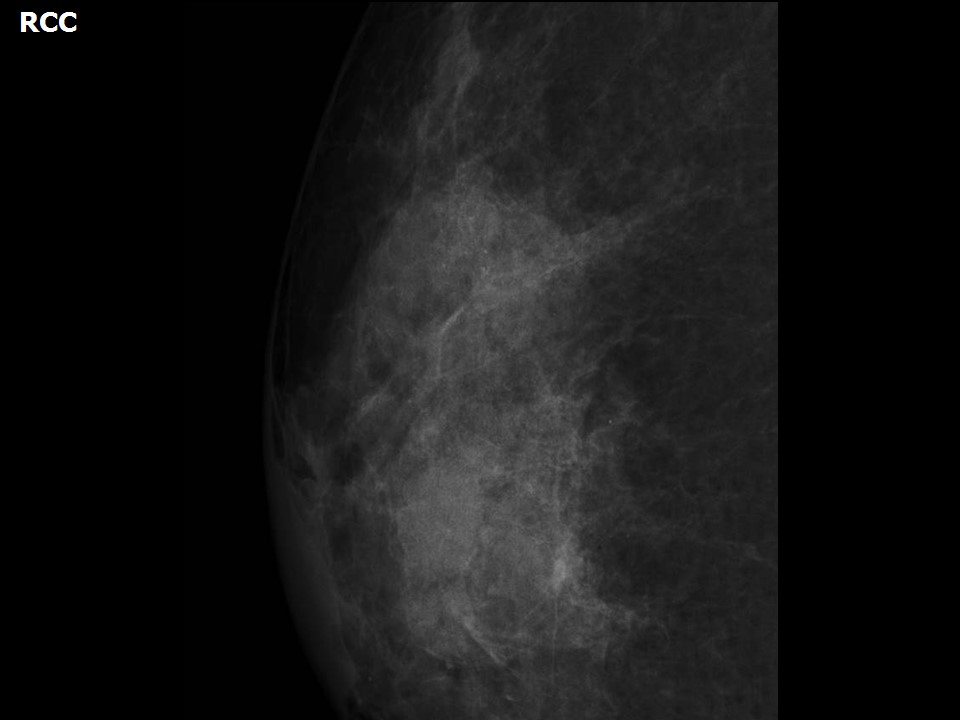
| Breast composition: | ACR category c (the breasts are heterogeneously dense, which may obscure small masses) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Right breast, central portion of the breast, central zone, anterior and middle thirds |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | Multiple |
| • Size: | 2.0 × 1.5 cm (largest in central quadrant at 12 o’clock) |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed |
| • Density: | Equal |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | Round, milk-of-calcium, regional |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | None |
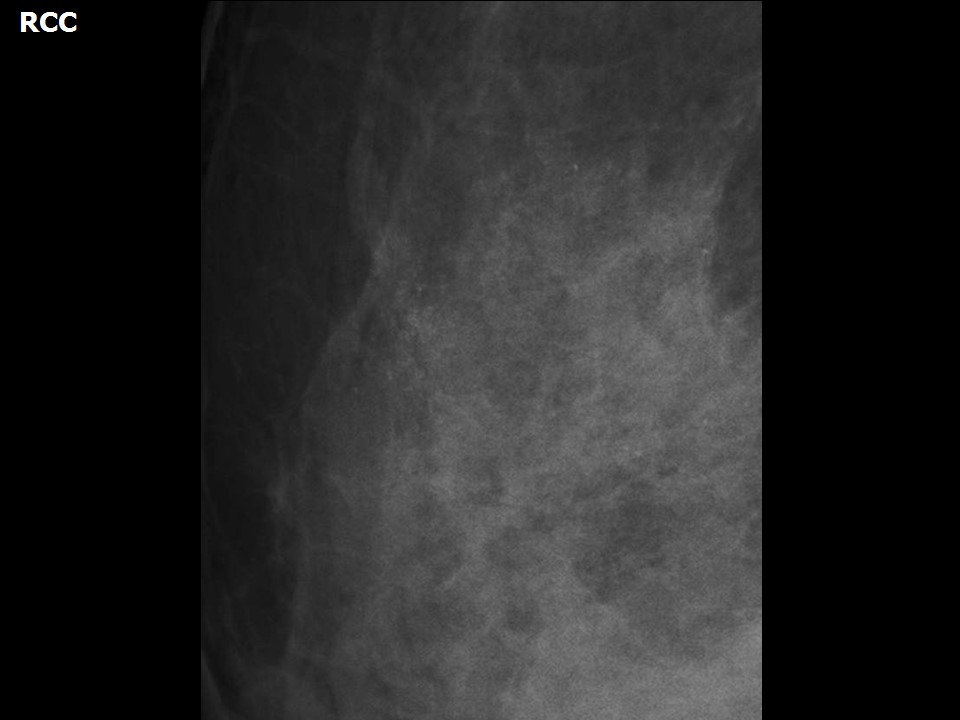
| Breast composition: | ACR category c (the breasts are heterogeneously dense, which may obscure small masses) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Left breast, upper outer quadrant at 2 o’clock, middle and posterior thirds |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | Multiple |
| • Size: | 4.0 × 2.0 cm (largest in left breast, upper outer quadrant at 1–2 o’clock) |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed |
| • Density: | Equal |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | Round, milk-of-calcium, regional |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | None |
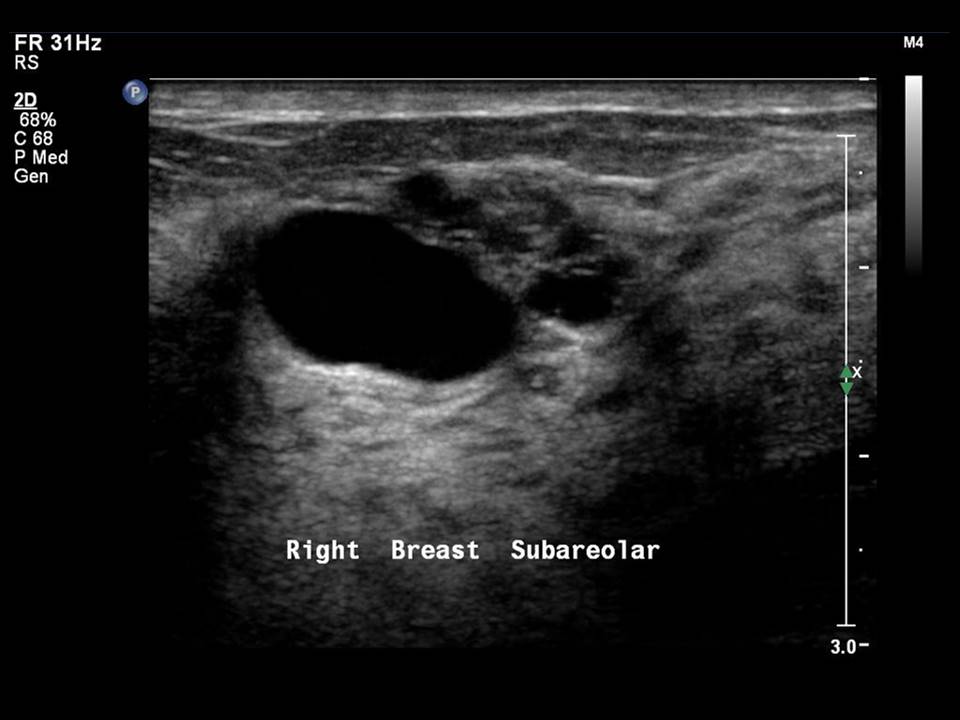
Ultrasound:
| Ultrasound features: Right breast, central portion of the breast | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Right breast, central portion of the breast |
| • Number: | Multiple |
| • Size: | Largest 2.5 × 1.0 cm |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Orientation: | Parallel |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed |
| • Echo pattern: | Anechoic |
| • Posterior features: | Posterior shadowing |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | None |
| ‣ Special cases: | Simple cyst |
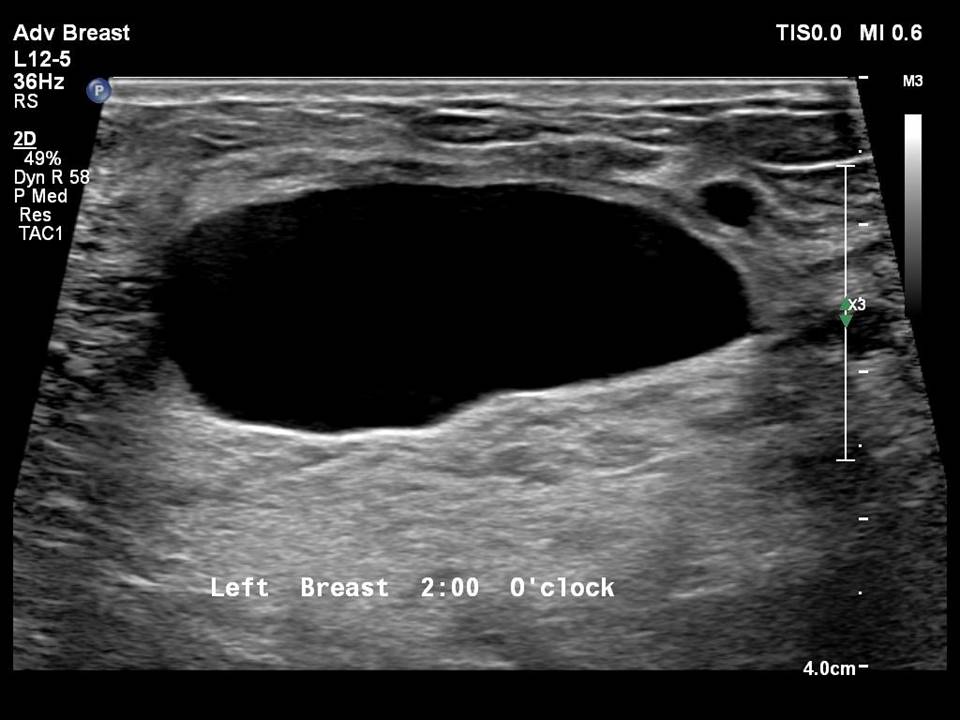
| Ultrasound features: Left breast, central portion of the breast | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Left breast, central portion of the breast |
| • Number: | Multiple |
| • Size: | Largest 3.5 × 1.5 cm |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Orientation: | Parallel |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed |
| • Echo pattern: | Anechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | None |
| ‣ Special cases: | Simple cyst |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: 2 (benign)Further assessment:
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytologyCytology:
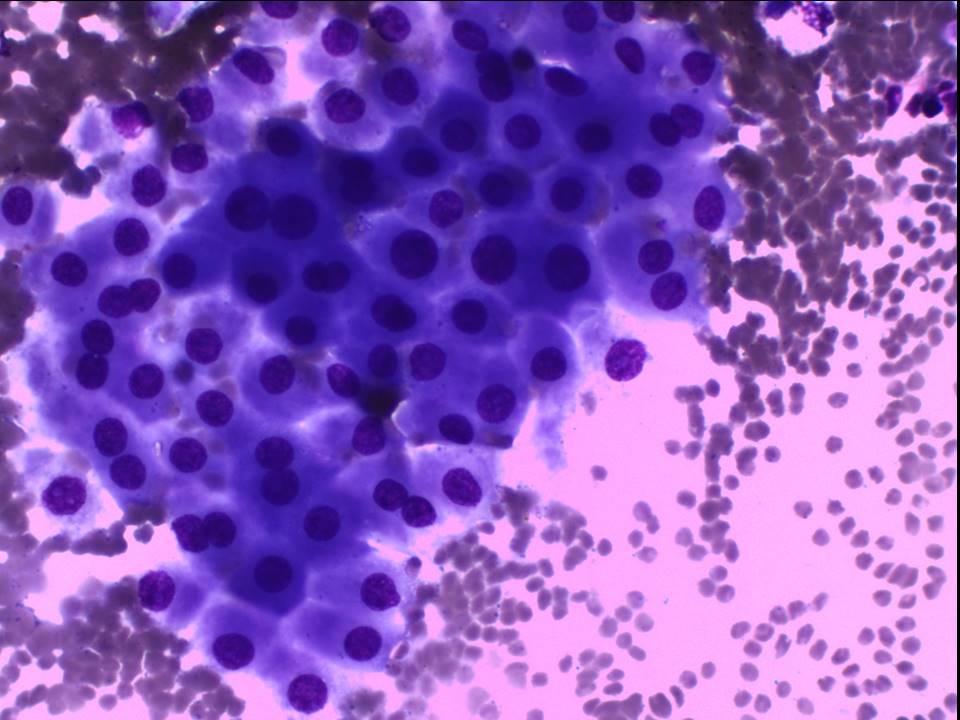
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC (cystic lesion) done on multiple occasions |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Right |
| • Quadrant: | Central and subareolar |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | 0.5–4.0 mL of brownish fluid aspirated on multiple occasions |
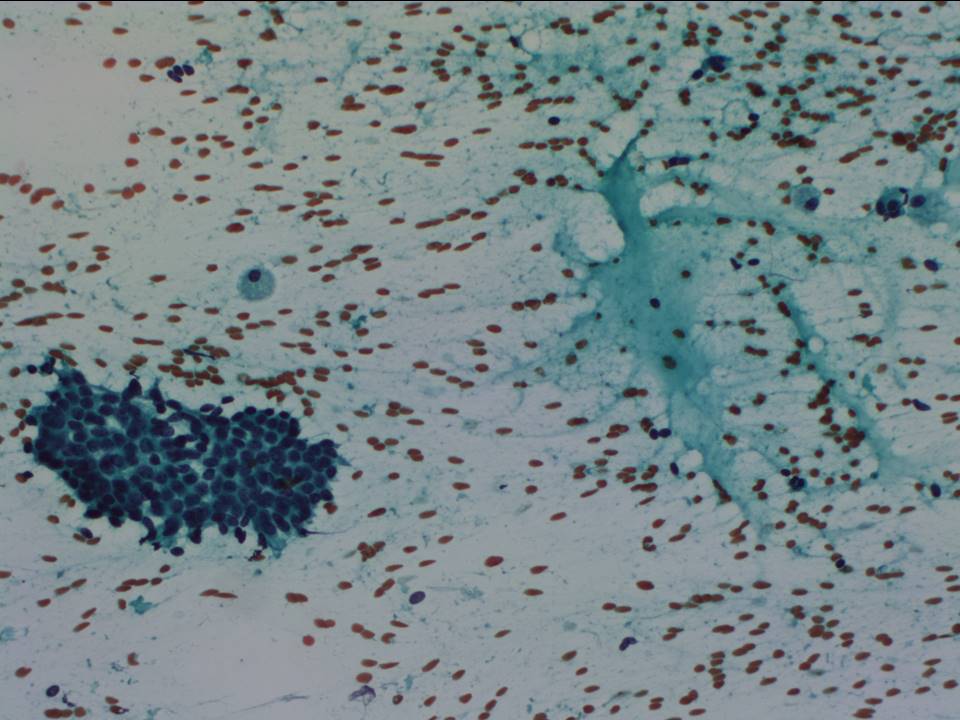
| ‣ Cytological description: | Smears reveal sheets of apocrine cells, a few sheets of tightly cohesive benign ductal epithelial cells, and numerous foamy macrophages on a proteinaceous background |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Benign |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Benign breast lesion; suggestive of proliferative fibrocystic changes |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
Case summary:
| Premenopausal woman presented with right breast lump and bilateral mastalgia diagnosed as fibrocystic changes with typically benign amorphous, round, and milk-of-calcium calcifications in both breasts, BI-RADS 2 on imaging and as proliferative fibrocystic changes on cytology. |
Learning points:
|