Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Filter by language: English / Русский
Go back to the list of case studies
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
| Case number: | 076 |
| Age: | 40 |
| Clinical presentation: | Premenopausal woman presented to surgical unit with pain in abdomen. Ultrasound of the abdomen revealed focal hepatic lesions of indeterminate aetiology, suspicious of metastatic foci. Clinical examination to look for primary revealed bilateral breast lumps. |
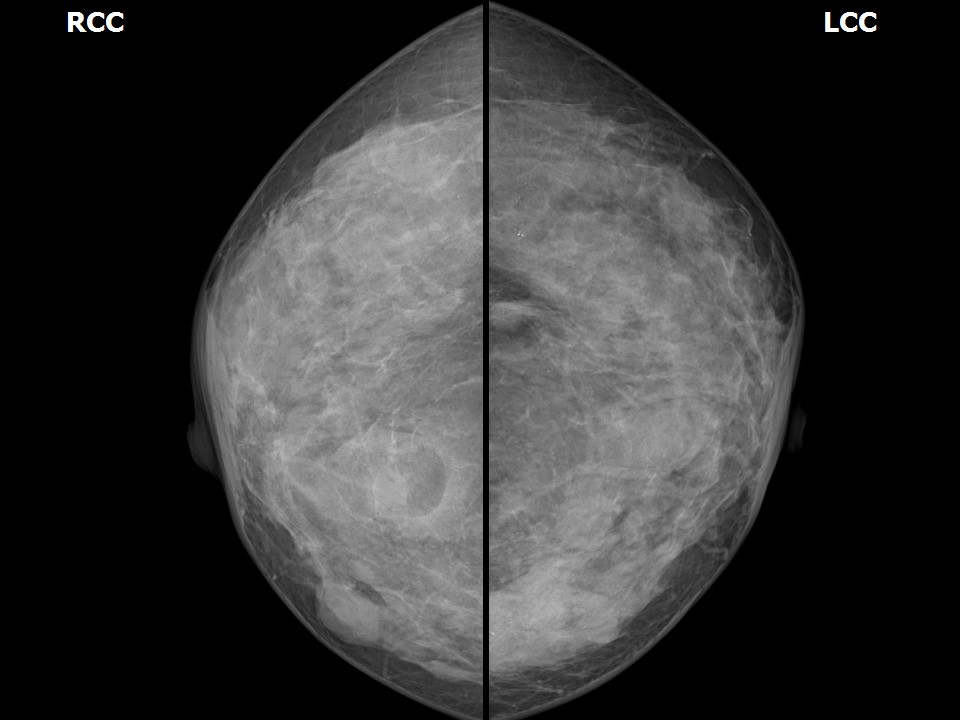
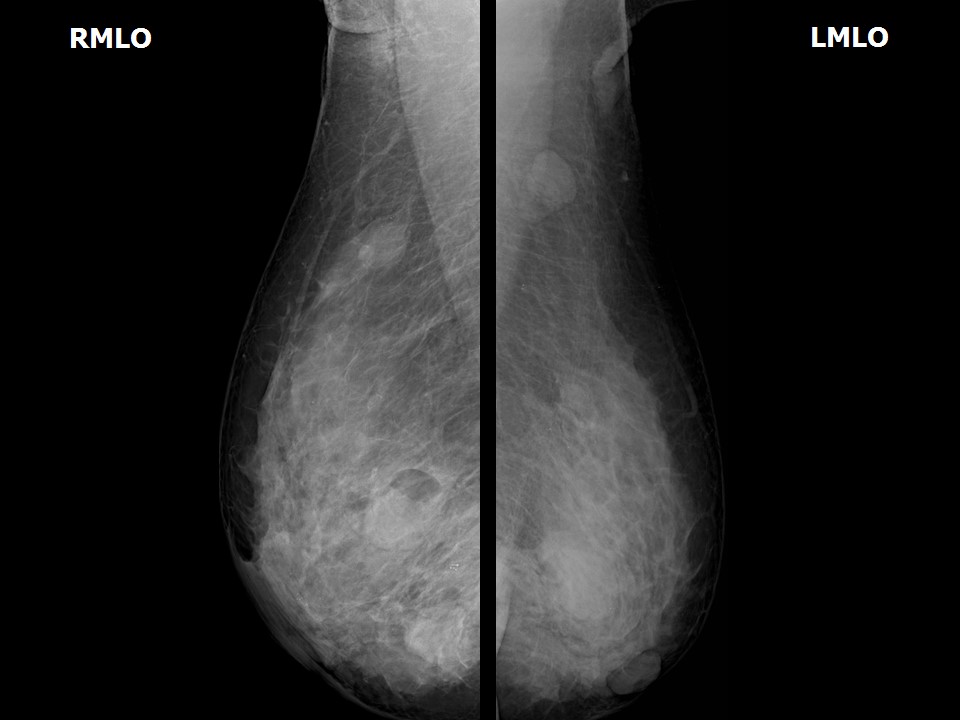
Mammography:
| Breast composition: | ACR category c (the breasts are heterogeneously dense, which may obscure small masses) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Right breast, upper outer quadrant at 10 o’clock, middle third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 1.8 × 0.8 cm |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Margins: | Indistinct |
| • Density: | Equal |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | None |
| Breast composition: | ACR category c (the breasts are heterogeneously dense, which may obscure small masses) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Right breast, upper inner quadrant at 1 o’clock, posterior third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 2.2 × 1.4 cm |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed |
| • Density: | Fat-containing |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | None |
| Breast composition: | ACR category c (the breasts are heterogeneously dense, which may obscure small masses) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Right breast, inner quadrants at 3 o’clock, middle third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 2.0 × 1.0 cm |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed |
| • Density: | Equal |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | None |
| Breast composition: | ACR category c (the breasts are heterogeneously dense, which may obscure small masses) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Left breast, inner quadrants at 9 o’clock, middle and posterior thirds |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 4.5 × 2.0 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Margins: | Spiculated |
| • Density: | High |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | Fine linear and pleomorphic microcalcifications |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
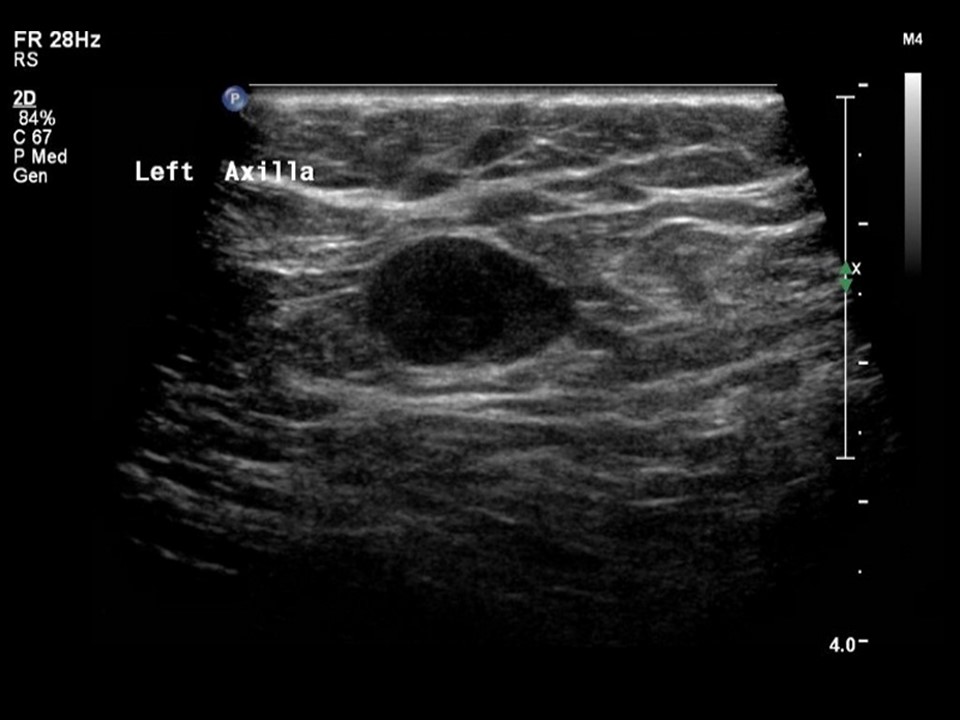
| ‣ Associated features: | Left axillary adenopathy and round enlarged node in left axilla with loss of fatty hilum |
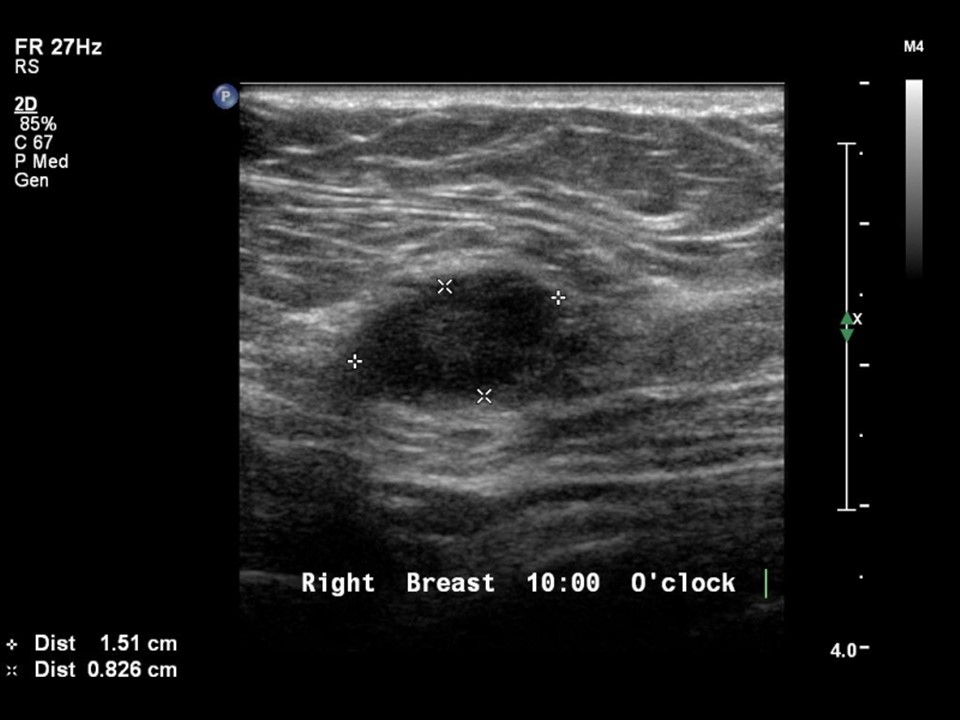
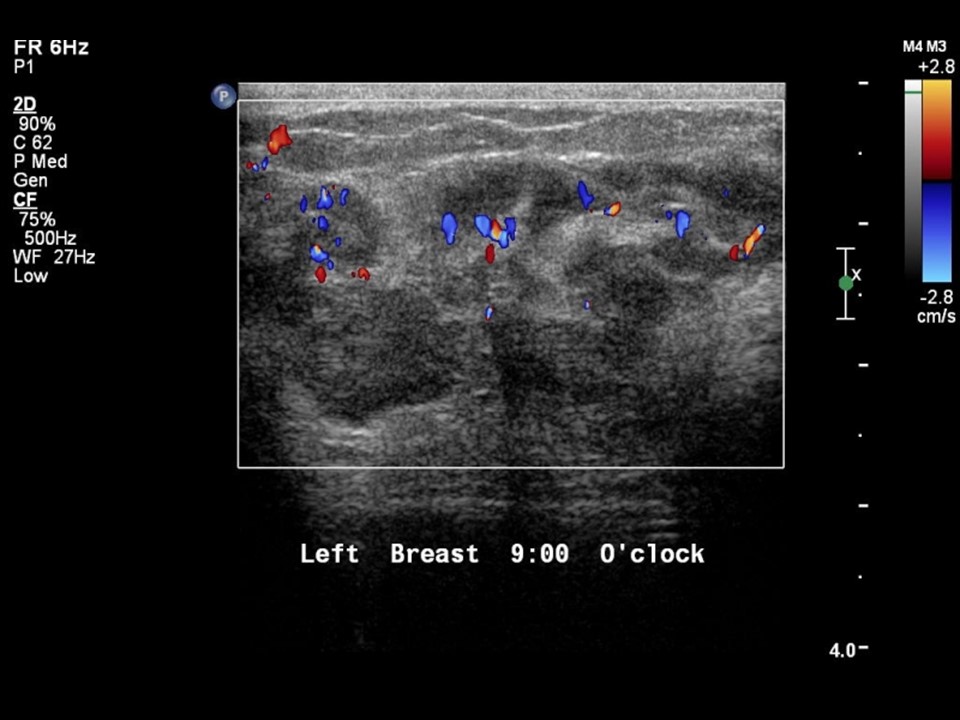
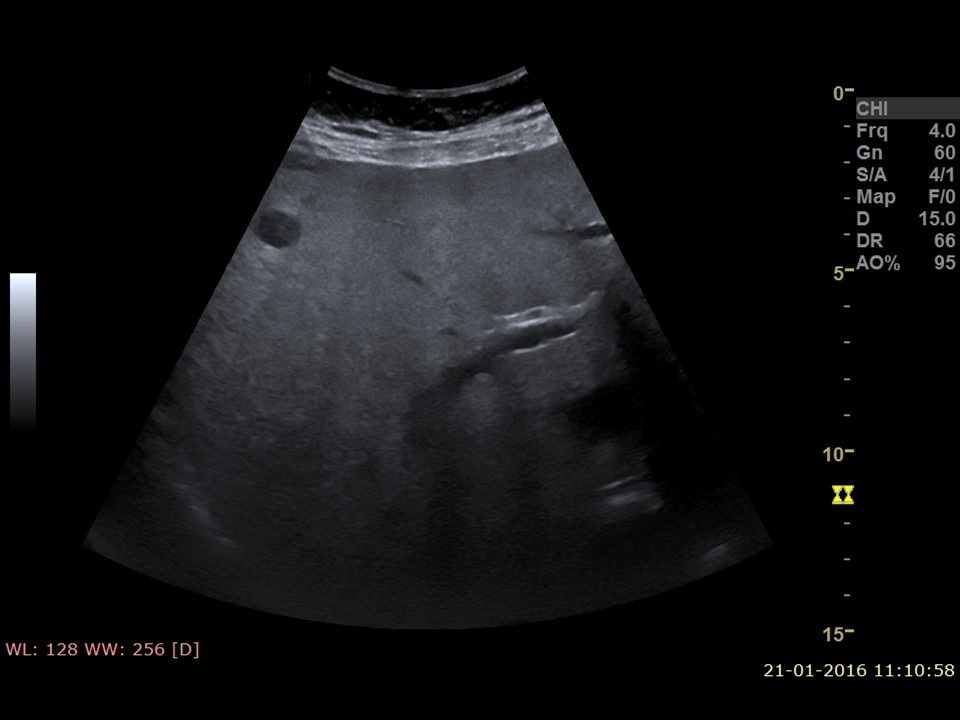
Ultrasound:
| Ultrasound features: Right breast, upper and lower quadrants at 4-12 o'clock | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Right breast, upper and lower quadrants at 4-12 o'clock |
| • Number: | Multiple |
| • Size: |
|
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Orientation: | Parallel |
| • Margins: | Lesion 1: Indistinct, lesions 2–5: Circumscribed |
| • Echo pattern: | Hypoechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | None |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
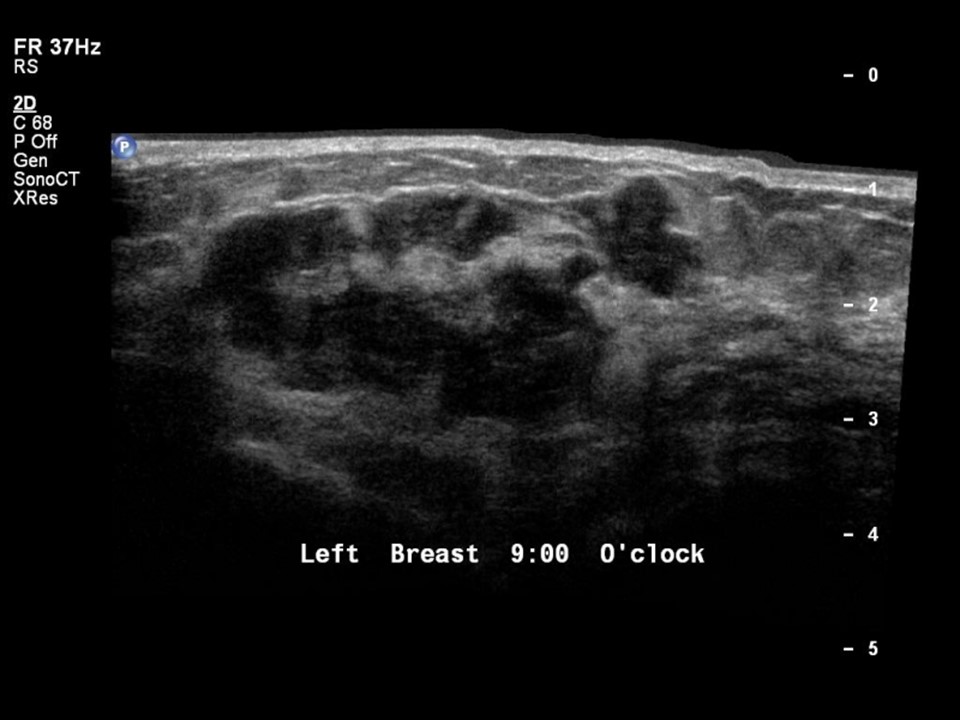
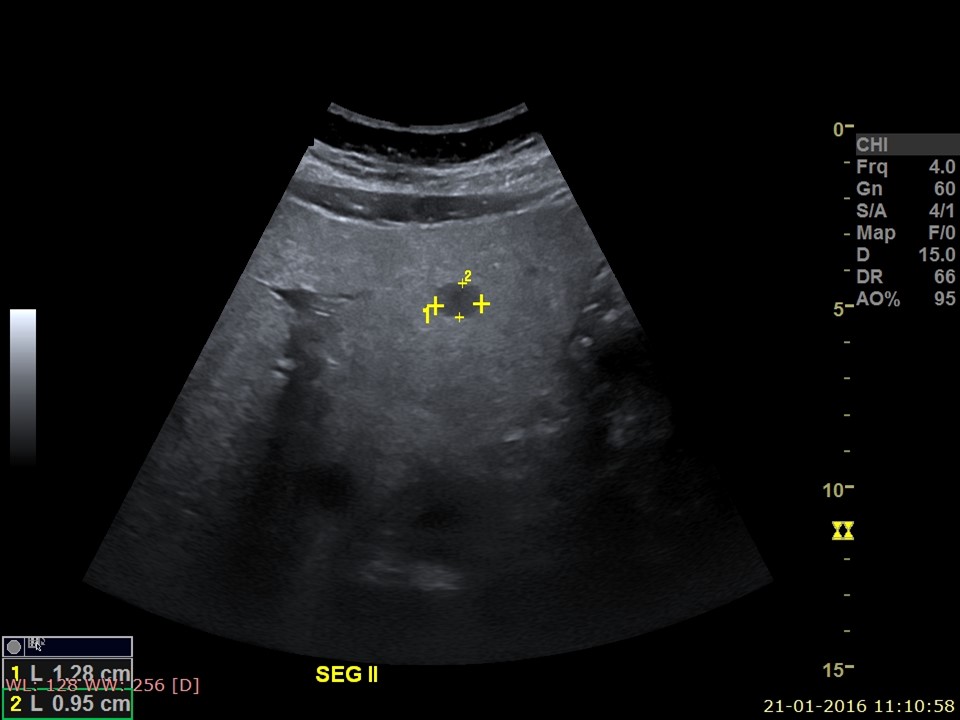
| Ultrasound features: Left breast, inner quadrants | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Left breast, inner quadrants |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 4.5 × 2.0 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Orientation: | Parallel |
| • Margins: | Angular |
| • Echo pattern: | Heteroechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | Present in mass |
| ‣ Associated features: | Internal vascularity and calcifications |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: 4C (high suspicion for malignancy)Further assessment:
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytologyCytology:
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Right |
| • Quadrant: | |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | Whitish |
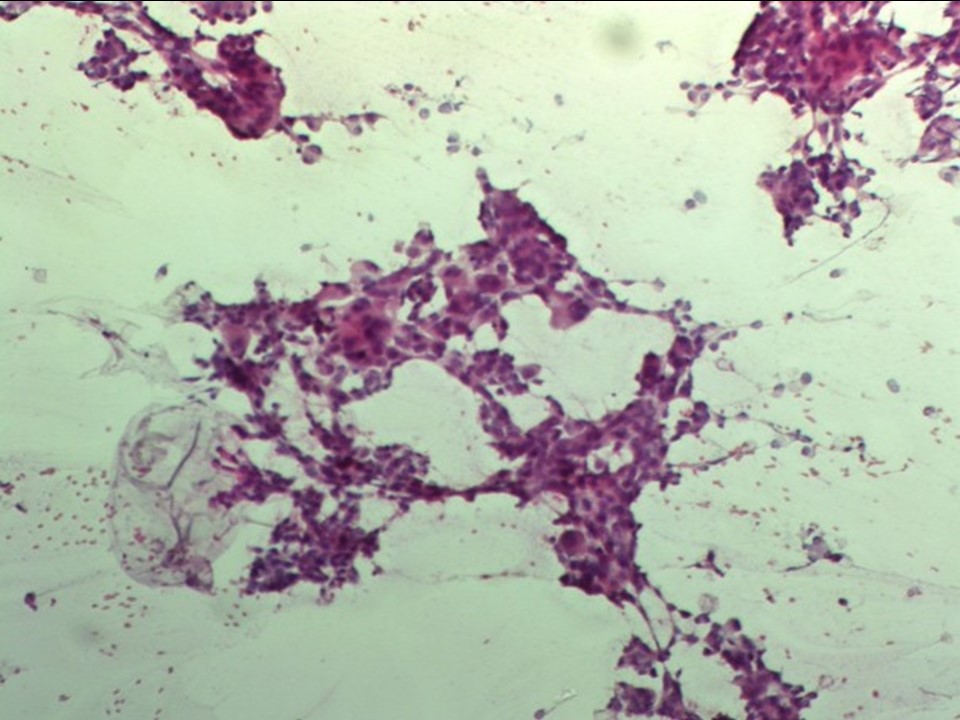
| ‣ Cytological description: | Smears from right breast lump reveal many loosely cohesive clusters and singly scattered atypical cells with large hyperchromatic and pleomorphic nuclei and moderate cytoplasm. Many large multinucleate cells seen |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Malignant |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Carcinoma |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Left |
| • Quadrant: | Inner |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | Whitish |
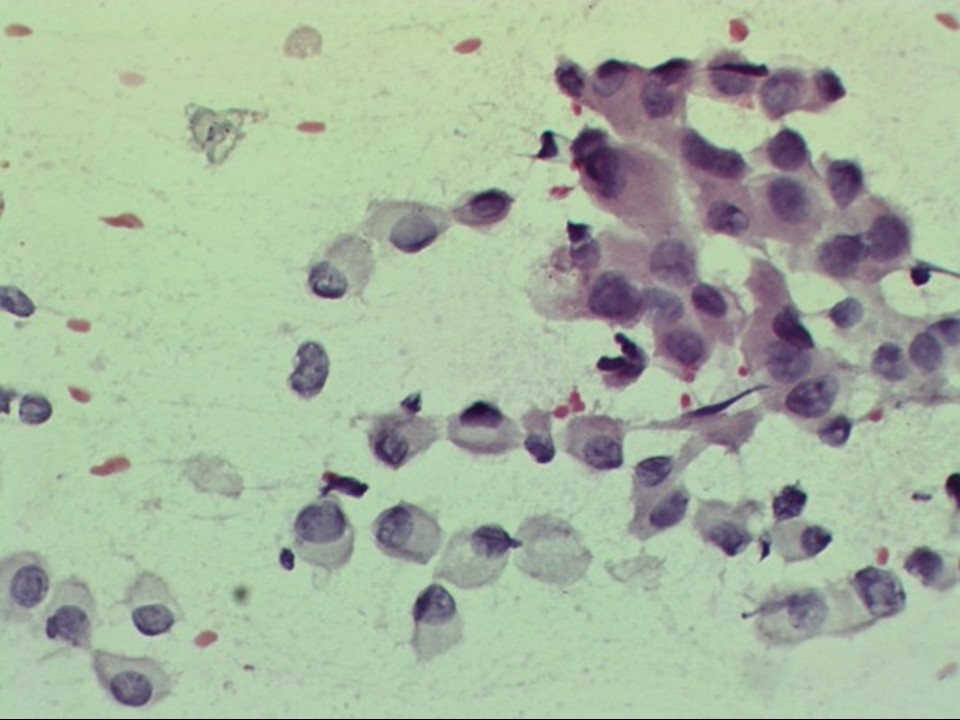
| ‣ Cytological description: | Smears reveal many loosely cohesive clusters and single scattered malignant cells with moderate cytoplasm and hyperchromatic pleomorphic nuclei. Nucleoli are seen in many cells. A few tightly cohesive benign clusters are also noted |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Malignant |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Carcinoma |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
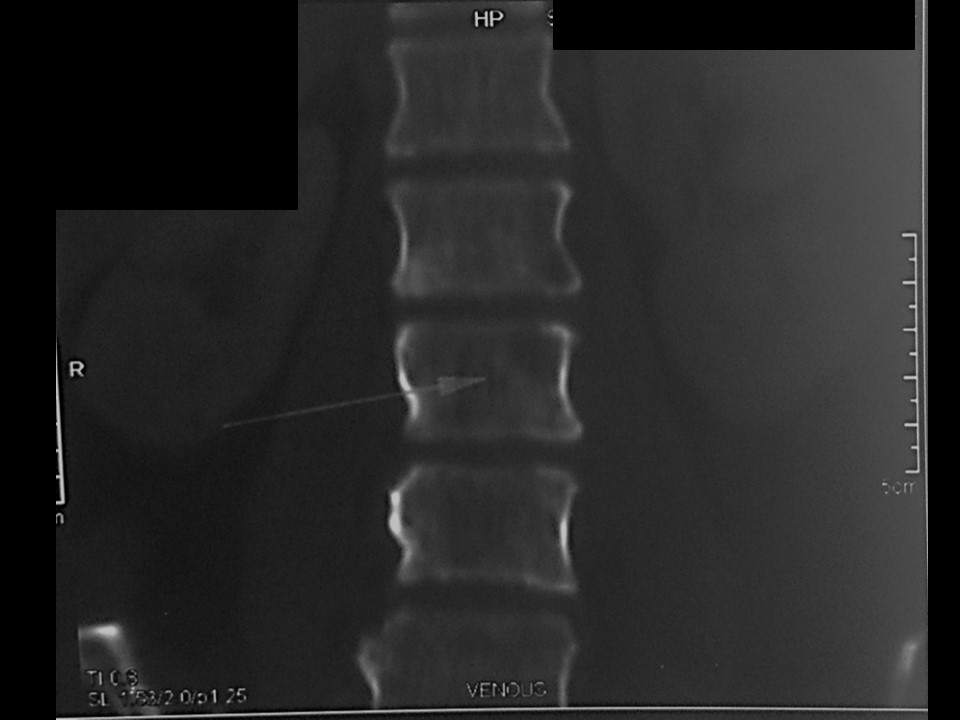
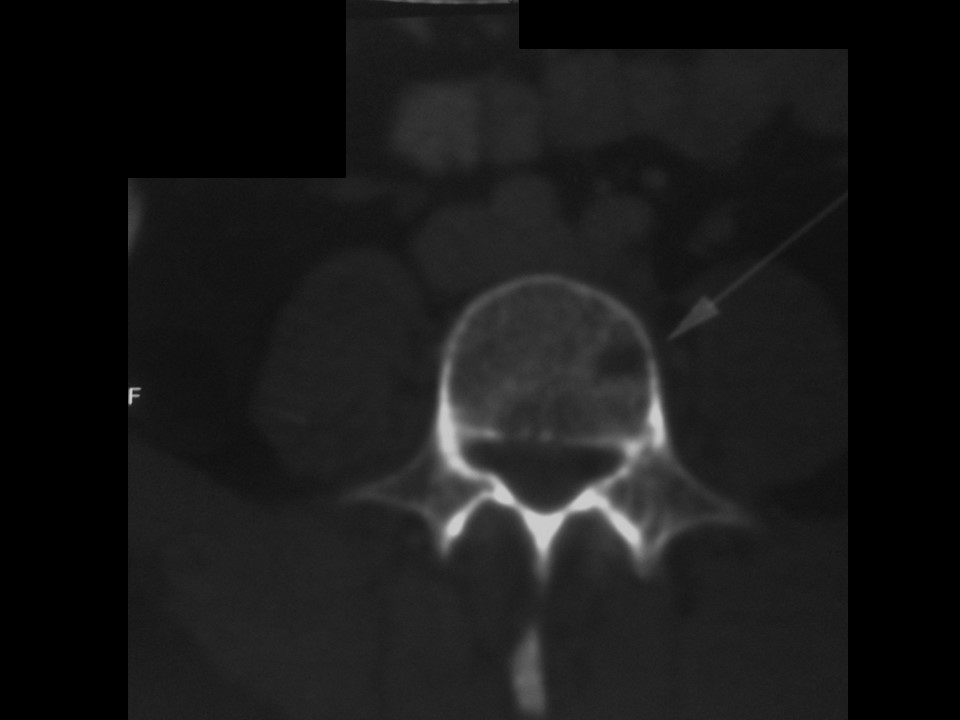
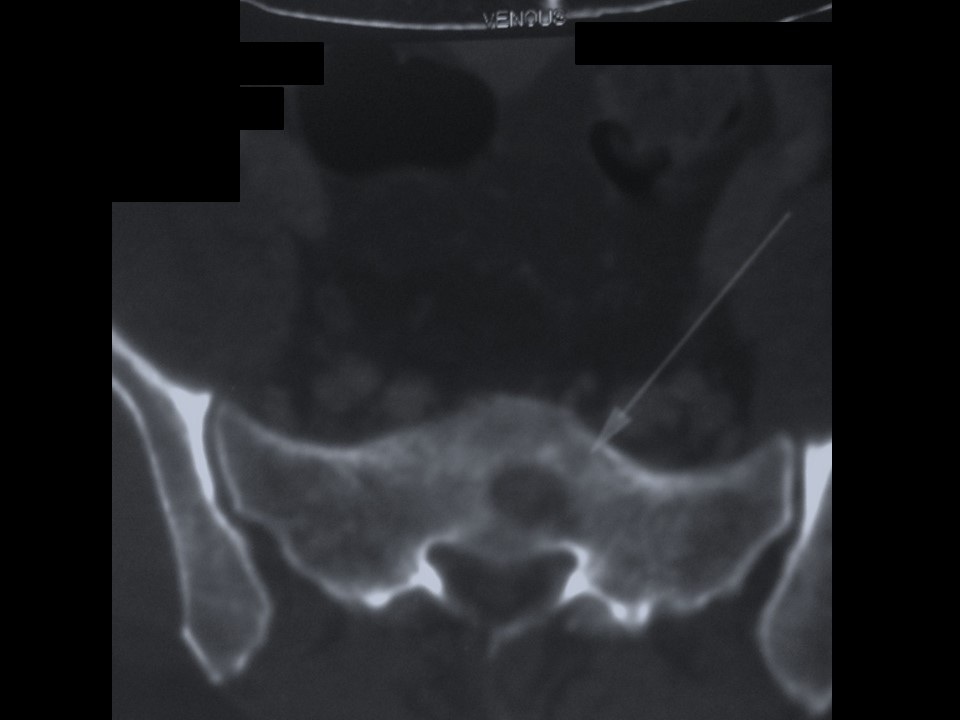
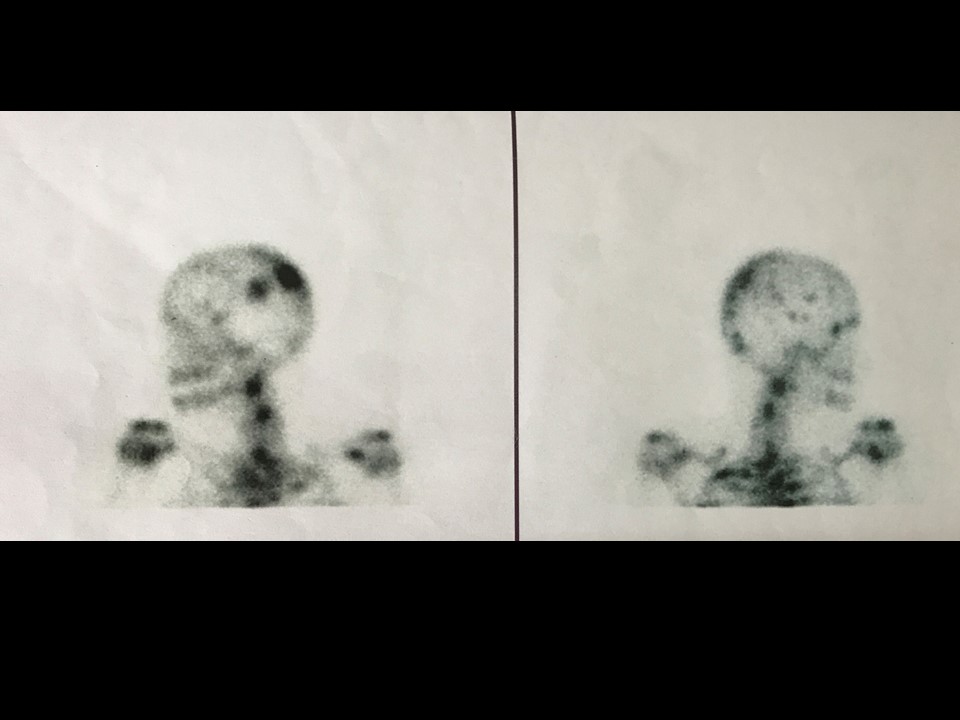
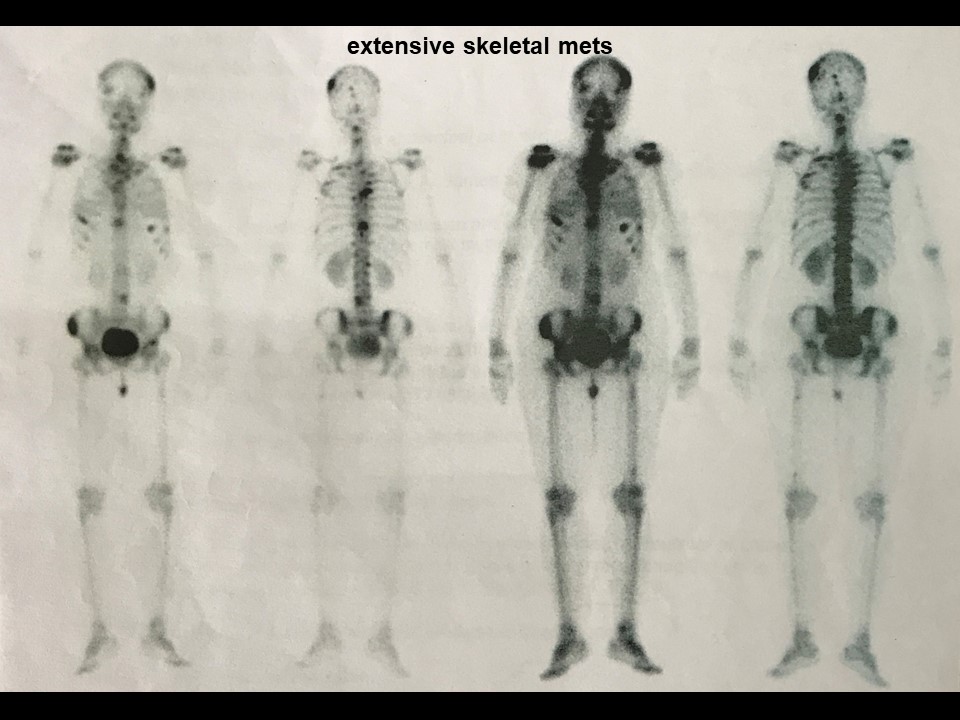
Systemic metastatic workup:
Case summary:
| Premenopausal woman presented with pain in abdomen. Ultrasound of the abdomen revealed focal hepatic lesions of indeterminate aetiology, suspicious of metastatic foci. Further clinical examination revealed bilateral breast lumps. Patient was diagnosed as left breast suspicious mass with enlarged left axillary node, likely metastatic node, and right breast mass with features suspicious for malignancy, BI-RADS 4C – bilateral – synchronous on imaging and as bilateral breast carcinoma on cytology. |
Learning points:
|