Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Filter by language: English / Русский
Go back to the list of case studies
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
| Case number: | 075 |
| Age: | 51 |
| Clinical presentation: | Postmenopausal woman with average risk of developing breast cancer presented with right breast lump noticed a few days ago. CBE revealed a hard lump in the medial quadrant of the right breast. Also palpable is a firm to hard lump in the upper quadrant of the left breast. |
Mammography:
| Breast composition: | ACR category b (there are scattered areas of fibroglandular density) | Mammography features: |
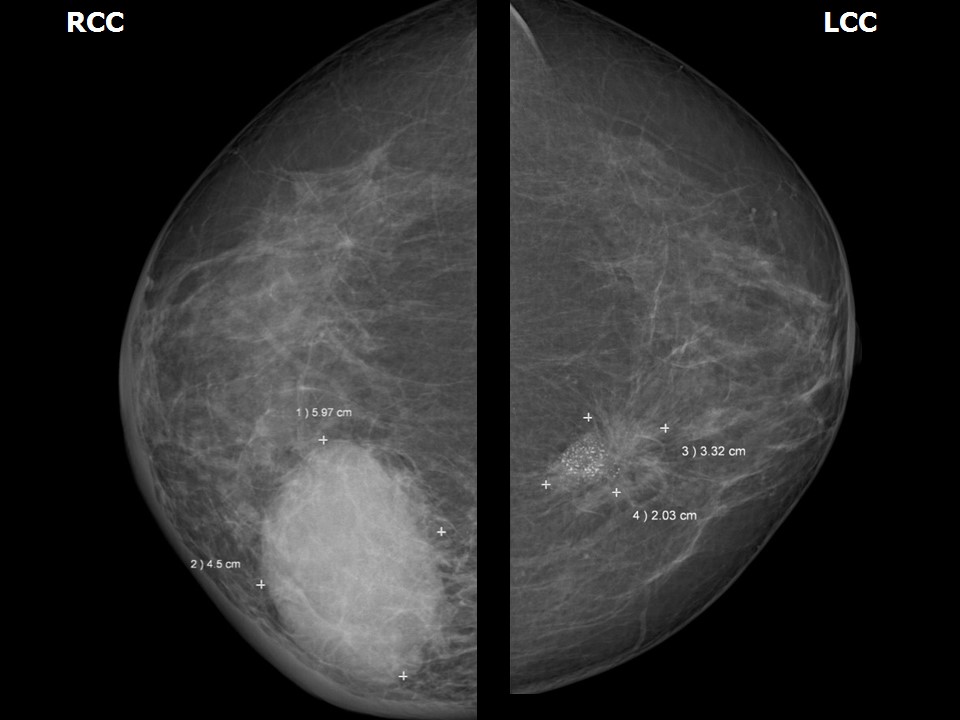
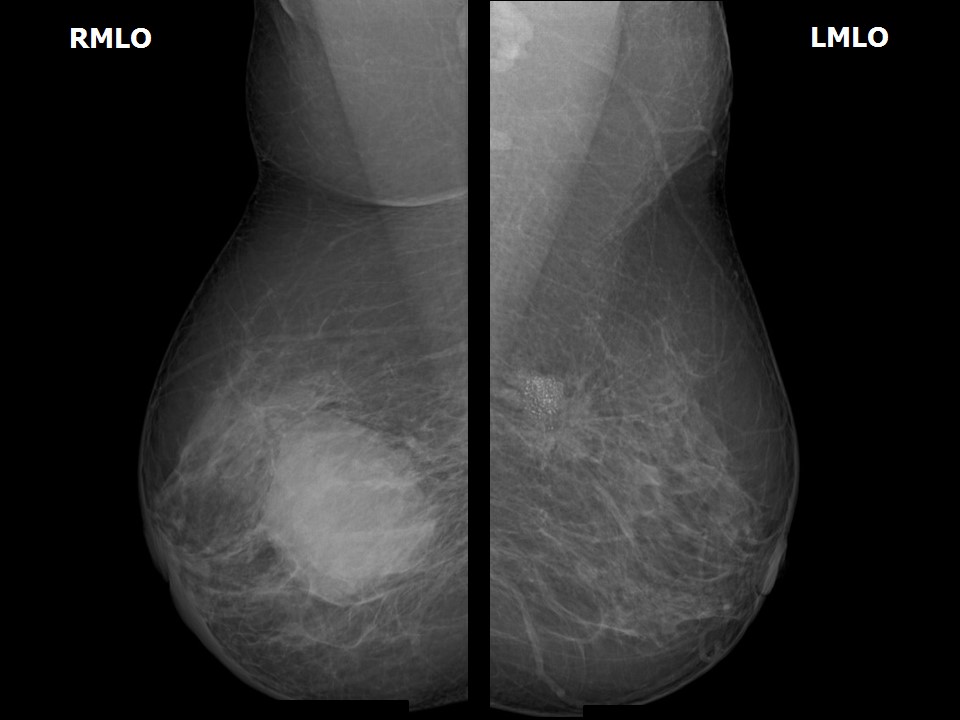
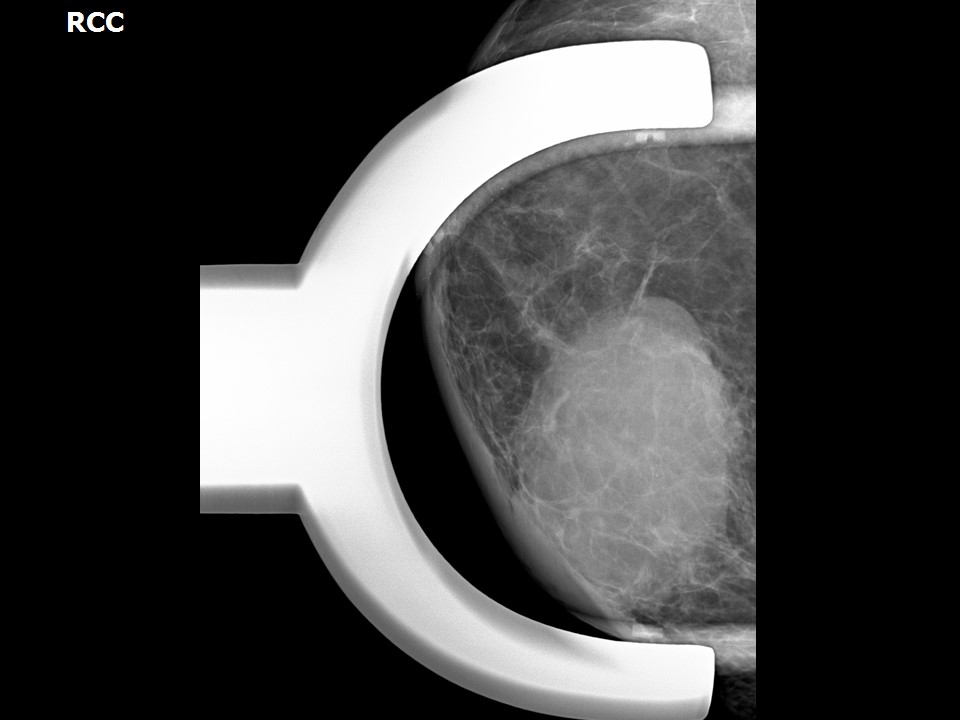
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Right breast, upper inner quadrant at 1–3 o’clock, posterior third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 6.5 × 4.5 cm |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Margins: | Indistinct |
| • Density: | High |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Trabecular thickening and skin thickening |
| Breast composition: | ACR category b (there are scattered areas of fibroglandular density) | Mammography features: |
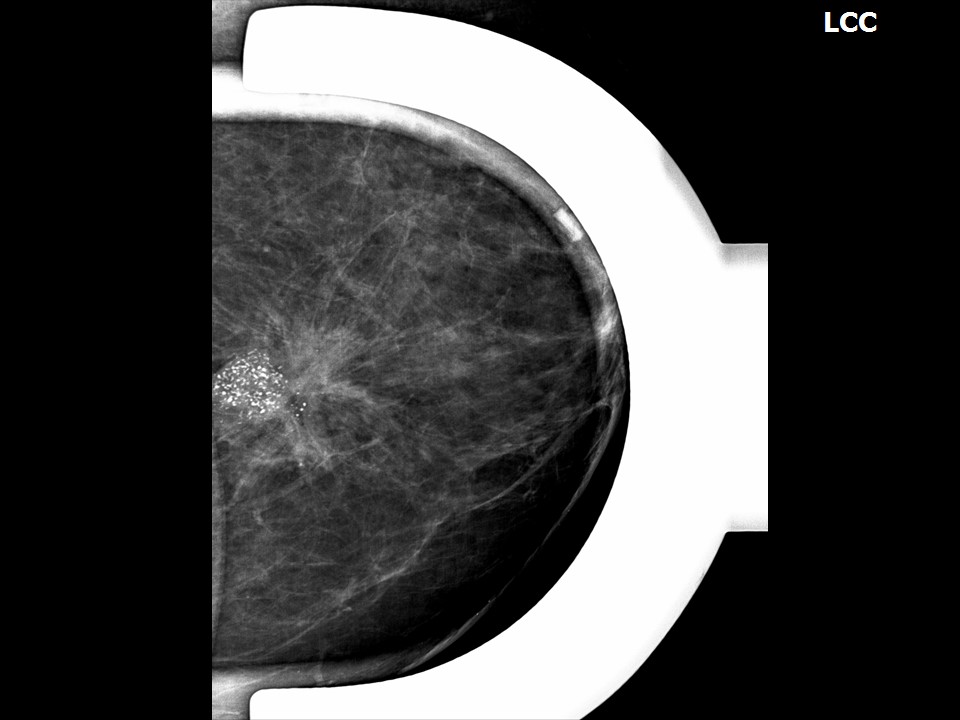
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Left breast, upper inner quadrant at 10 o’clock, posterior third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 3.5 × 2.0 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Margins: | Spiculated |
| • Density: | High |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | Fine pleomorphic |
| • Distribution: | Grouped |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Fine pleomorphic calcifications and high-density lymph nodes |
Ultrasound:
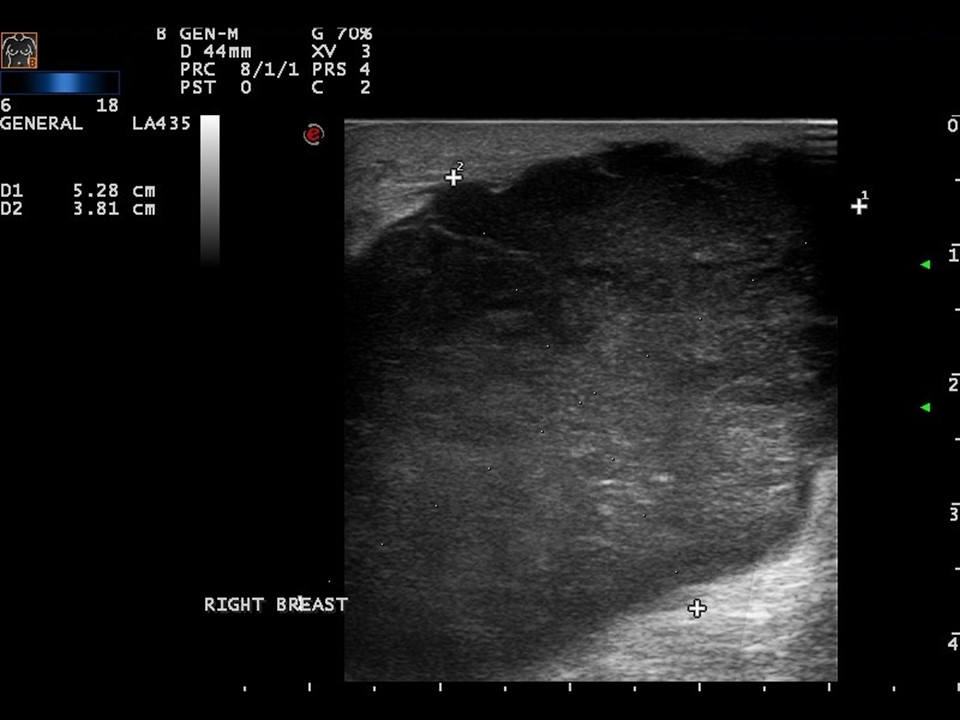
| Ultrasound features: Right breast, upper inner quadrant at 1-3 o’clock | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Right breast, upper inner quadrant at 1-3 o’clock |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 6.0 × 4.5 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Orientation: | Not parallel |
| • Margins: | Indistinct |
| • Echo pattern: | Hypoechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
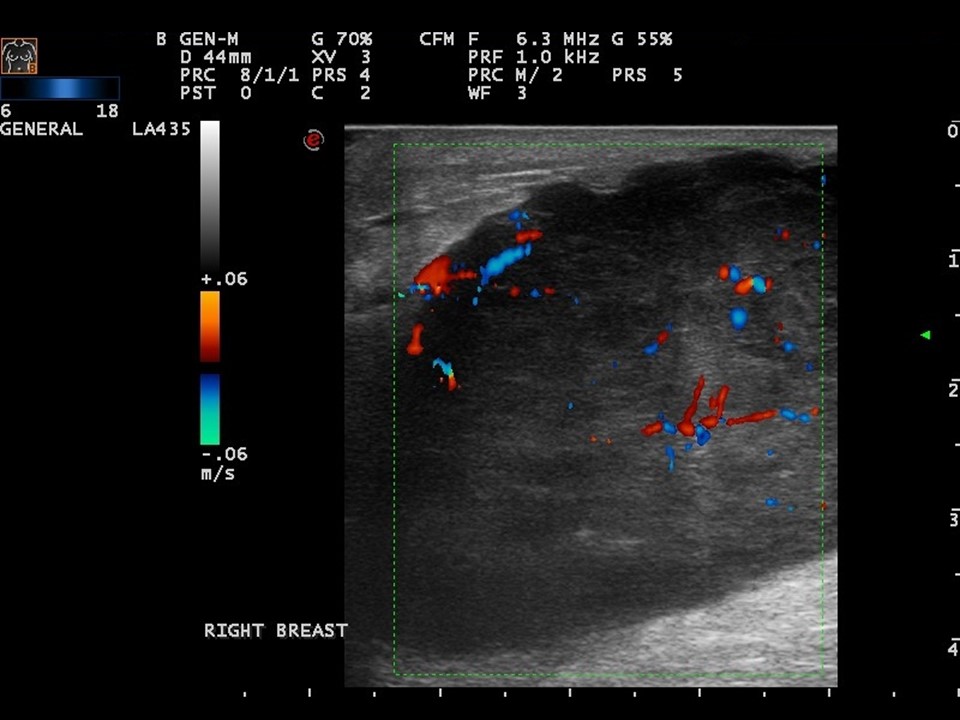
| ‣ Associated features: | Increased internal vascularity |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
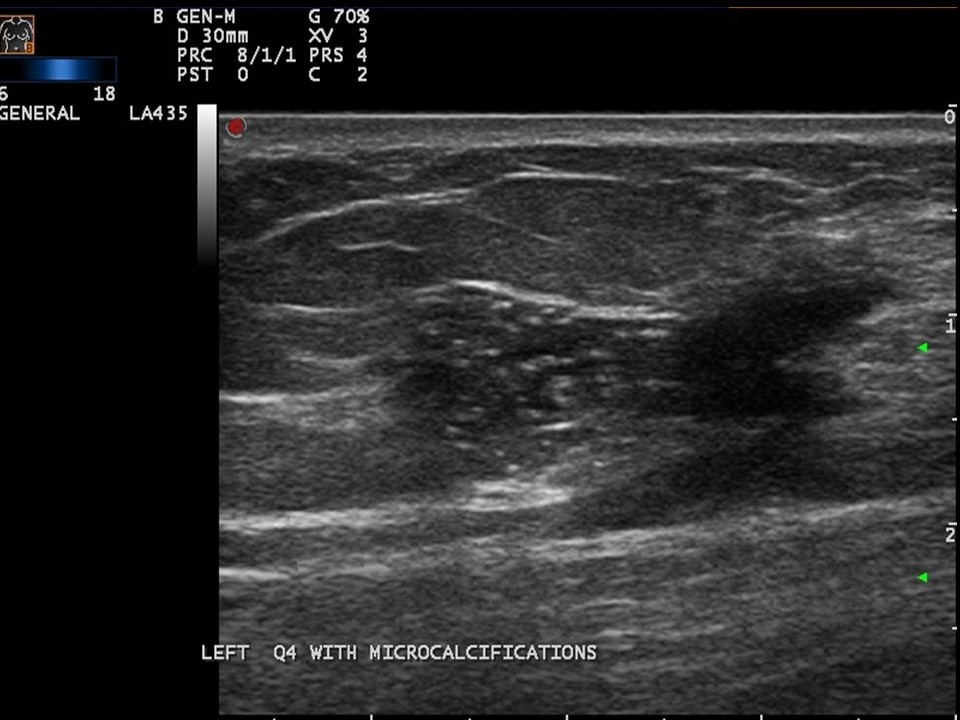
| Ultrasound features: Left breast, upper inner quadrant at 10 o’clock | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Left breast, upper inner quadrant at 10 o’clock |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 3.3 × 2.0 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Orientation: | Not parallel |
| • Margins: | Spiculated |
| • Echo pattern: | Hypoechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | Present in mass |
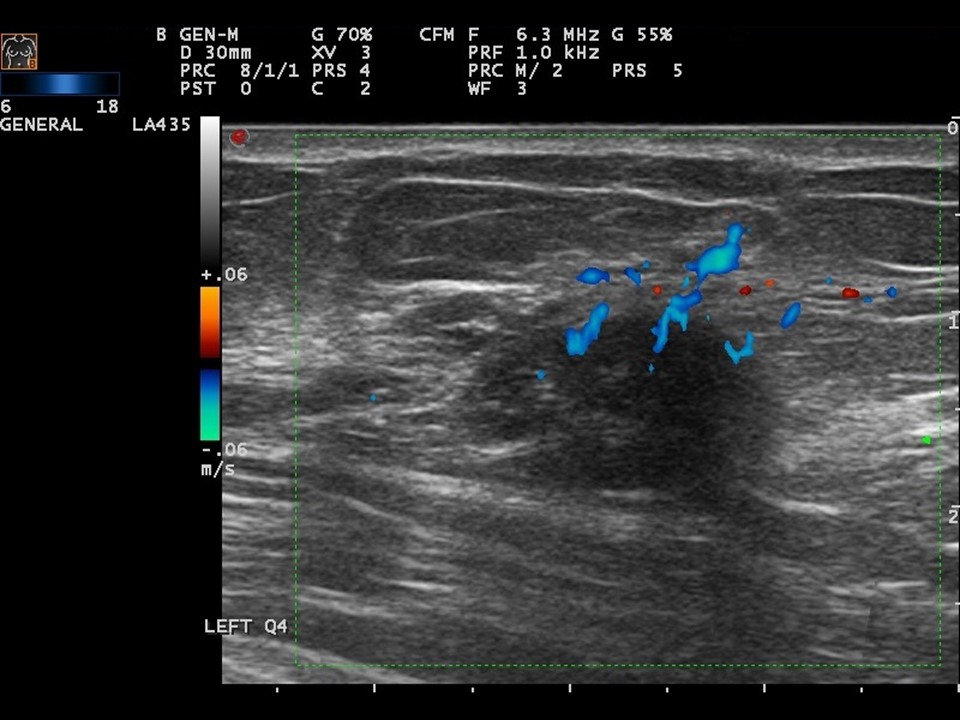
| ‣ Associated features: | Increased internal vascularity |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: 5 (highly suggestive of malignancy)Further assessment:
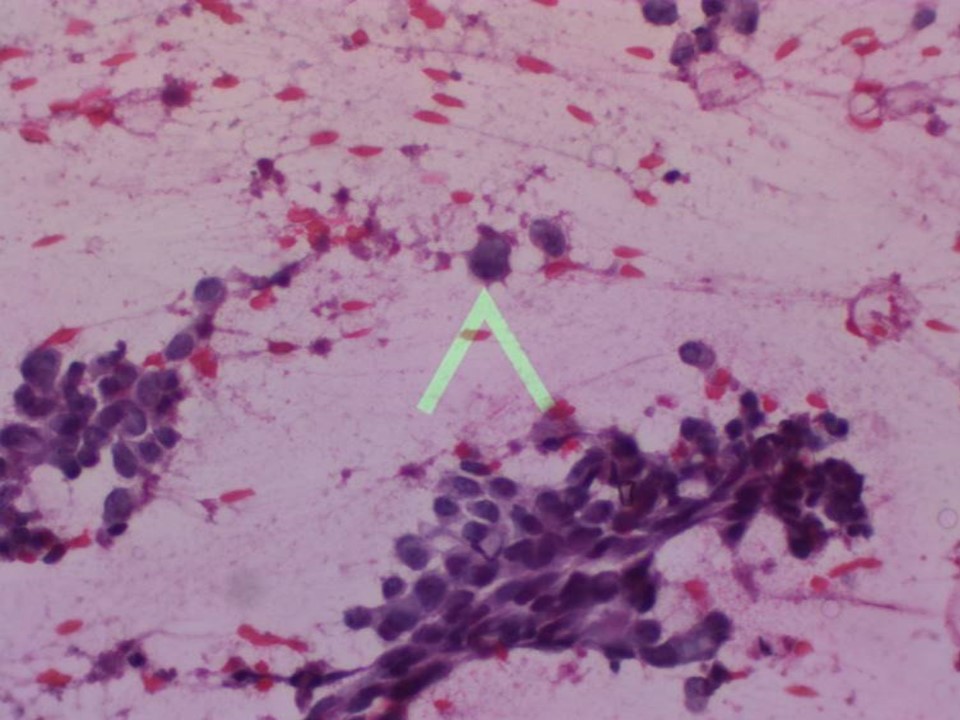
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytology and for core biopsyCytology:
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC (solid lesion) |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Right |
| • Quadrant: | Medial to nipple |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | |
| ‣ Cytological description: | Smears show many single isolated malignant ductal cells and dyscohesive cell clusters |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Malignant |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Carcinoma |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
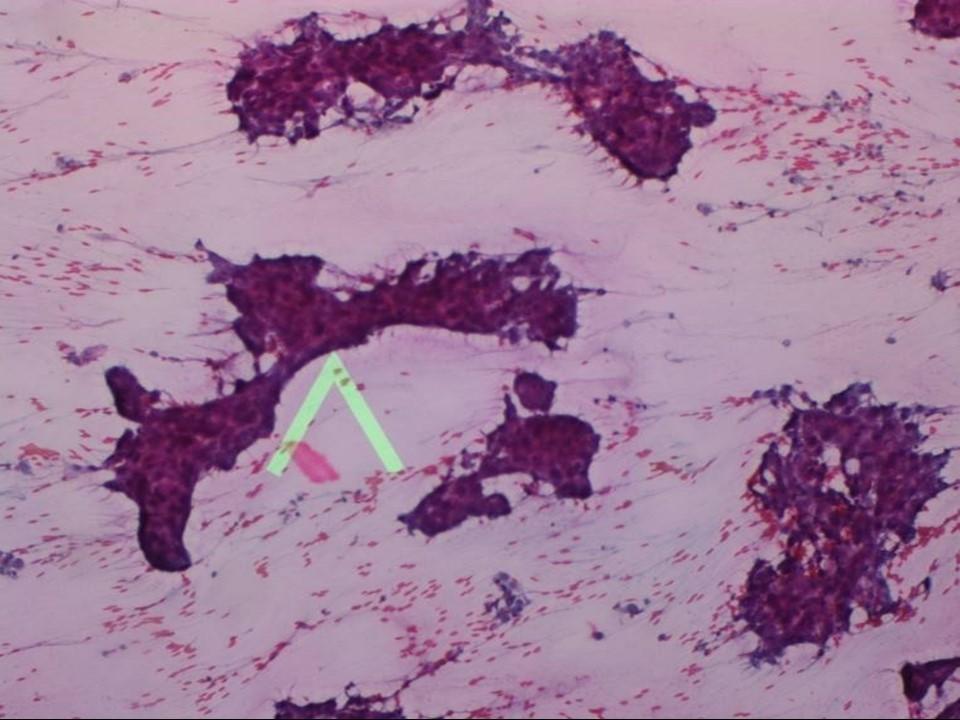
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC (solid lesion) |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Left |
| • Quadrant: | Upper inner |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | |
| ‣ Cytological description: | Smears are cellular and show sheets and clusters of ductal cells suspicious for malignancy. Myoepithelial cell rimming is seen in some tissue fragments |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Suspicious, probably in situ or invasive carcinoma |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Suspicious for malignancy |
| ‣ Comments: | A cytopathological distinction between DCIS and invasive ductal carcinoma is not possible in most cases. Therefore, traditionally, both forms of cancer are grouped under the broad cytological category of “mammary carcinoma”. Subsequent needle core biopsy showed only DCIS with no invasive component |
Histopathology:
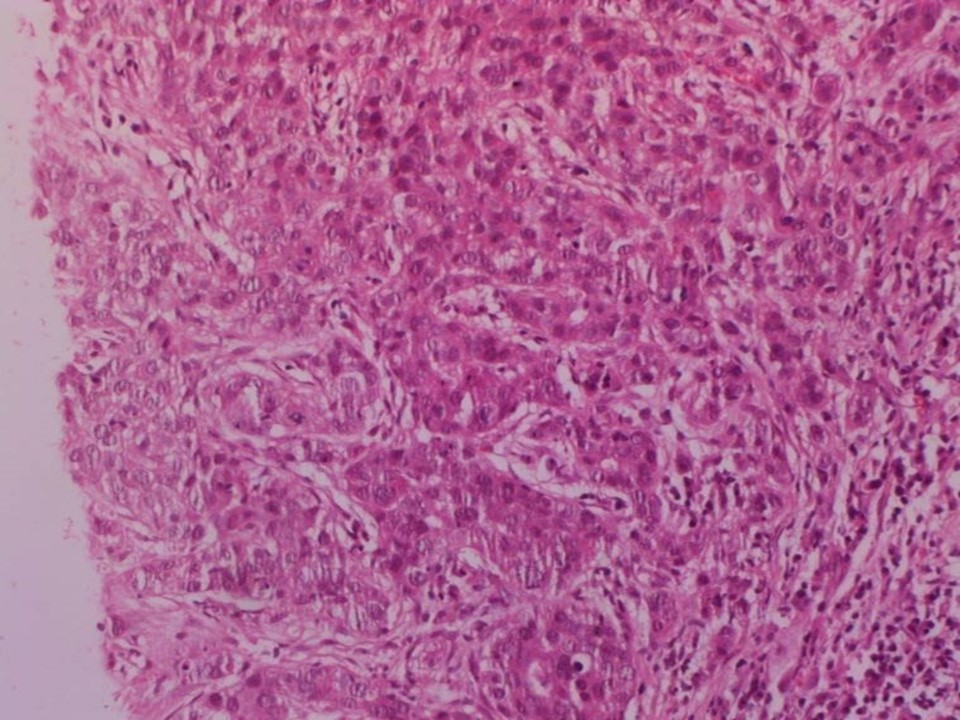
Core needle biopsy
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | Core needle biopsy |
| ‣ Laterality: | Right |
| ‣ Macroscopy: | Six cores |
| ‣ Histological type: | Invasive carcinoma of no special type |
| ‣ Histological grade: | Grade 2 (3 + 3 + 1 = 7) |
| ‣ Mitosis: | 6 |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | Comedo DCIS – high grade |
| ‣ Margins: | |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | |
| ‣ Comments: |
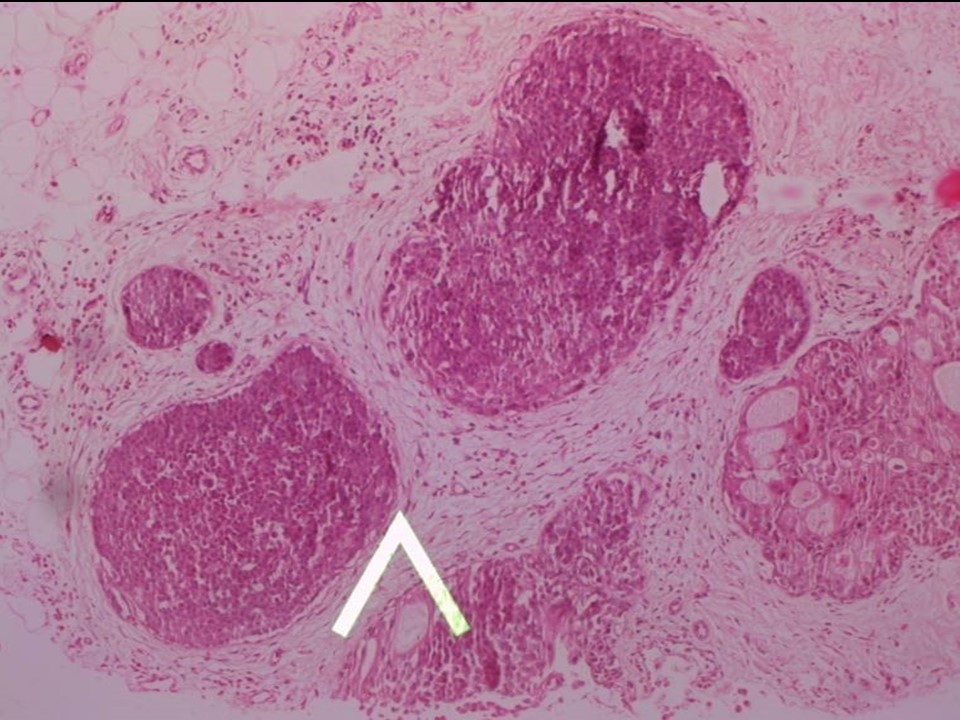
Core needle biopsy
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | Core needle biopsy |
| ‣ Laterality: | Left |
| ‣ Macroscopy: | Five cores |
| ‣ Histological type: | Invasive carcinoma not identified |
| ‣ Histological grade: | |
| ‣ Mitosis: | |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | Solid and cribriform DCIS – intermediate grade |
| ‣ Margins: | |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | |
| ‣ Comments: |
Case summary:
| Postmenopausal woman presented with bilateral breast lumps. Diagnosed as left breast carcinoma with pleomorphic microcalcifications and metastatic left axillary node and right breast carcinoma, BI-RADS 5 – bilateral – synchronous on imaging, as breast carcinoma on cytology bilaterally, and as invasive breast carcinoma of no special type on the right and DCIS intermediate grade on the left on histopathology of needle core biopsy. |
Learning points:
|