Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Filter by language: English / Русский
Go back to the list of case studies
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
| Case number: | 069 |
| Age: | 60 |
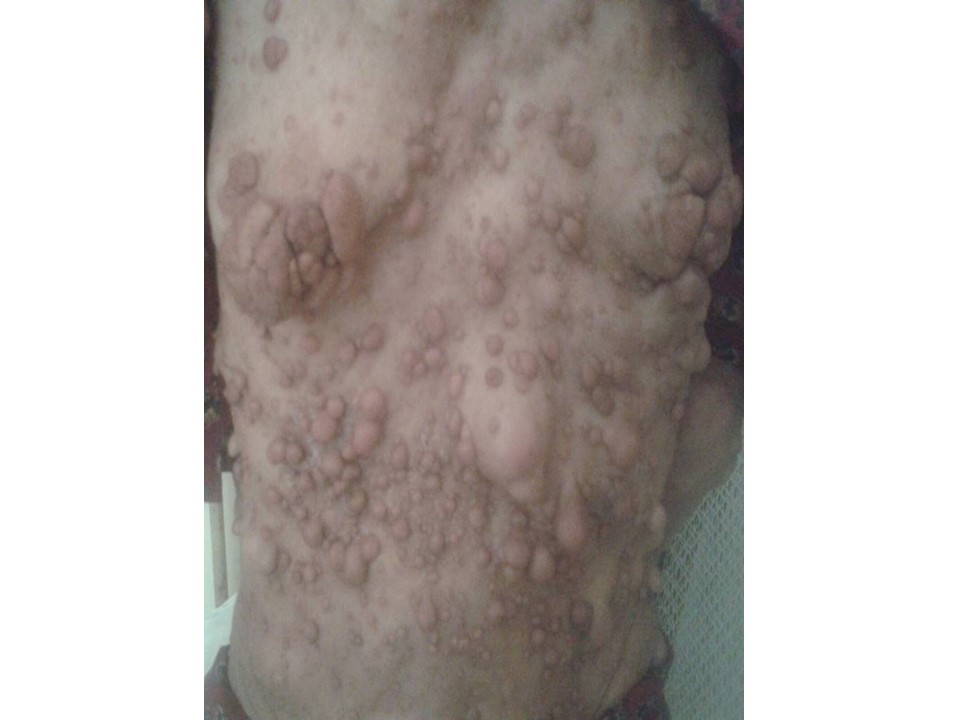
| Clinical presentation: | Postmenopausal woman with average risk of developing breast cancer and known neurofibromatosis, involving the entire body including the breast, presented with a left breast lump. Examination revealed a hard lump 4 cm in diameter and fixed to the pectoralis muscle. |
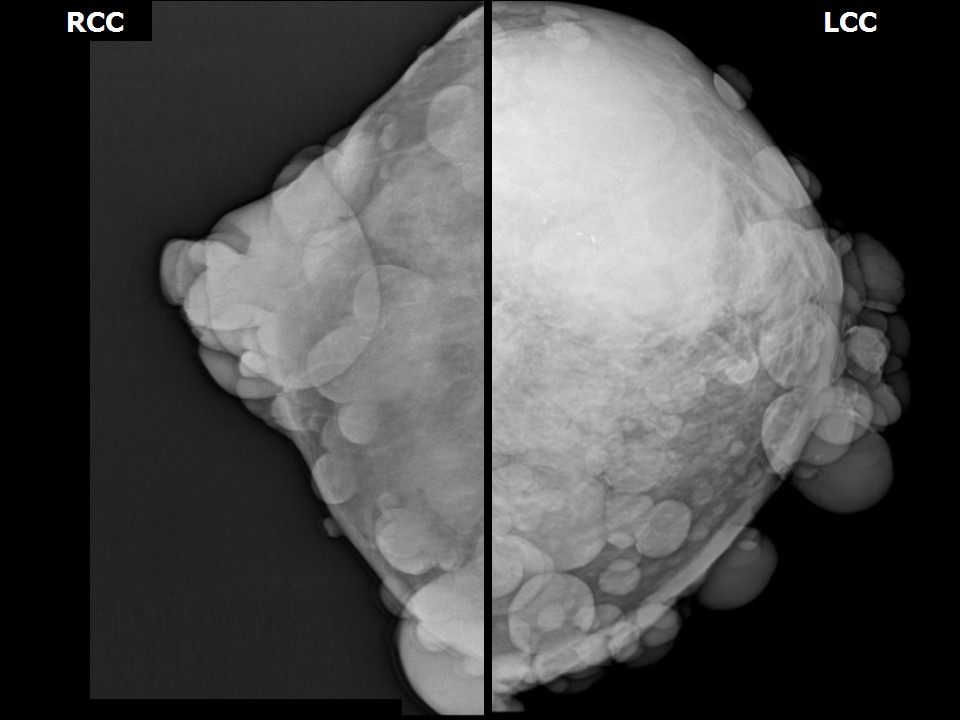
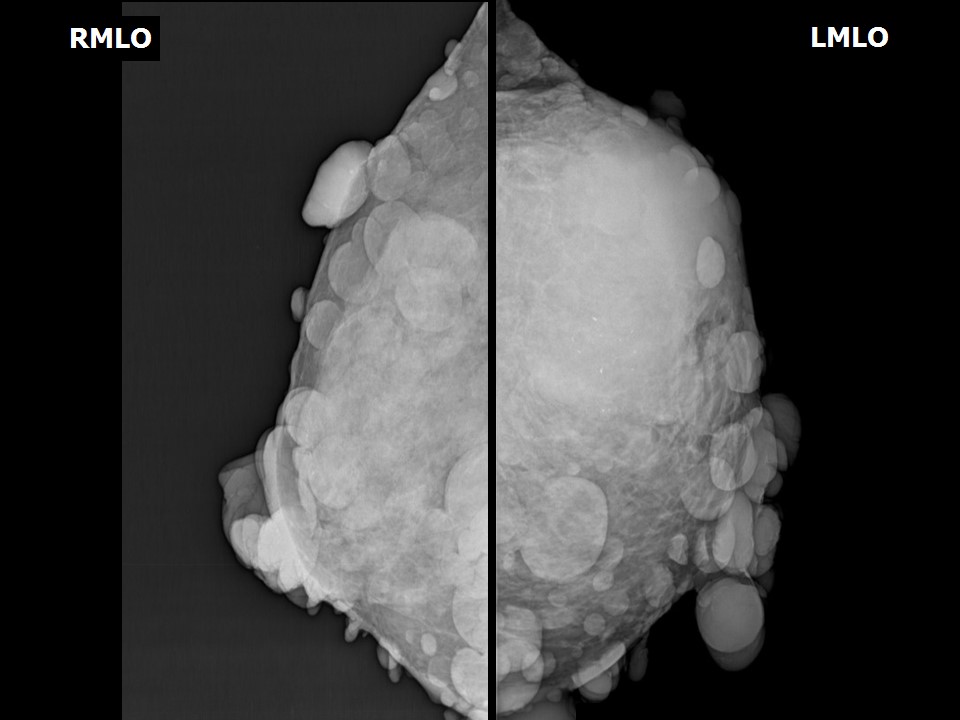
Mammography:
| Breast composition: | ACR category c (the breasts are heterogeneously dense, which may obscure small masses) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Left breast, upper outer quadrant at 12–3 o’clock, anterior, middle, and posterior thirds |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 10.0 × 5.0 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Margins: | Indistinct |
| • Density: | High |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | Coarse |
| • Distribution: | Regional |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | Present |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | Focal |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Architectural distortion and calcifications |
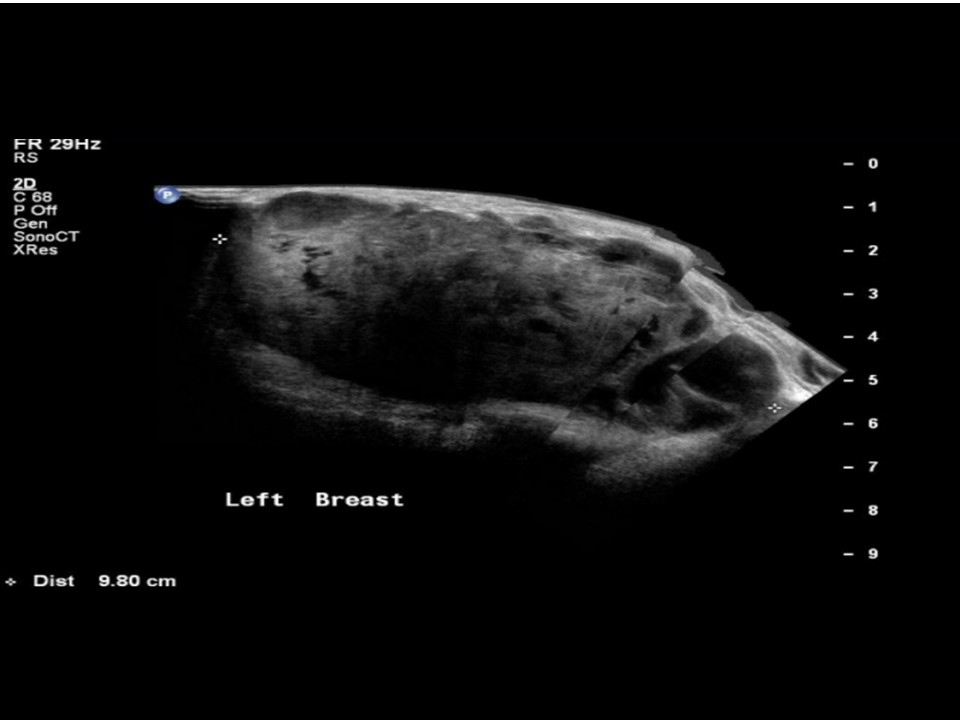
Ultrasound:
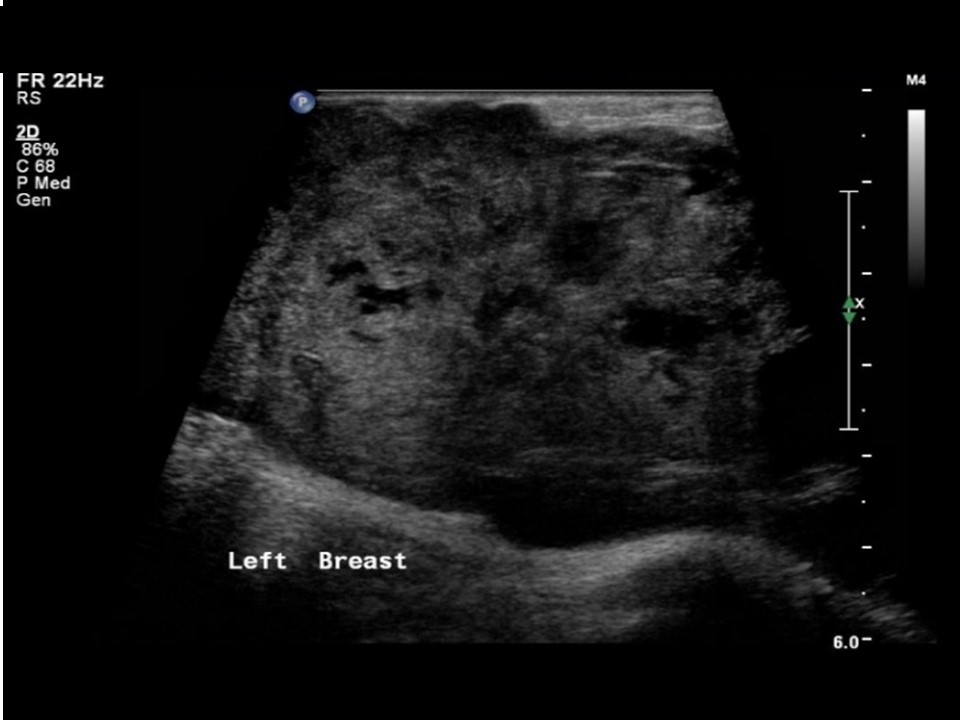
| Ultrasound features: Left breast, upper outer quadrant at 12-3 o’clock | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Left breast, upper outer quadrant at 12-3 o’clock |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 10.0 × 7.0 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Orientation: | Not parallel |
| • Margins: | Indistinct |
| • Echo pattern: | Heterogeneous with multiple necrotic areas within |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
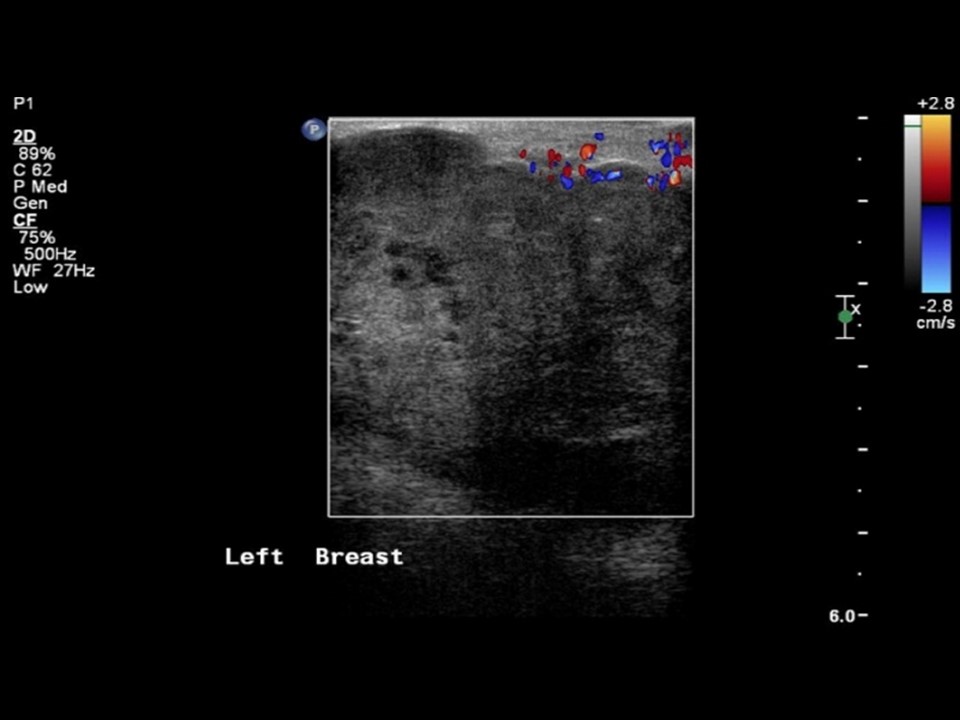
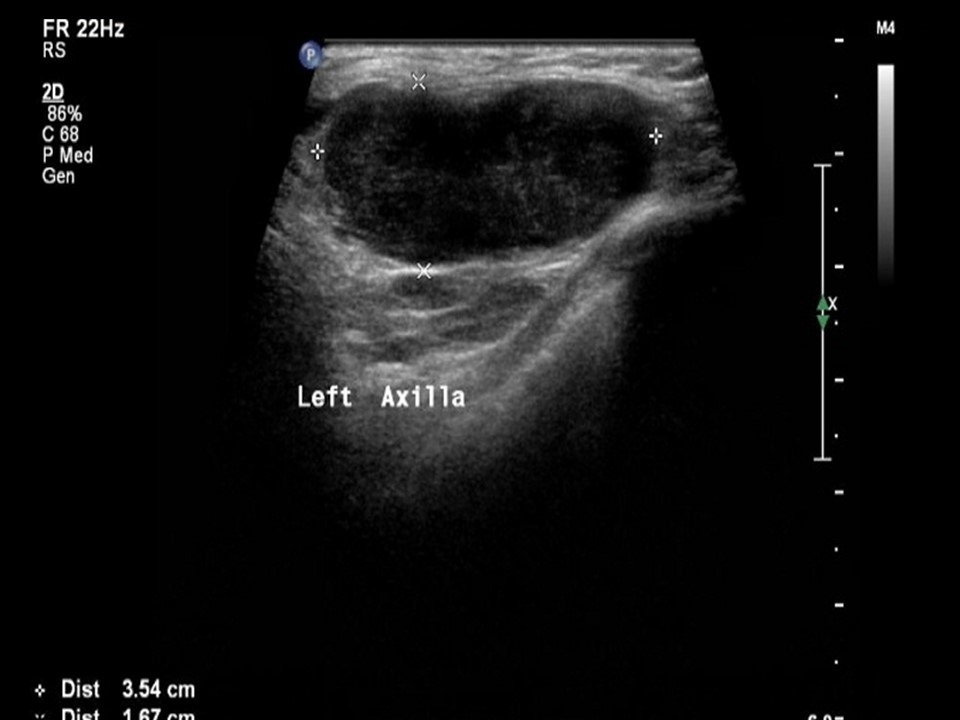
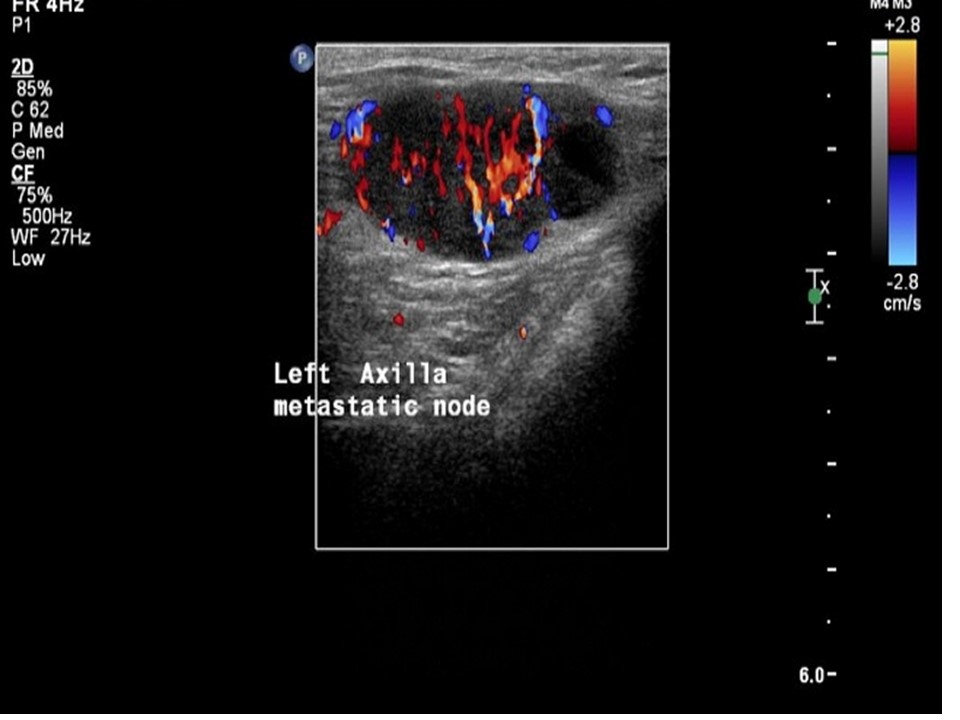
| ‣ Associated features: | Architectural distortion, internal vascularity, axillary lymphadenopathy, and enlarged node (3.6 × 2.5 cm) with loss of normal morphology and increased vascularity |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: 5 (highly suggestive of malignancy)Further assessment:
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytologyCytology:
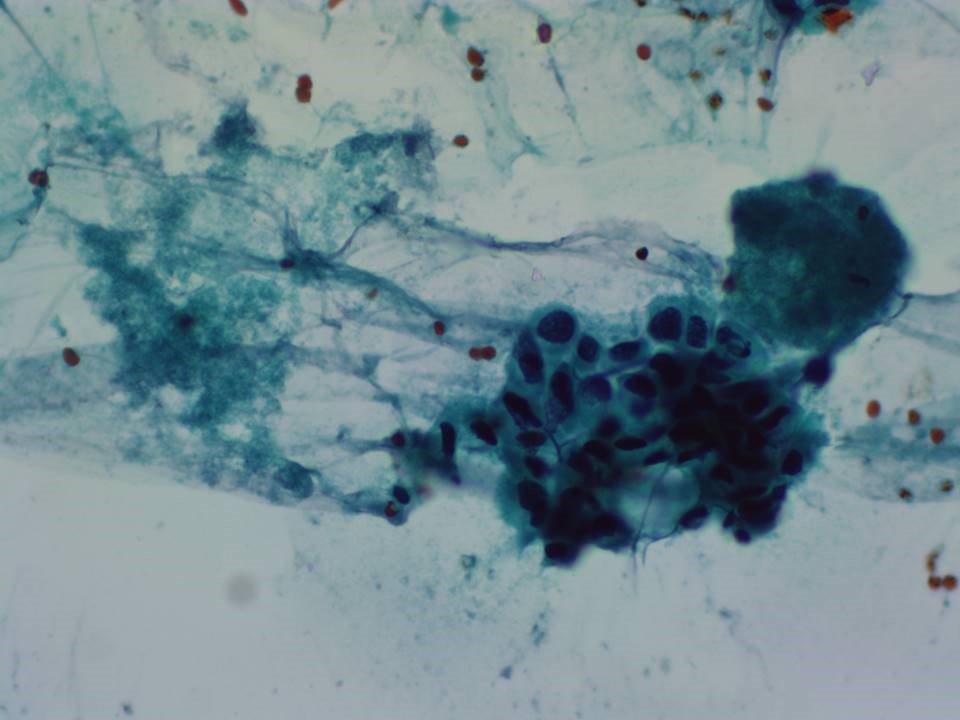
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC (solid lesion) |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Left |
| • Quadrant: | Upper outer |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | Thick whitish material |
| ‣ Cytological description: | Smear shows abundant necrotic material, probably tumour necrosis. Very few highly pleomorphic malignant cells seen in one smear |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Malignant |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Carcinoma |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
Histopathology:
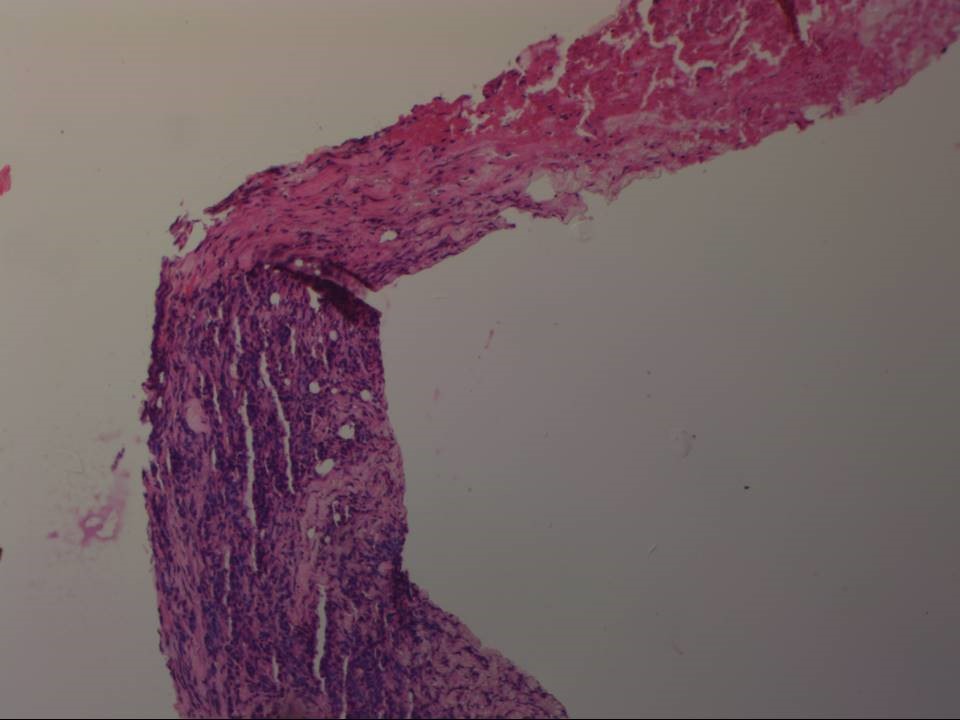
Core needle biopsy
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | Core needle biopsy |
| ‣ Laterality: | Left |
| ‣ Macroscopy: | Four cores |
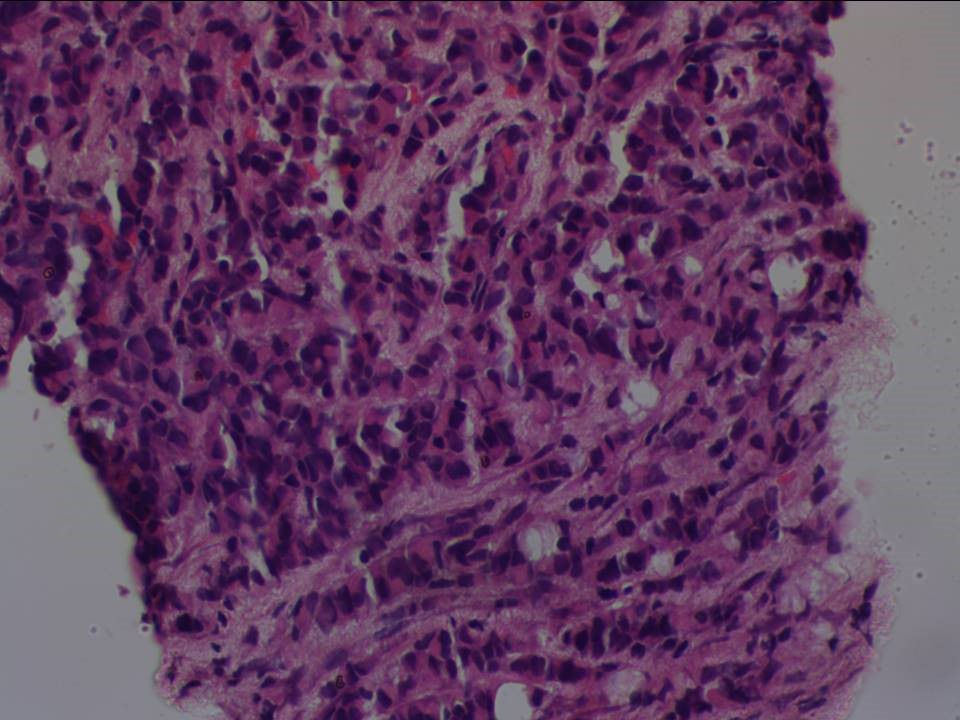
| ‣ Histological type: | Invasive carcinoma of no special type |
| ‣ Histological grade: | Grade 3 (3 + 3 + 2 = 8) |
| ‣ Mitosis: | 15 |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | |
| ‣ Margins: | |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | |
| ‣ Comments: | Extensive tumour necrosis seen |
MRM
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | MRM |
| ‣ Laterality: | Left |
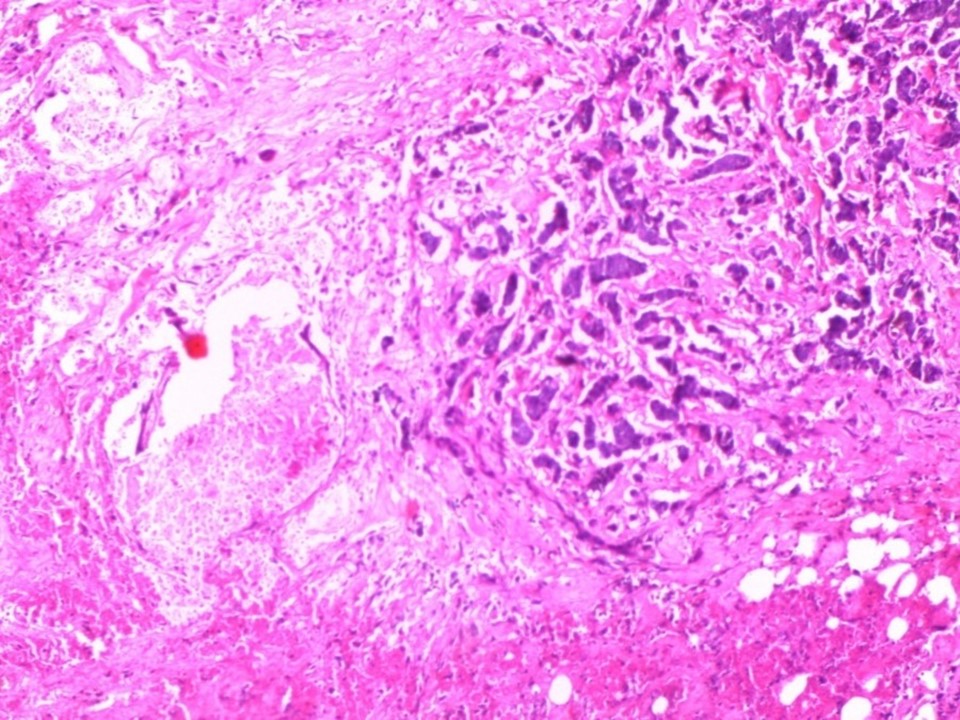
| ‣ Macroscopy: | Cut surface shows a well-circumscribed tumour (4.0 × 4.0 × 2.0 cm), greyish white, firm with soft areas. The skin flap over the MRM showed multiple neurofibromas ranging from 0.5 cm to 2.0 cm in diameter |
| ‣ Histological type: | Invasive carcinoma of no special type |
| ‣ Histological grade: | Grade 3 (3 + 3 + 2 = 8) |
| ‣ Mitosis: | 12 |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | 4.0 cm in greatest dimension |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | 1/18 |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | Not identified |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | Not identified |
| ‣ Margins: | Free of tumour |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | PT2N1 |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | |
| ‣ Comments: | Sections from the tumour reveal large areas of necrosis with a few preserved islands of tumour tissue. Many of the areas of tumour necrosis are rimmed by foamy histiocytes |
Case summary:
| Postmenopausal woman, known case of neurofibromatosis, presented with lump in the left breast. Diagnosed as left breast carcinoma with coarse calcifications and enlarged left axillary node of altered morphology, probably metastatic, BI-RADS 5 on imaging, as breast carcinoma on cytology, and as invasive breast carcinoma of no special type, pT2N1 on histopathology. Bilateral breast dermal neurofibroma nodules are seen in this case of neurofibromatosis. |
Learning points:
|