Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Go back to the list of case studies
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
| Case number: | 068 |
| Age: | 37 |
| Clinical presentation: | Premenopausal woman with average risk of developing breast cancer, who had twice undergone surgery for fibroadenomas, presented with a large recurrent lump in the right breast. Examination revealed a large lobulated lump in the right breast. |
Mammography:
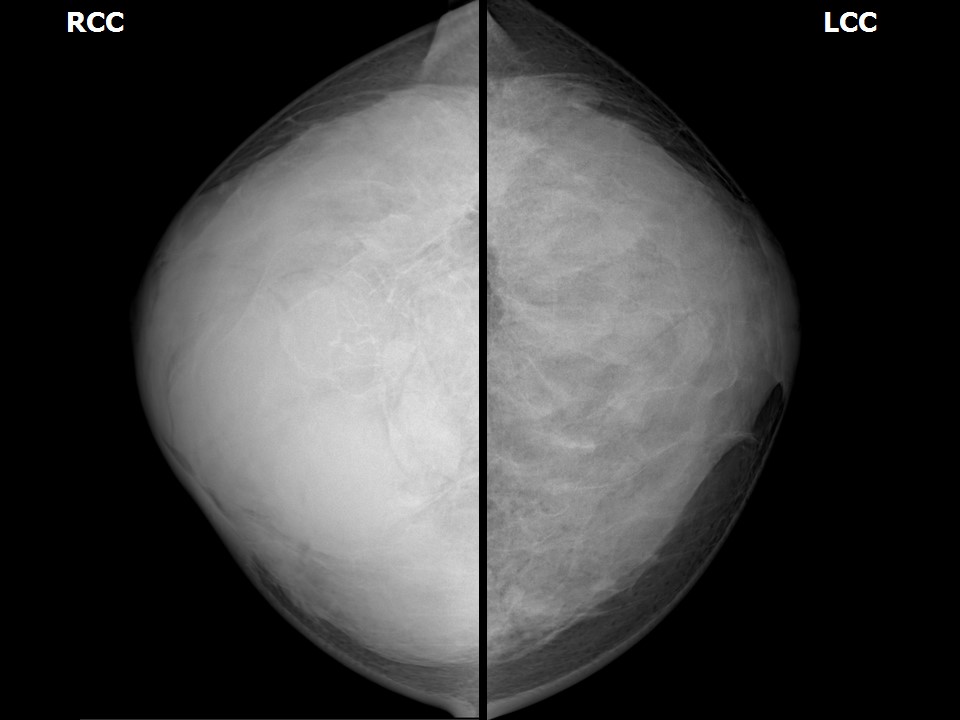
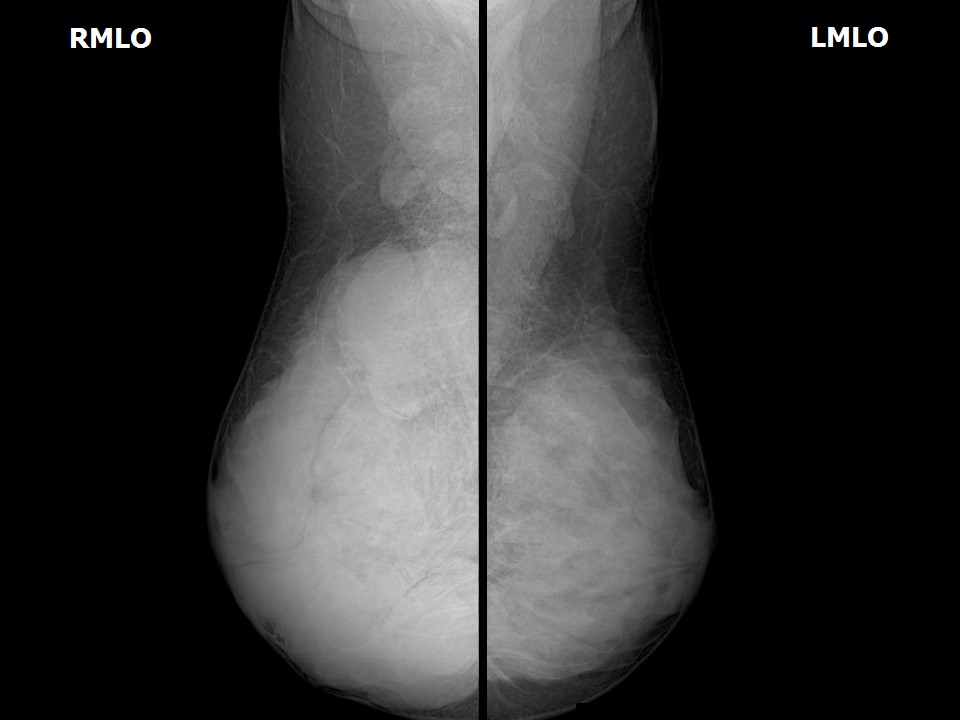
| Breast composition: | ACR category d (the breasts are extremely dense, which lowers the sensitivity of mammography) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Right breast, all quadrants, entire breast, anterior, middle, and posterior thirds, almost entire parenchyma |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | Multiple |
| • Size: | Largest > 5.0 cm in greatest dimension |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed |
| • Density: | Equal |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | Present |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | Global |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Architectural distortion |
Ultrasound:
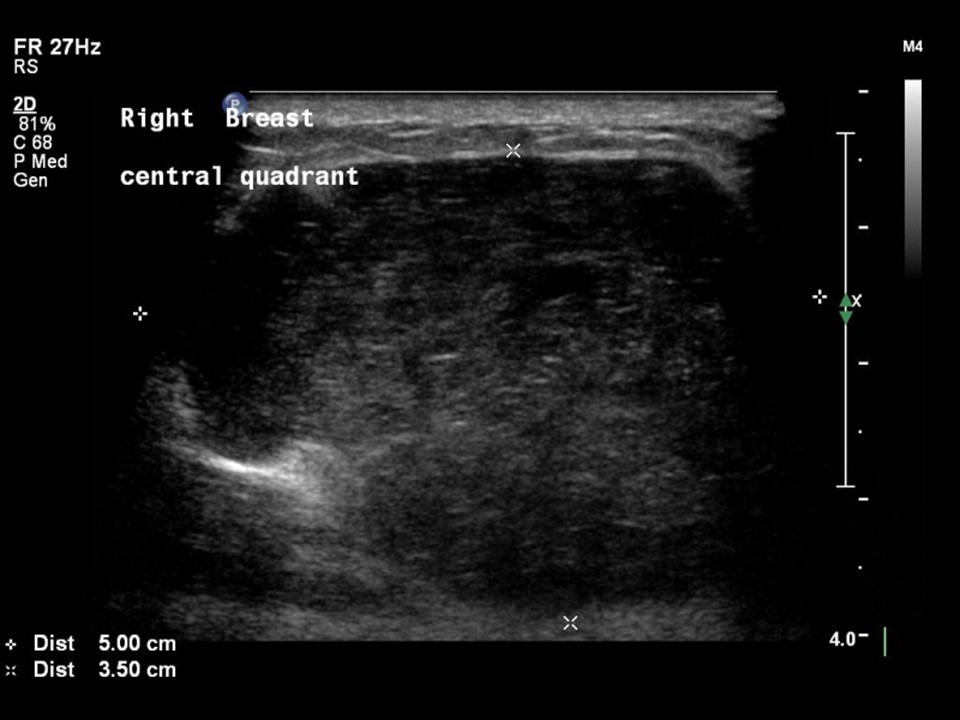
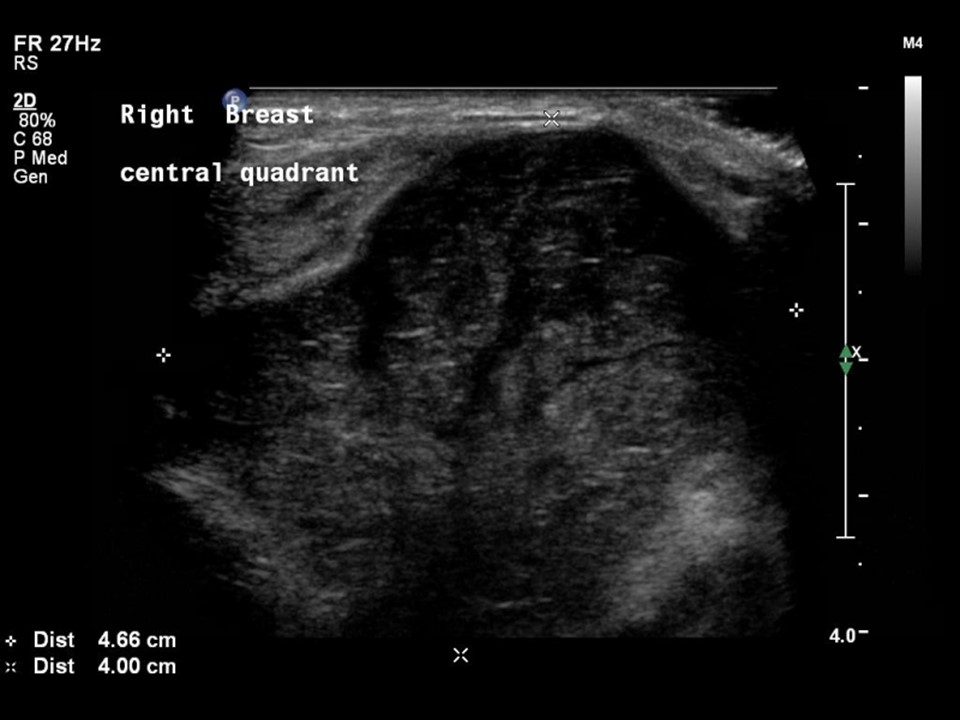
| Ultrasound features: Right breast, central portion of the breast | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Right breast, central portion of the breast |
| • Number: | Multiple |
| • Size: | Largest 5.0 × 3.5 cm |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Orientation: | Parallel |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed |
| • Echo pattern: | Heteroechoic with necrotic areas |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
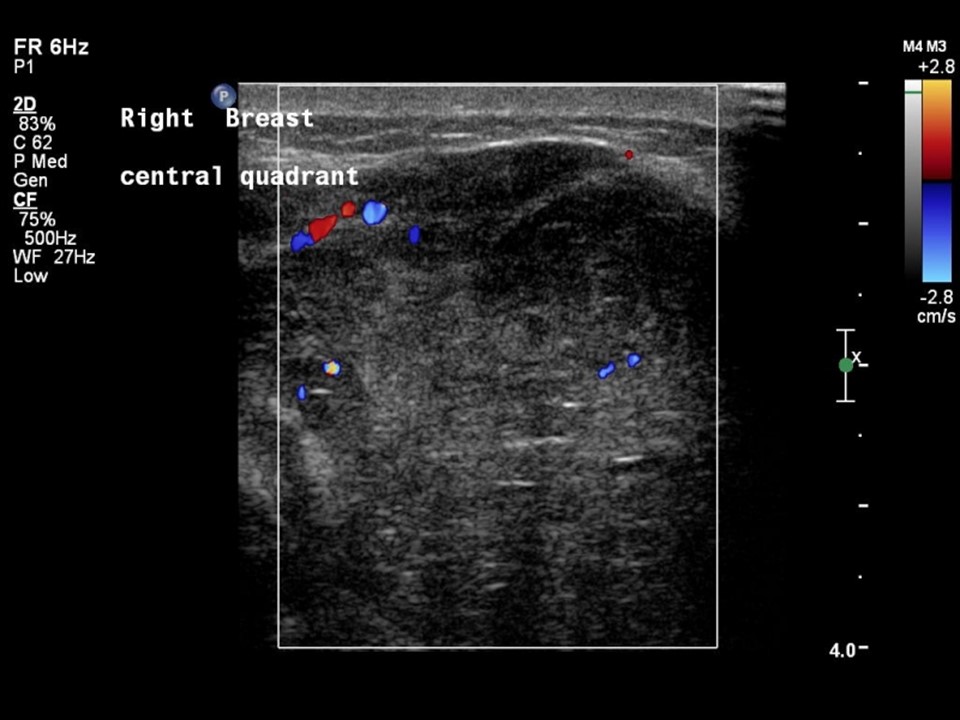
| ‣ Associated features: | Architectural distortion, internal vascularity |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
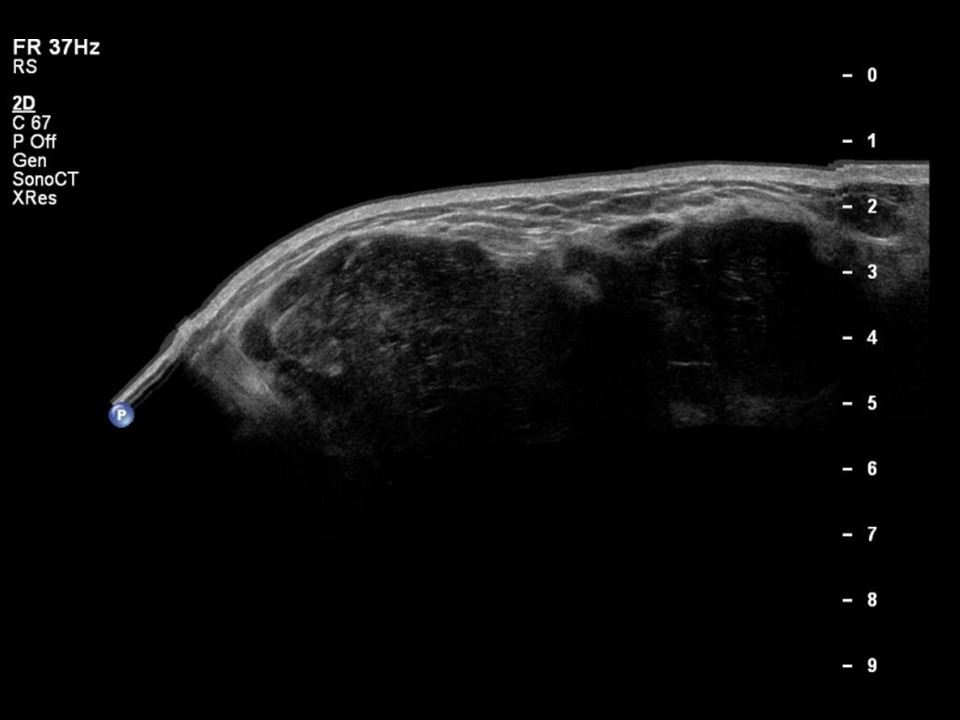
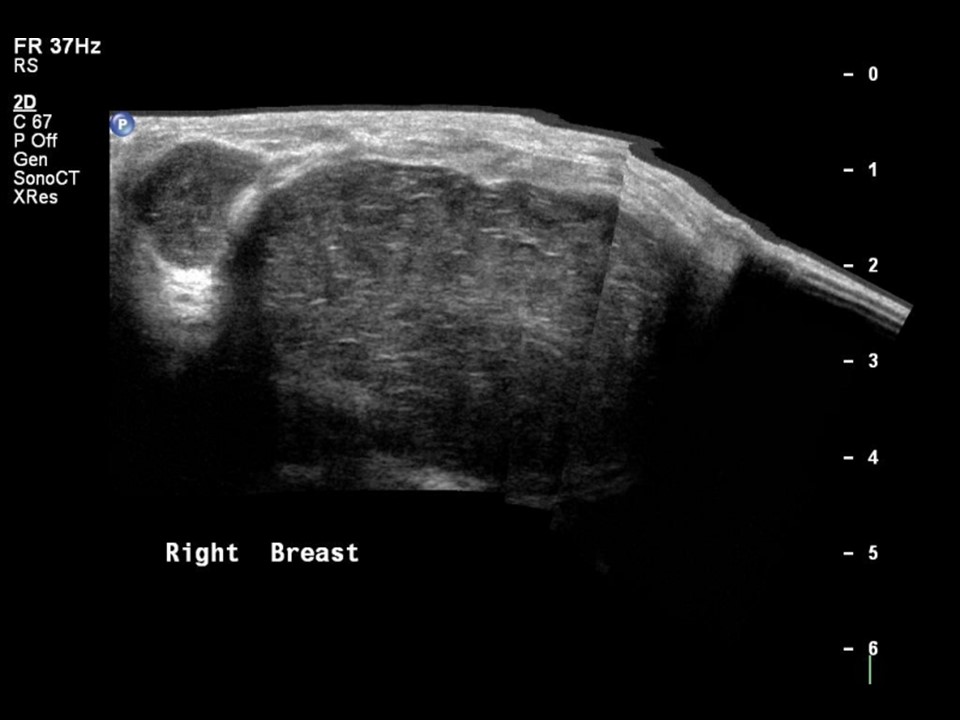
| Ultrasound features: Right breast, multiple in all quadrants | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Right breast, multiple in all quadrants |
| • Number: | Multiple |
| • Size: | Largest 4.7 × 4.0 cm |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Orientation: | Parallel |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed |
| • Echo pattern: | Heteroechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Architectural distortion and internal vascularity |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
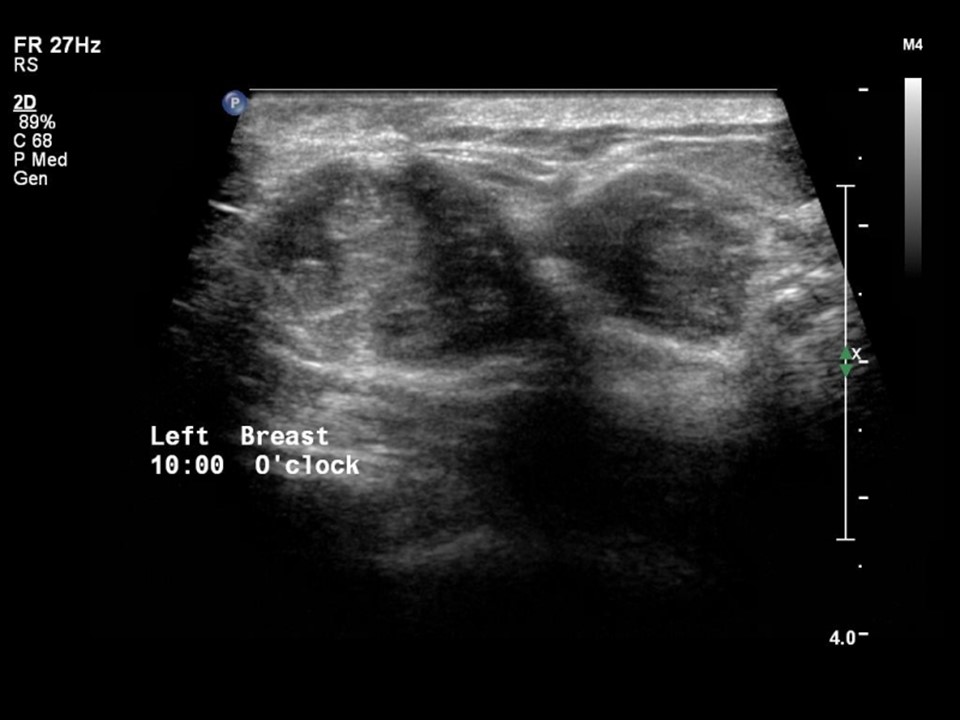
| Ultrasound features: Two lesions in left breast, upper inner quadrant at 10 o’clock | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Two lesions in left breast, upper inner quadrant at 10 o’clock |
| • Number: | 2 |
| • Size: | Largest 2.8 × 1.8 cm |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Orientation: | Parallel |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed |
| • Echo pattern: | Heteroechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Internal vascularity |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: 2 (benign)Further assessment:
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytologyCytology:
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Right |
| • Quadrant: | |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | Whitish |
| ‣ Cytological description: | Smears are very cellular and show plenty of tightly cohesive sheets of benign ductal epithelial cells. Many stromal tissue fragments are seen along with dispersed plump spindle nuclei |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Benign |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Benign phyllodes to be considered in view of the many hypercellular stromal fragments |
| ‣ Comments: | Pitfall: The cytomorphology of benign phyllodes tumour is similar to that of fibroadenoma but the stromal fragments are more cellular and contain larger and more atypical spindle cells. A definitive diagnosis is not possible in all cases, and core or excisional biopsy may be necessary |
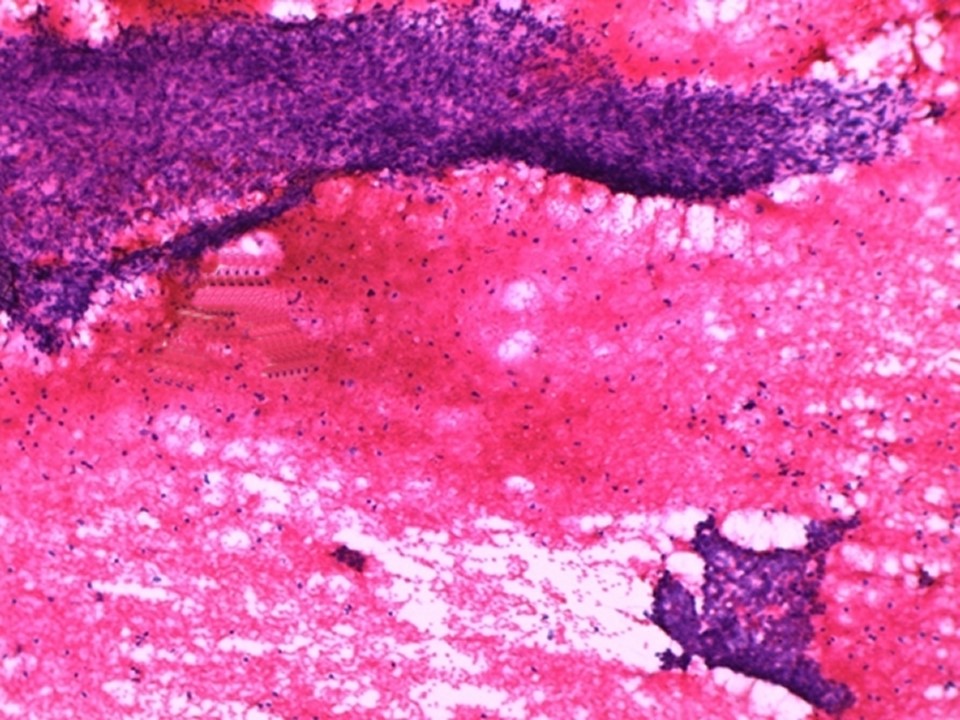
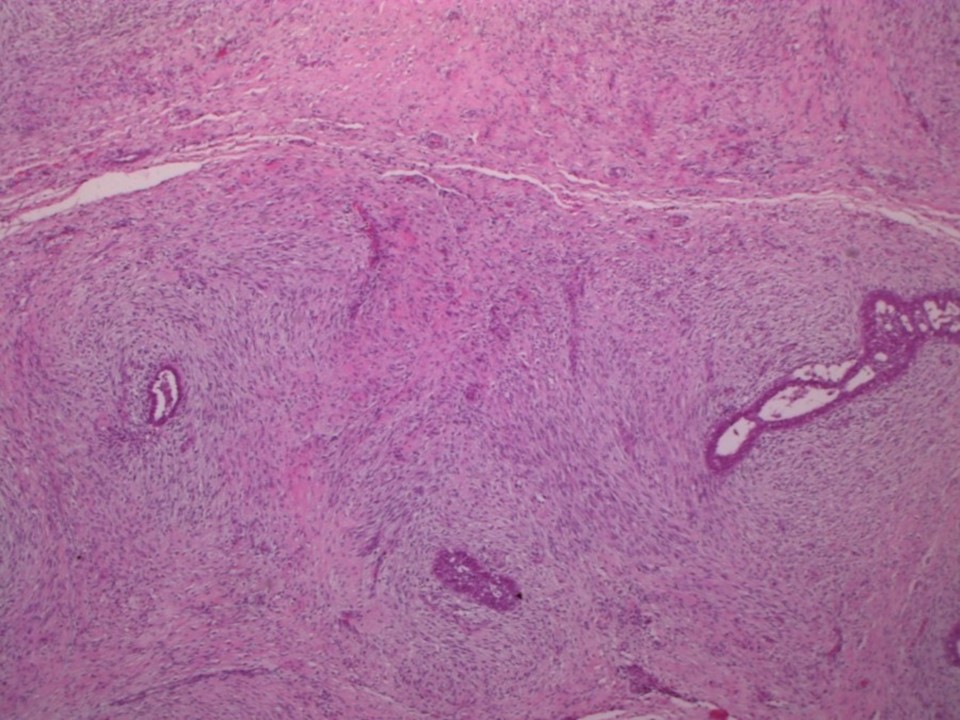
Histopathology:
Lumpectomy
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | Lumpectomy |
| ‣ Laterality: | Right |
| ‣ Macroscopy: | Single, well-encapsulated, firm mass (11.0 × 10.0 × 8.0 cm). Cut section shows greyish white areas with whorled appearance and a few visible clefts. Some areas appear fleshy |
| ‣ Histological type: | Benign phyllodes tumour |
| ‣ Histological grade: | |
| ‣ Mitosis: | 2 |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | |
| ‣ Margins: | |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | |
| ‣ Comments: | Focal cribriform ductal hyperplasia and an occasional duct papilloma are noted in the surrounding breast tissue.
Details of histopathology report of surgery done later: 1. Right radical mastectomy specimen (19.0 × 19.0 × 7.0 cm) with circular piece of skin (17.0 cm in diameter) include nipple and areola. Skin surface shows an 8.5 cm scar from previous surgery. Posterior surface shows muscle. Cut surface shows a large, fleshy, lobulated tumour (12.5 × 12.0 × 5.0 cm) almost replacing the entire breast with a few haemorrhagic areas. The tumour is 3.0 cm from the lateral margin, 2.0 cm from the medial margin, 0.2 cm from the superior margin and 2.5 cm from the inferior margin. The tumour is 1.0 cm from the base and 0.5 cm from the skin. Twelve nodes were dissected from the axillary tail, the largest of which was 2.5 cm in diameter. A single lymph node was sent for frozen section diagnosis and reported as benign phyllodes tumour. 2. Left lumpectomy (10.5 × 9.0 × 5.0 cm). Elliptical piece of skin (6.5 × 4.5 cm) showing 2.0 cm scar from previous surgery. Cut surface shows a bulging tumour (2.5 × 1.5 × 1.3 cm). Adjacent normal breast shows dense whitish areas of fibrosis. Microscopy of both specimens reported as benign phyllodes tumour with clear surgical margins and uninvolved nodes |
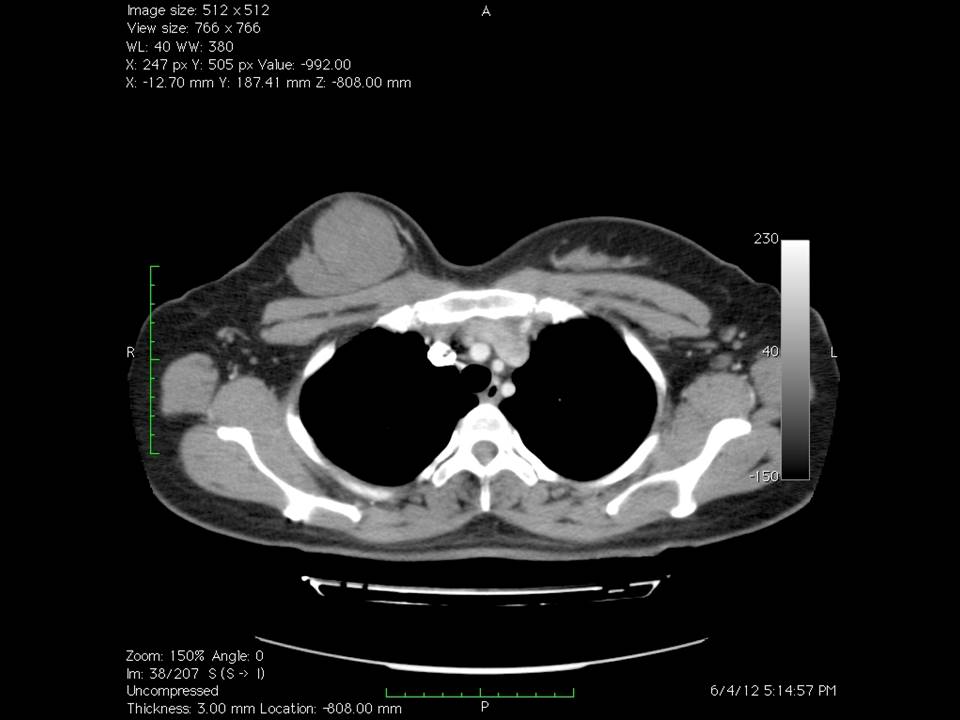
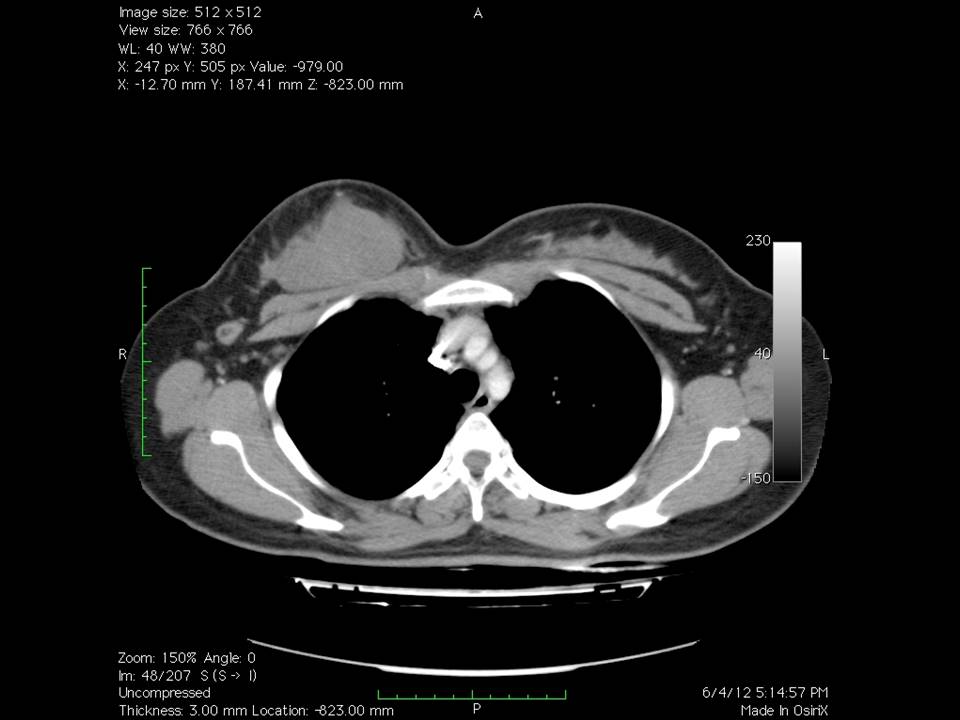
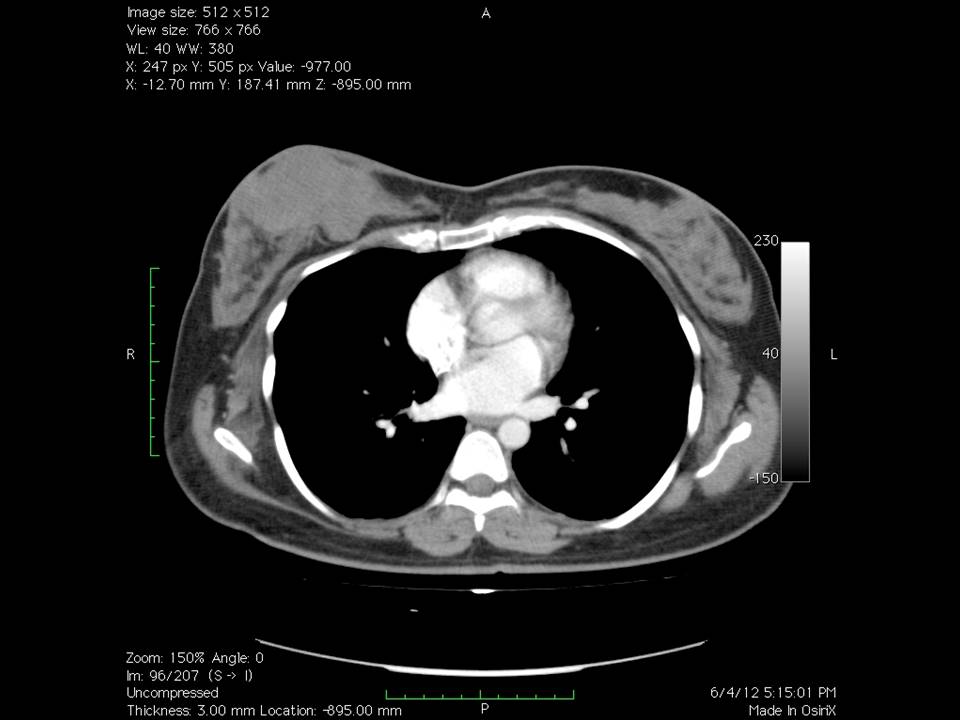
CT scan:
Case summary:
| Premenopausal woman presented with large right breast lump. Diagnosed as BI-RADS 2 on imaging and as benign phyllodes on cytology and histopathology. |
Learning points:
|