Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Filter by language: English / Русский
Go back to the list of case studies
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
| Case number: | 067 |
| Age: | 53 |
| Clinical presentation: | Postmenopausal woman with average risk of developing breast cancer presented with painful right breast lump. On examination, she was found to have a freely mobile soft to firm lump in the right breast. |
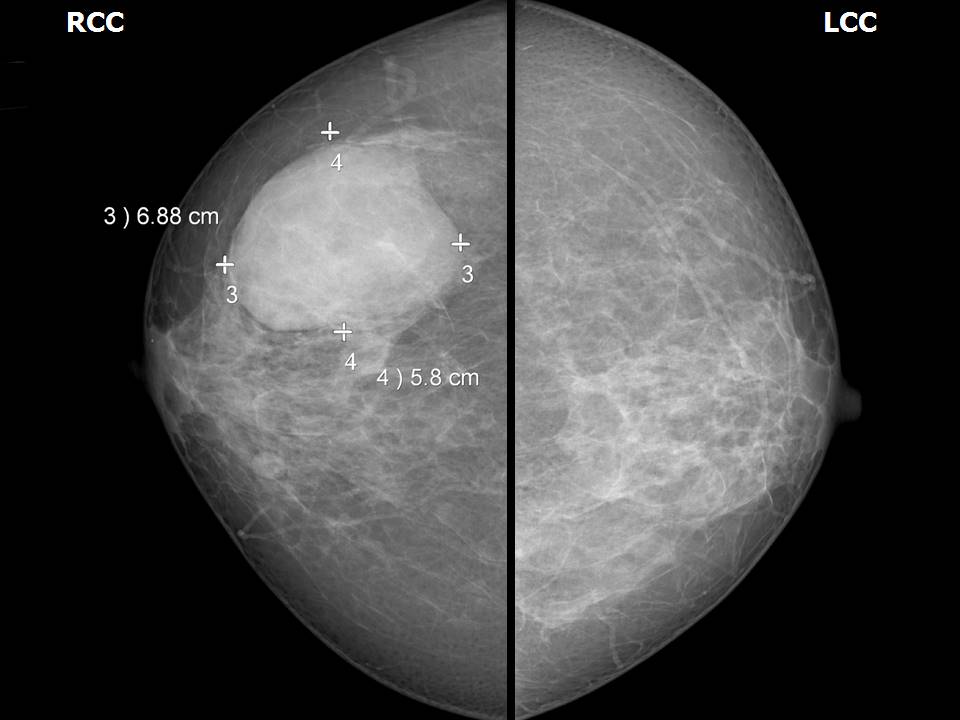
Mammography:
| Breast composition: | ACR category b (there are scattered areas of fibroglandular density) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Right breast, lower outer quadrant at 7–8 o’clock, middle third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 7.0 × 6.0 × 6.7 cm |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed with perilesional halo |
| • Density: | High |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | None |
| Breast composition: | ACR category b (there are scattered areas of fibroglandular density) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Right breast, lower inner quadrant at 5 o’clock, middle third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 1.0 × 0.6 cm |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Margins: | circumscribed |
| • Density: | Equal |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | None |
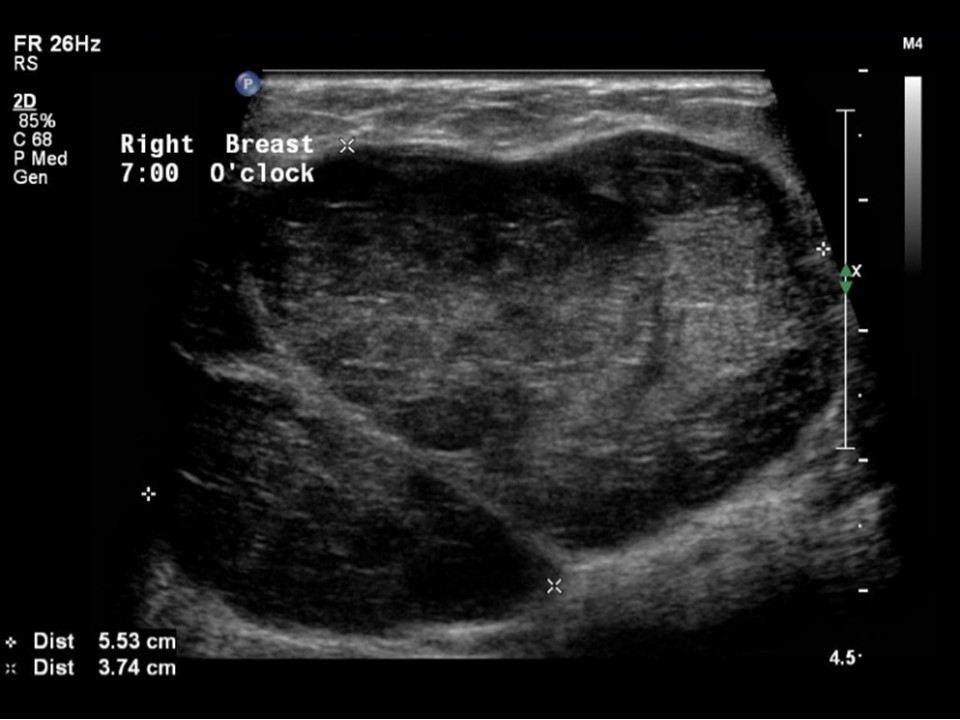
Ultrasound:
| Ultrasound features: Right breast, lower outer quadrant at 7 o’clock | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Right breast, lower outer quadrant at 7 o’clock |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 5.5 × 3.8 cm |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Orientation: | Parallel |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed |
| • Echo pattern: | Heteroechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
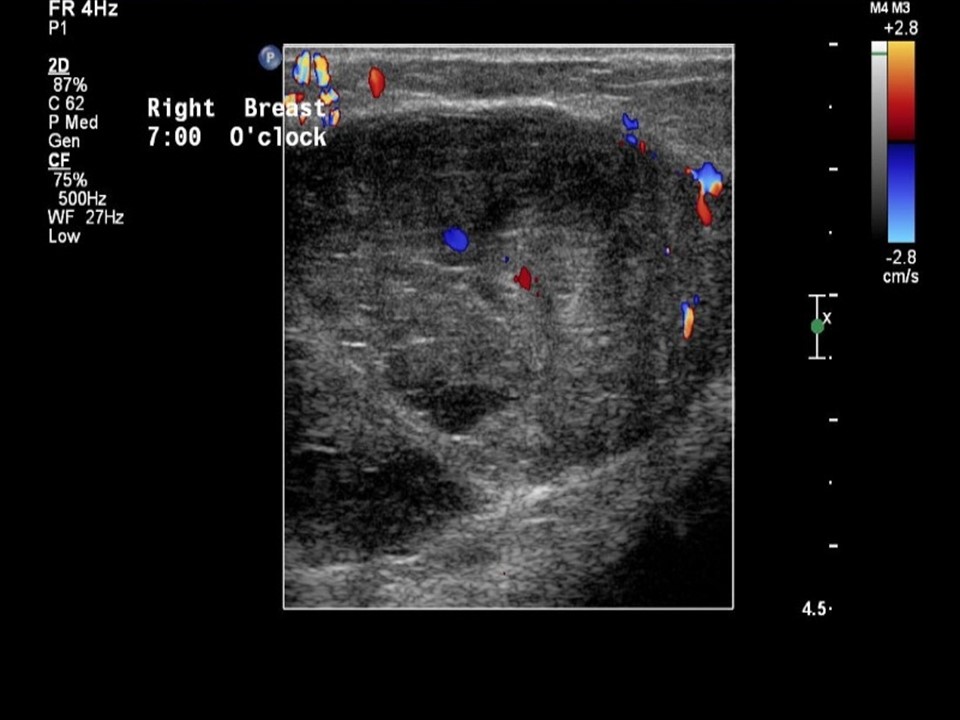
| ‣ Associated features: | Internal vascularity |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: 4A (low level of suspicion for malignancy)Further assessment:
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytologyCytology:
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Right |
| • Quadrant: | Outer |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | Whitish fluid |
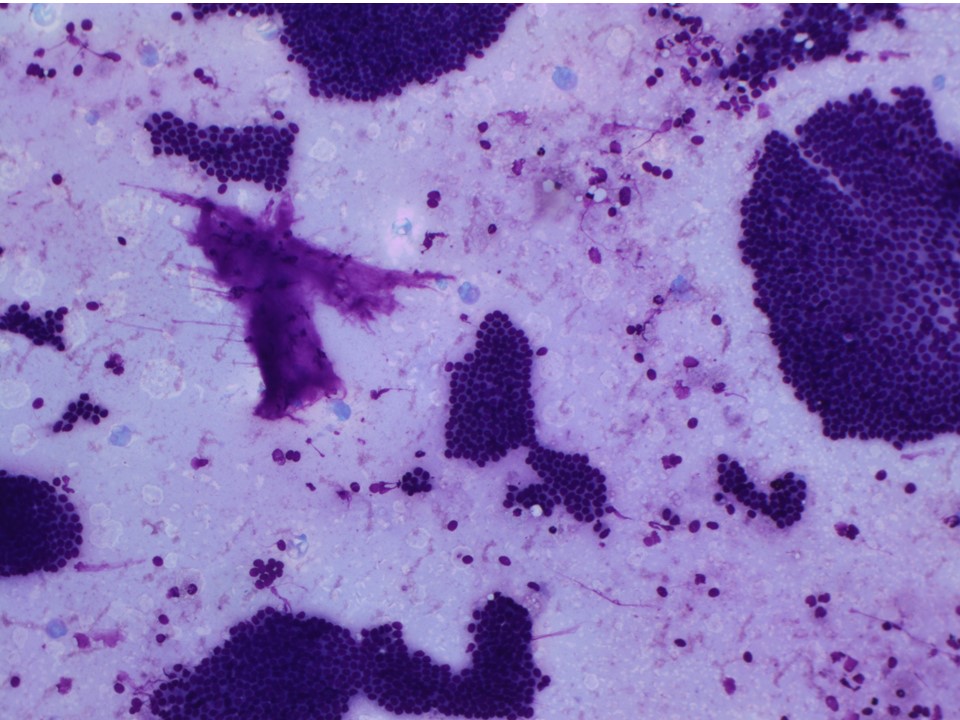
| ‣ Cytological description: | Smears are cellular and show monolayered clusters and sheets of ductal epithelial cells. Myoepithelial cells are seen. A few clusters of apocrine cells are seen. Background shows many foamy cells, macrophages, and haemorrhage |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Benign |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Benign proliferative breast lesion |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
Histopathology:
Lumpectomy
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | Lumpectomy |
| ‣ Laterality: | Right |
| ‣ Macroscopy: | Breast specimen (6.0 × 5.0 × 3.0 cm) with smooth external surface. Cut surface shows a large cystic area (4.0 × 4.0 × 2.0 cm) with a pedunculated papillary structure. Surrounding breast tissue contains smaller cysts with papillae |
| ‣ Histological type: | Multiple benign papillomas. Sections from the papillary lesions reveal multiple benign papillomas with well-developed fibrovascular cores and broad club-like papillae and arborescent fronds. The broader papillae contain glands. Both the fibrovascular cores and the glandular components are lined by epithelial cells with a prominent myoepithelial layer |
| ‣ Histological grade: | |
| ‣ Mitosis: | |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | |
| ‣ Margins: | |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | |
| ‣ Comments: | Negative for malignancy |
Case summary:
| Postmenopausal woman presented with painful right breast lump. Diagnosed as mass of suspicious morphology, BI-RADS 4A on imaging, as benign proliferative lesion on cytology, and as multiple benign papillomas on histopathology. |
Learning points:
|