Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Filter by language: English / Русский
Go back to the list of case studies
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
1. Right breast microdochectomy specimen
| Case number: | 064 |
| Age: | 82 |
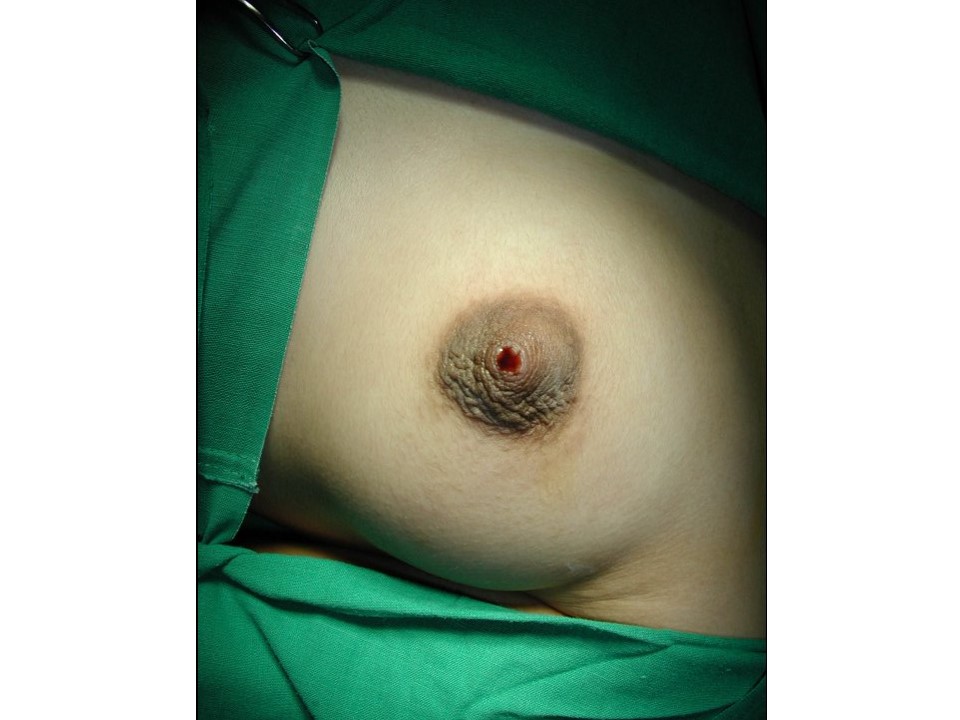
| Clinical presentation: | Postmenopausal woman with average risk of developing breast cancer presented with blood-stained discharge from the right nipple. On examination, no palpable breast lump was found. |
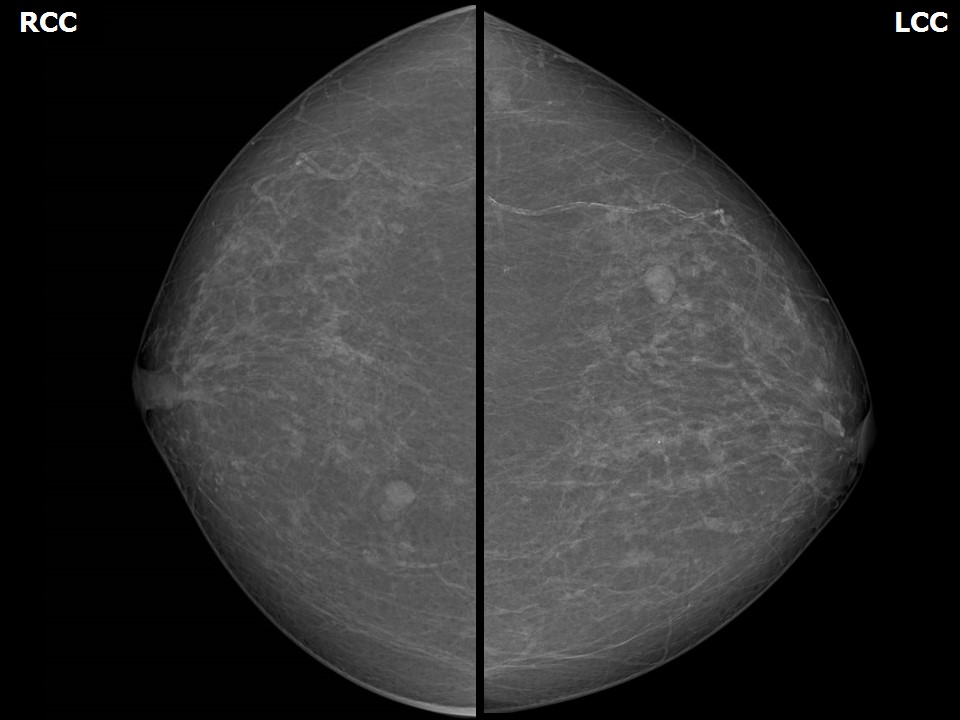
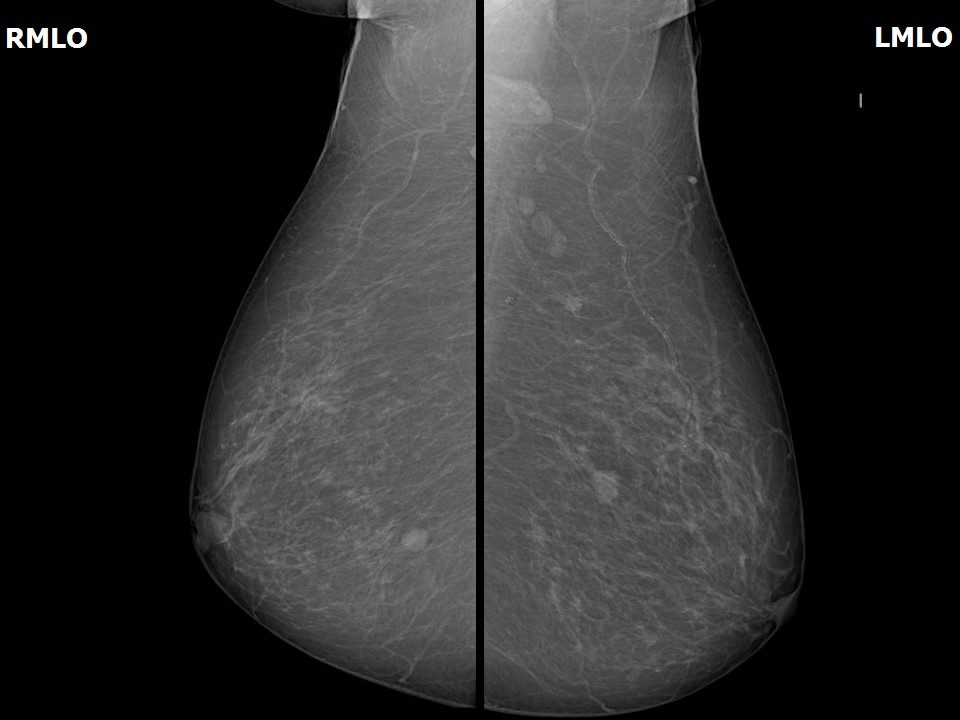
Mammography:
| Breast composition: | ACR category a (the breasts are almost entirely fatty) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Right breast, central portion of the breast, central zone, anterior third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 1.0 cm in greatest dimension |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed |
| • Density: | Equal |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | Present |
| ‣ Associated features: | Nipple retraction |
| Breast composition: | ACR category a (the breasts are almost entirely fatty) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Right breast, lower inner quadrant at 5 o’clock, posterior third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 0.8 cm |
| • Shape: | Round |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed |
| • Density: | Equal |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | Present |
| ‣ Associated features: | None |
| Breast composition: | ACR category a (the breasts are almost entirely fatty) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Left breast, upper inner quadrant at 10–11 o’clock, middle third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | Multiple |
| • Size: | Largest < 1.0 cm |
| • Shape: | Round |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed |
| • Density: | Equal |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | None |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | None |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | Present |
| ‣ Associated features: | None |
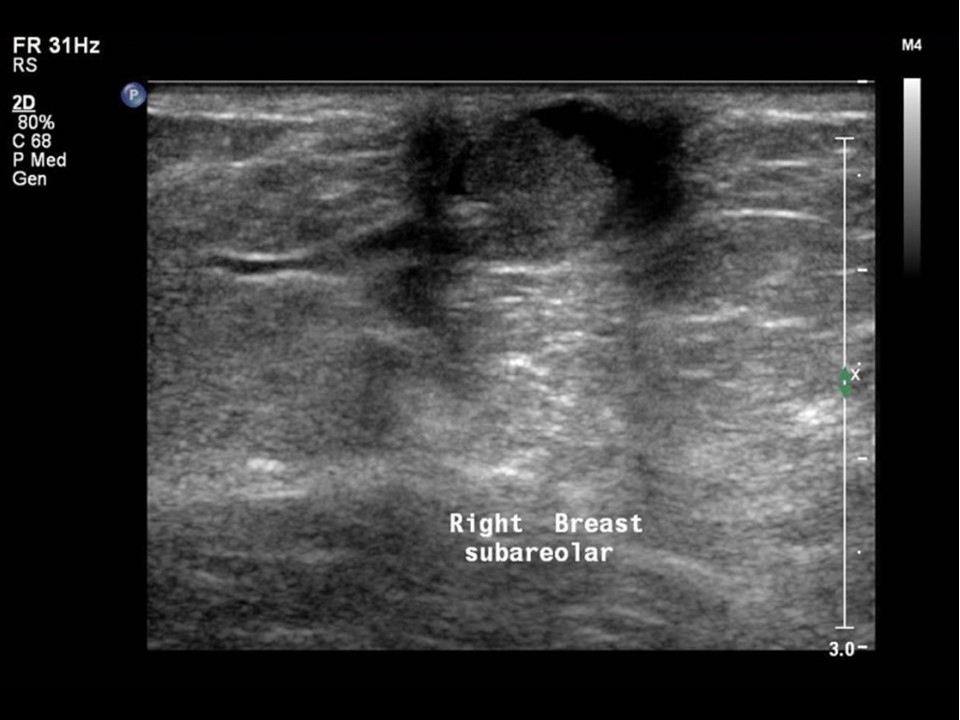
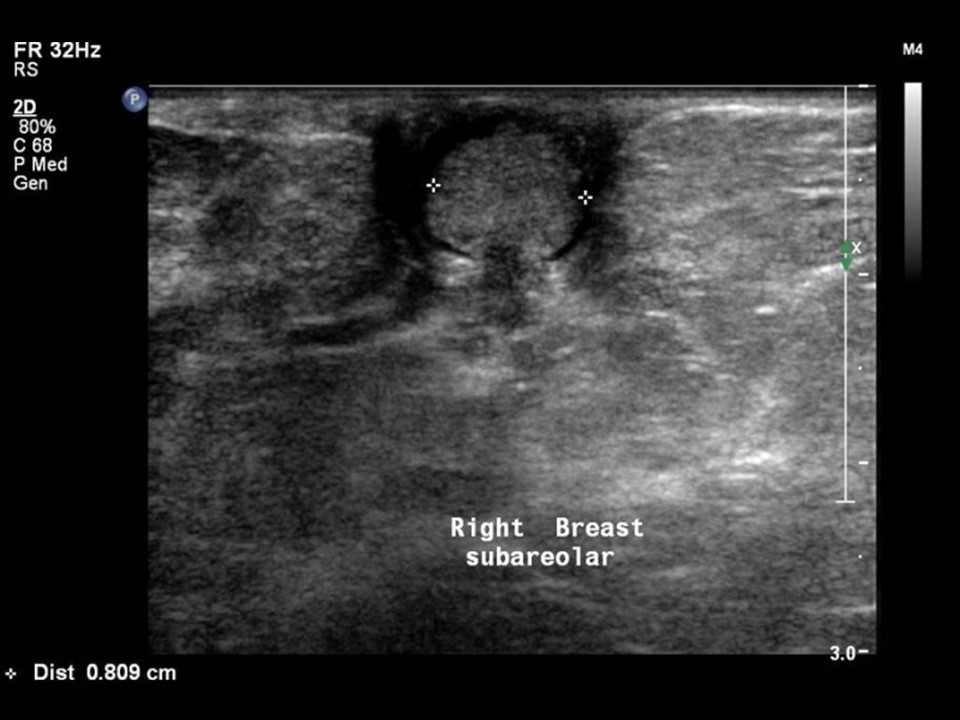
Ultrasound:
| Ultrasound features: Right breast, central portion of the breast | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Right breast, central portion of the breast |
| • Number: | 1 (in intraductal lesion) |
| • Size: | 0.8 cm in greatest dimension |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Orientation: | Not parallel |
| • Margins: | Indistinct |
| • Echo pattern: | Isoechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Solitary dilated duct in subareolar region |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
| Ultrasound features: Left breast, scattered in the central portion of the breast | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Left breast, scattered in the central portion of the breast |
| • Number: | Multiple |
| • Size: | Largest 0.7 cm |
| • Shape: | Round |
| • Orientation: | Parallel |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed |
| • Echo pattern: | Anechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | None |
| ‣ Special cases: | Simple cyst |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: 4B (moderate suspicion of malignancy)Further assessment:
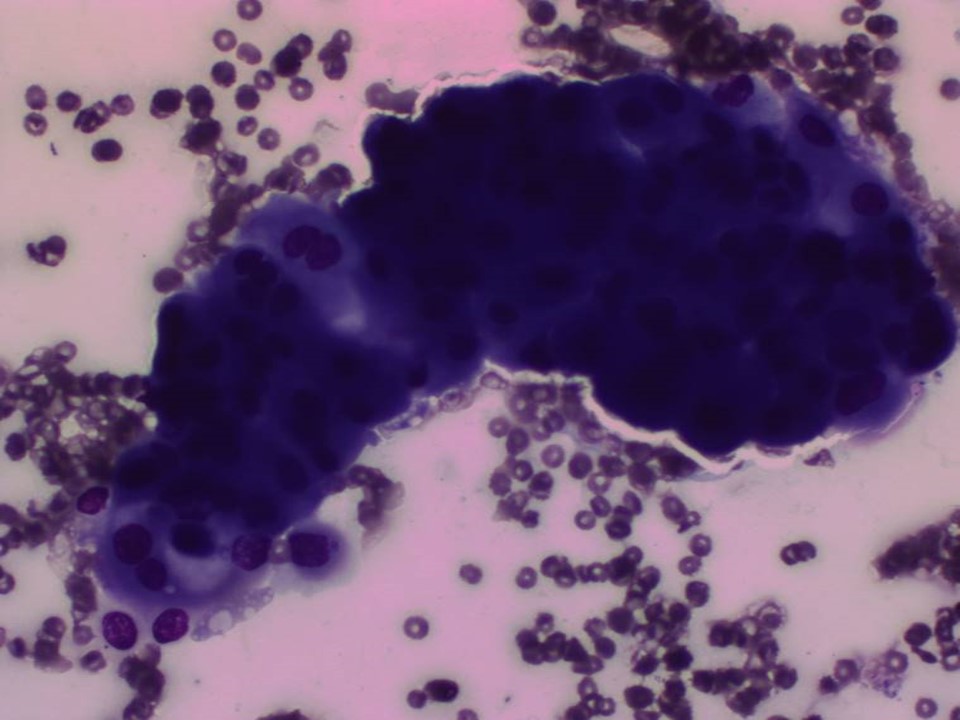
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytologyCytology:
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | Nipple discharge |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Right |
| • Quadrant: | |
| • Localization technique: | |
| • Nature of aspirate: | Greenish brown discharge |
| ‣ Cytological description: | Smear reveals a few three-dimensional clusters of ductal epithelial cells showing mild to moderate atypia. Background shows a few foamy cells, macrophages, and RBCs |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Atypical, probably benign |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Papillary lesion with atypia |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
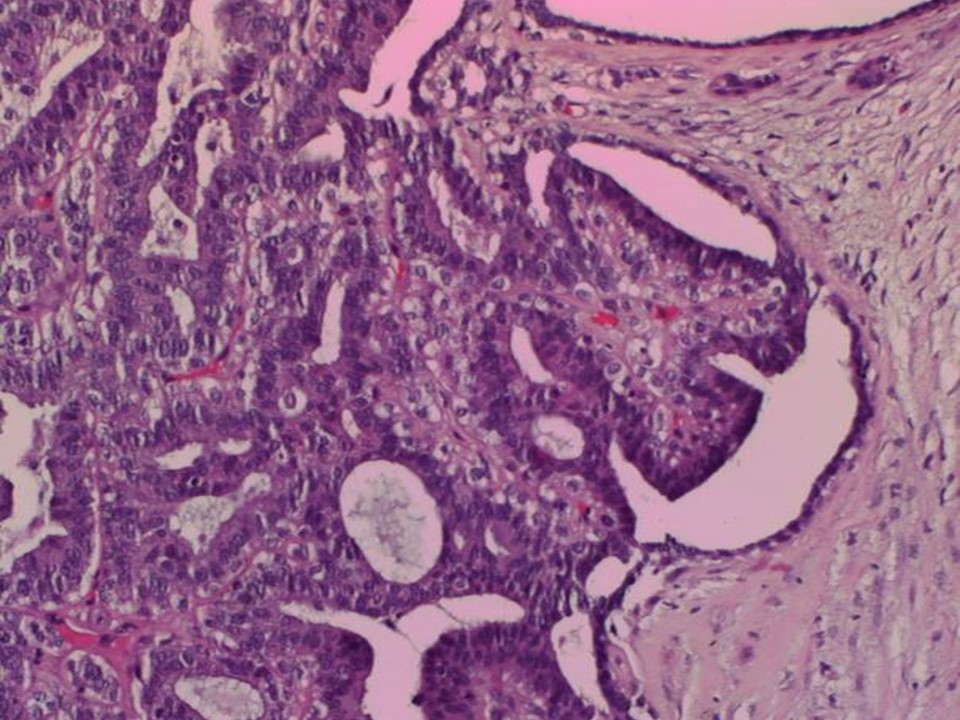
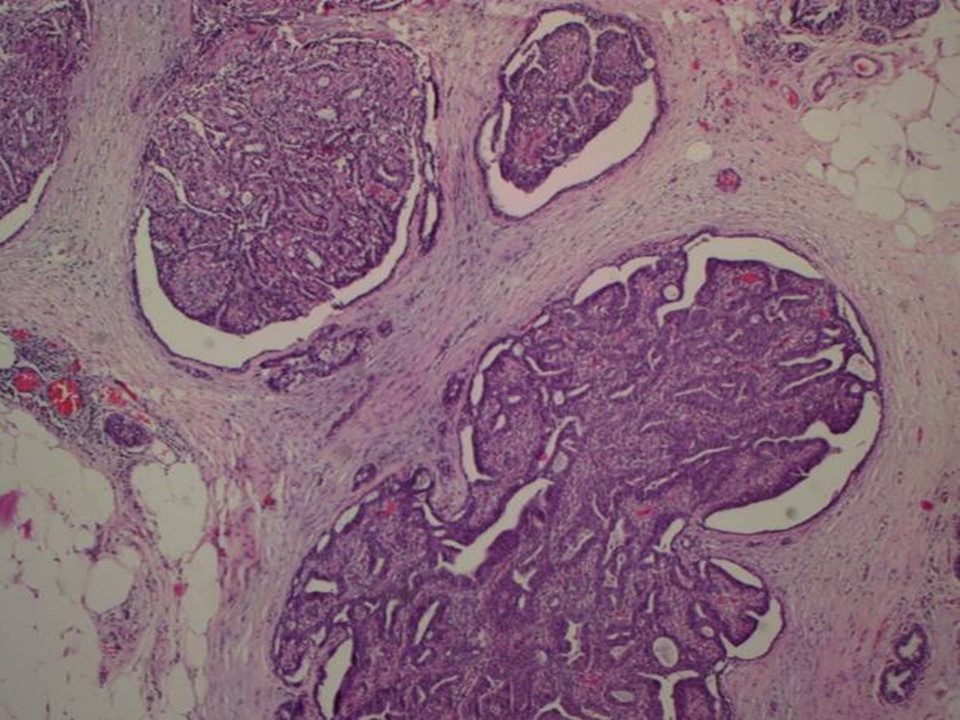
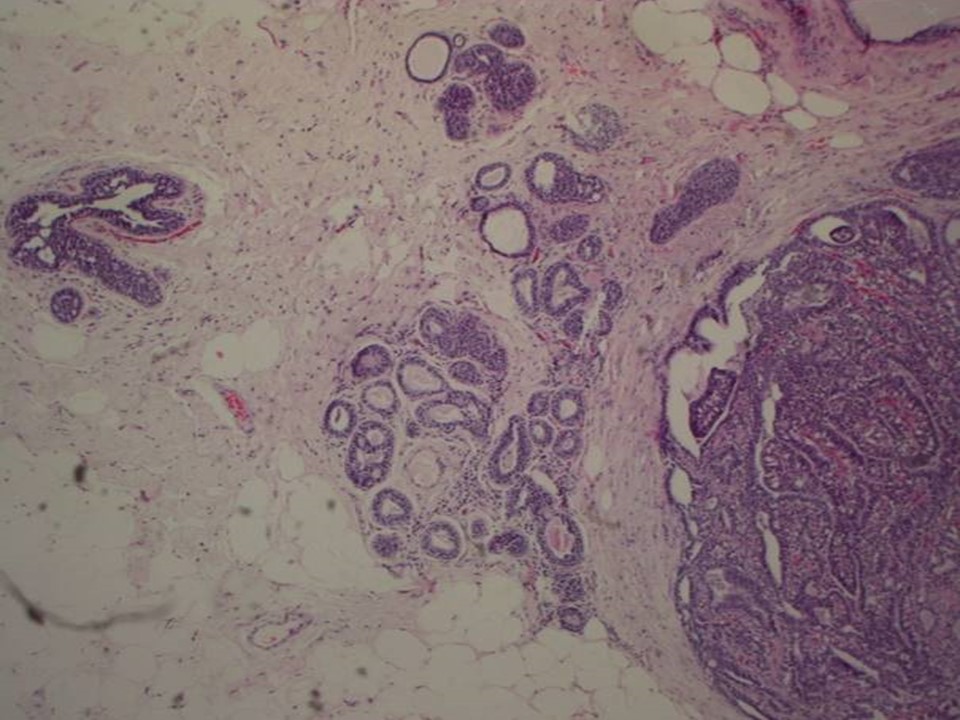
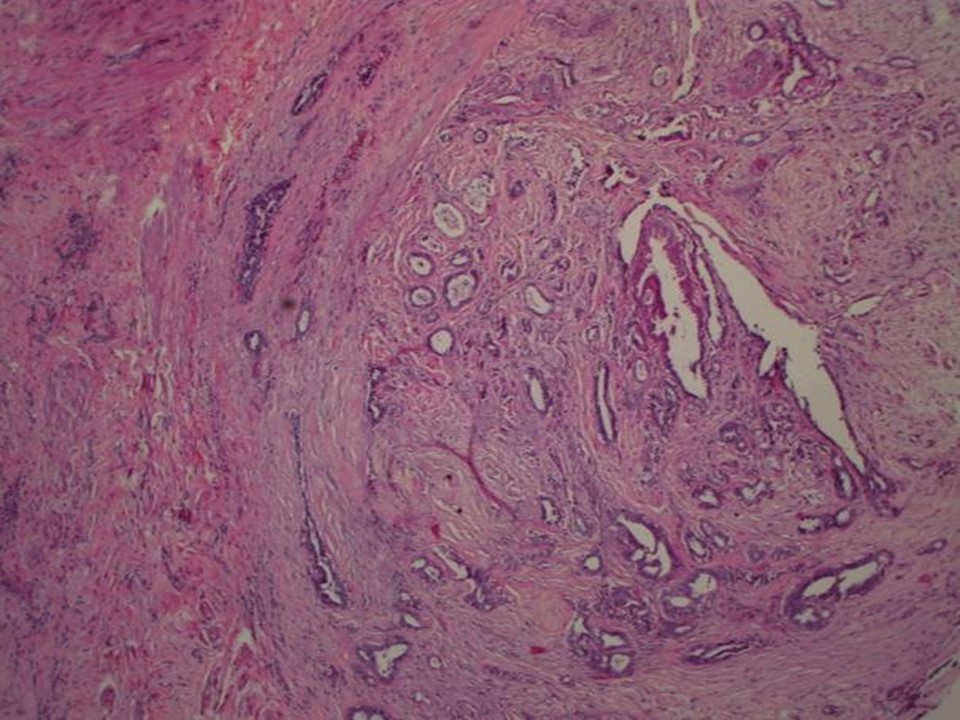
Histopathology:
1. Right breast microdochectomy specimen
2. Part of the underlying breast tissue
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | 1. Right breast microdochectomy specimen
2. Part of the underlying breast tissue |
| ‣ Laterality: | Right |
| ‣ Macroscopy: | 1. Single skin-covered bit (2.3 × 1.7 × 1.5 cm). On cut section a papillary structure (0.6 × 0.5 × 0.4 cm). Adjacent to this there is a firm whitish nodule (0.5 cm in diameter)
2. Also received separately two fibrofatty tissue bits (3.0 × 1.5 × 1.0 cm each). On cut section, whitish areas (0.5 × 0.5 × 0.5 cm) are seen |
| ‣ Histological type: | Sections reveal a few dilated ducts showing papillary proliferation with fibrovascular cores. The papillary fronds and ducts are lined by two cell layers with focal area showing epithelial hyperplasia. The adjacent ducts show epithelial hyperplasia focally. The section from the adjacent nodule shows nodular fibrosis with entrapped ducts; occasional ducts show apocrine metaplasia, consistent with a duct adenoma. Sections from the separately received fibrofatty tissue show dilated ducts with papillomatosis. There is no evidence of malignancy in the section studied |
| ‣ Histological grade: | |
| ‣ Mitosis: | |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | |
| ‣ Margins: | |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | |
| ‣ Comments: |
Case summary:
| Postmenopausal woman presented with right breast blood-stained nipple discharge. Diagnosed as subareolar solitary dilated duct with intraductal solid lesion. BI-RADS 4B on imaging, as papillary lesion with atypia on cytology, and as dilated ducts with papillomatosis, papillary proliferation, duct adenoma on histopathology. |
Learning points:
|