Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Filter by language: English / Русский
Go back to the list of case studies
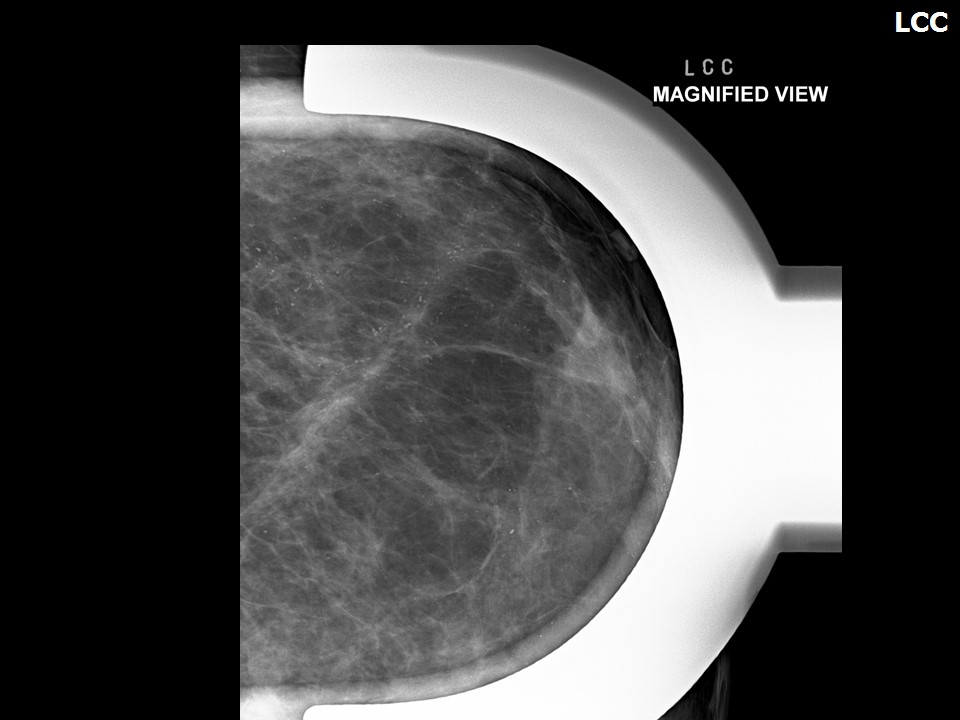
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
BI-RADS Category (July 2013): 6 (known biopsy-proven malignancy)
| Case number: | 060 |
| Age: | 54 |
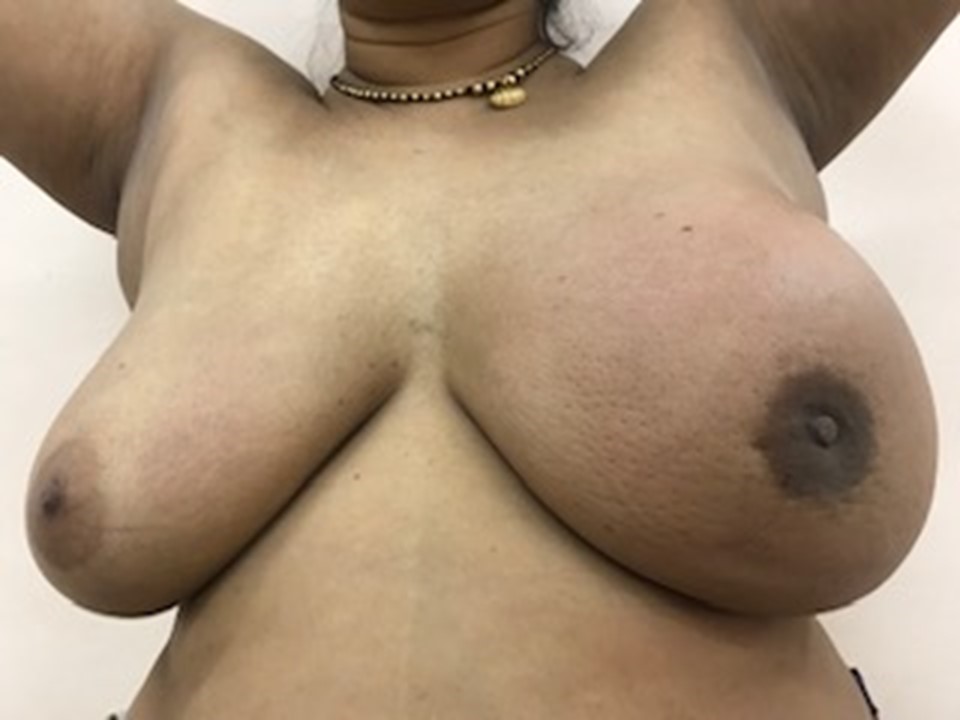
| Clinical presentation: | Postmenopausal woman with increased risk of developing breast cancer in view of family history presented with acute-onset left mastalgia and unilateral breast enlargement of the left breast. On examination, the left breast showed an area of acute tenderness and lumpish feel in the upper outer quadrant. |
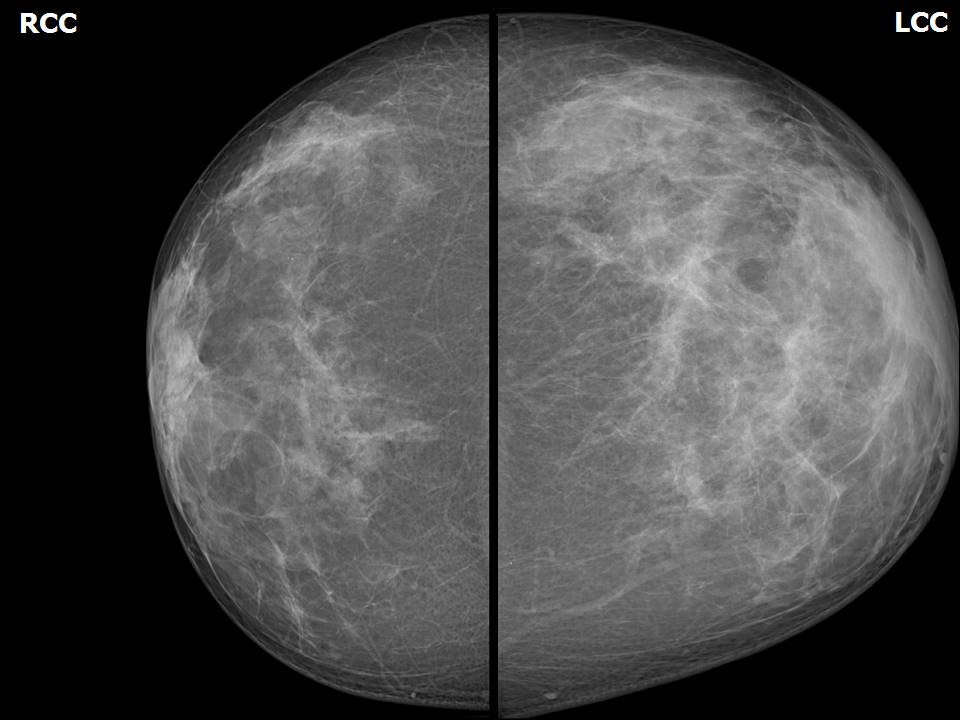
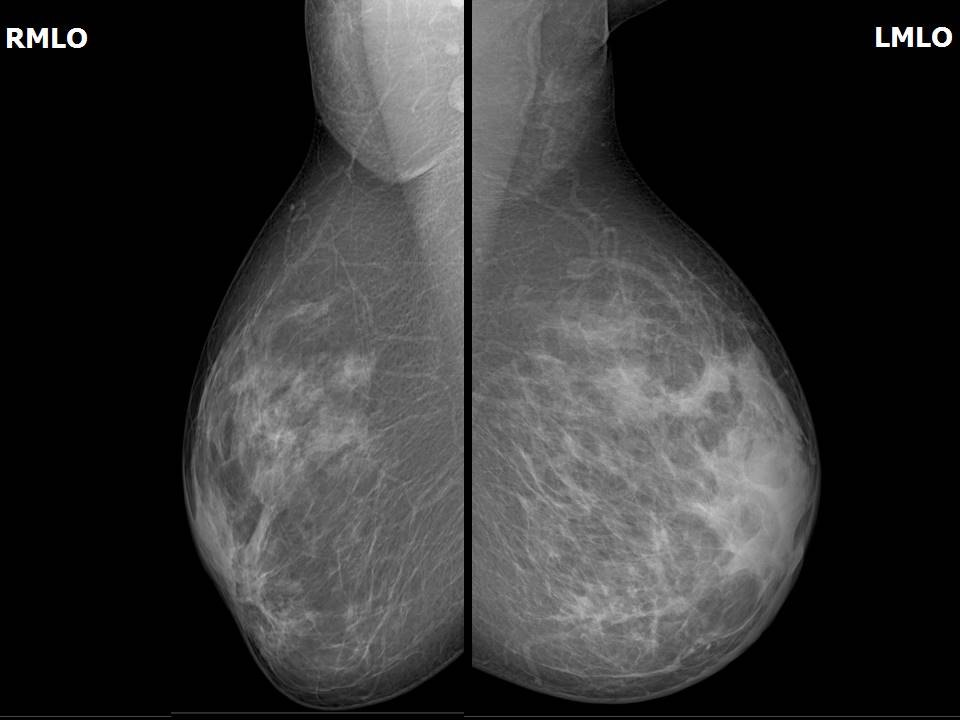
Mammography:
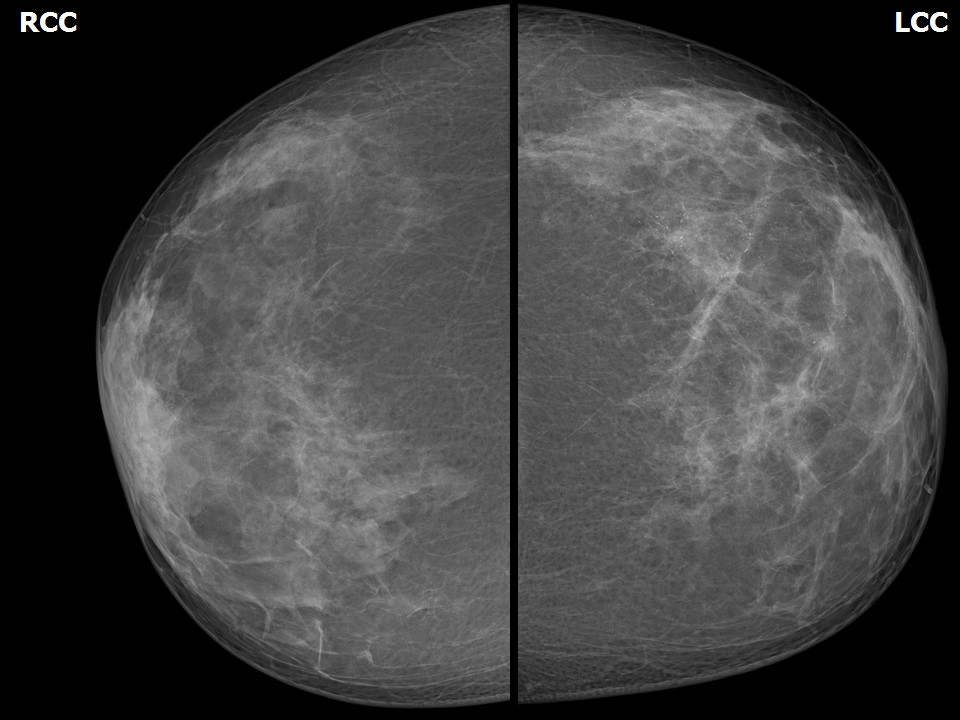
| Breast composition: | ACR category c (the breasts are heterogeneously dense, which may obscure small masses) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | April 2013: Left breast, upper outer quadrant at 1– 2 o’clock, anterior and middle thirds |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | No |
| • Size: | No |
| • Shape: | None |
| • Margins: | None |
| • Density: | None |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | Fine pleomorphic |
| • Distribution: | segmental |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | Present |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | Focal |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Skin thickening, trabecular thickening, axillary lymphadenopathy, architectural distortion, and fine pleomorphic microcalcifications |
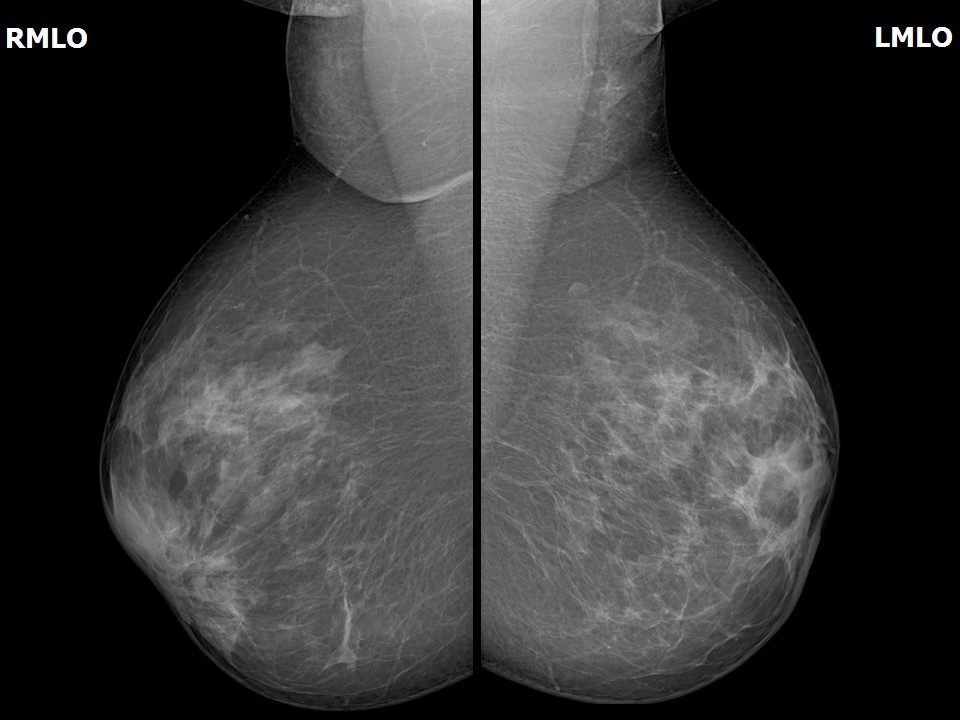
| Breast composition: | ACR category c (the breasts are heterogeneously dense, which may obscure small masses) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | July 2013: Left breast, upper outer quadrant at 1–2 o’clock, anterior and middle thirds |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | No |
| • Size: | No |
| • Shape: | None |
| • Margins: | None |
| • Density: | None |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | Fine pleomorphic |
| • Distribution: | segmental |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | Present |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | Focal |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Residual skin thickening and trabecular thickening with fine pleomorphic microcalcifications |
Ultrasound:
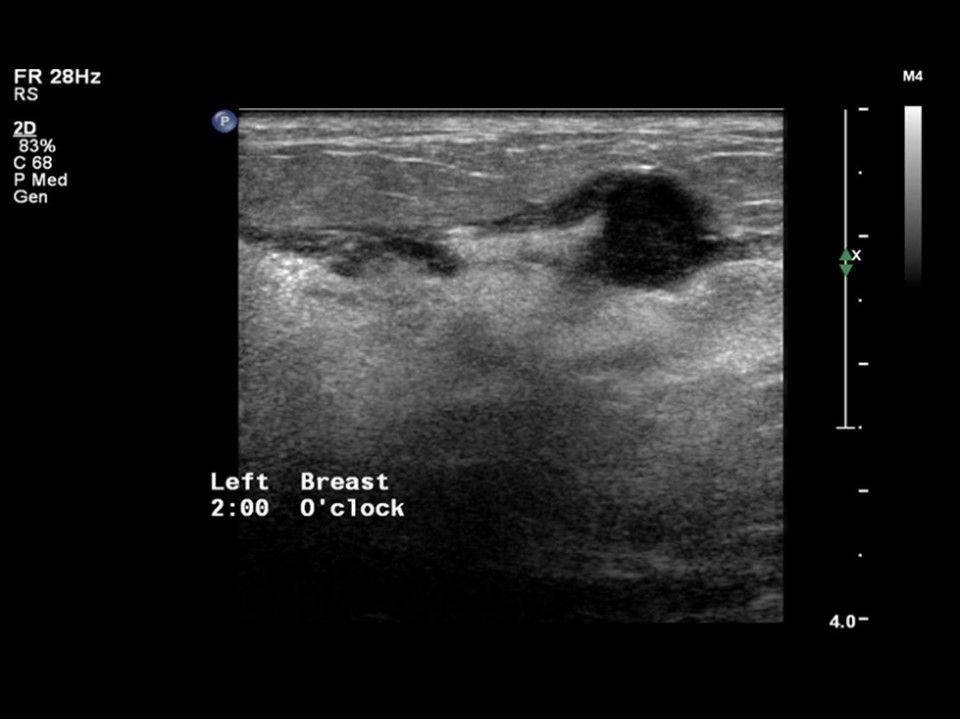
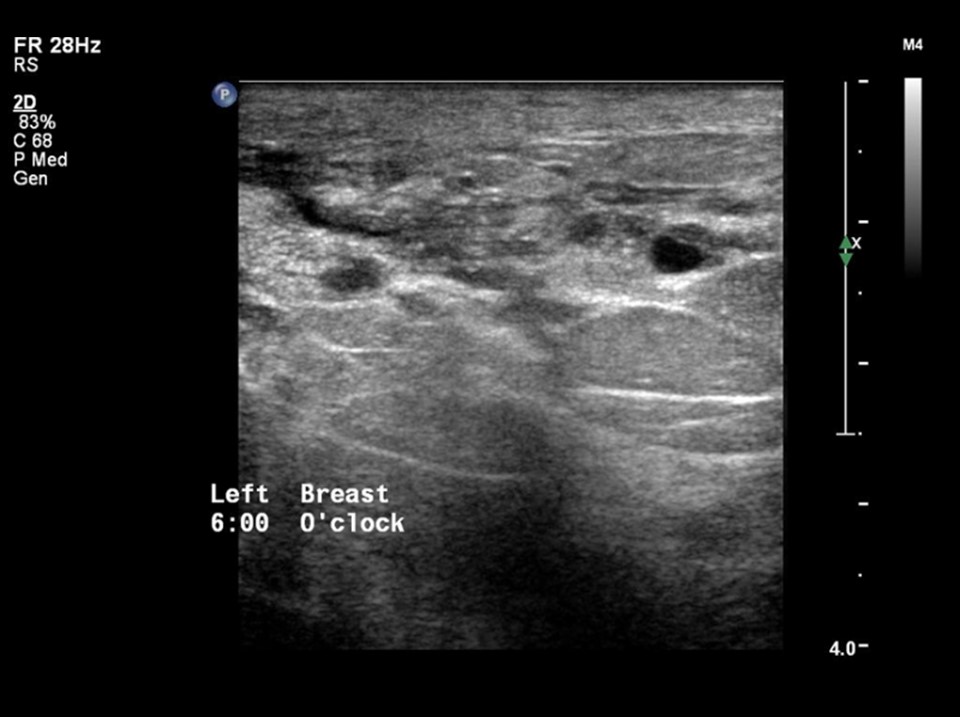
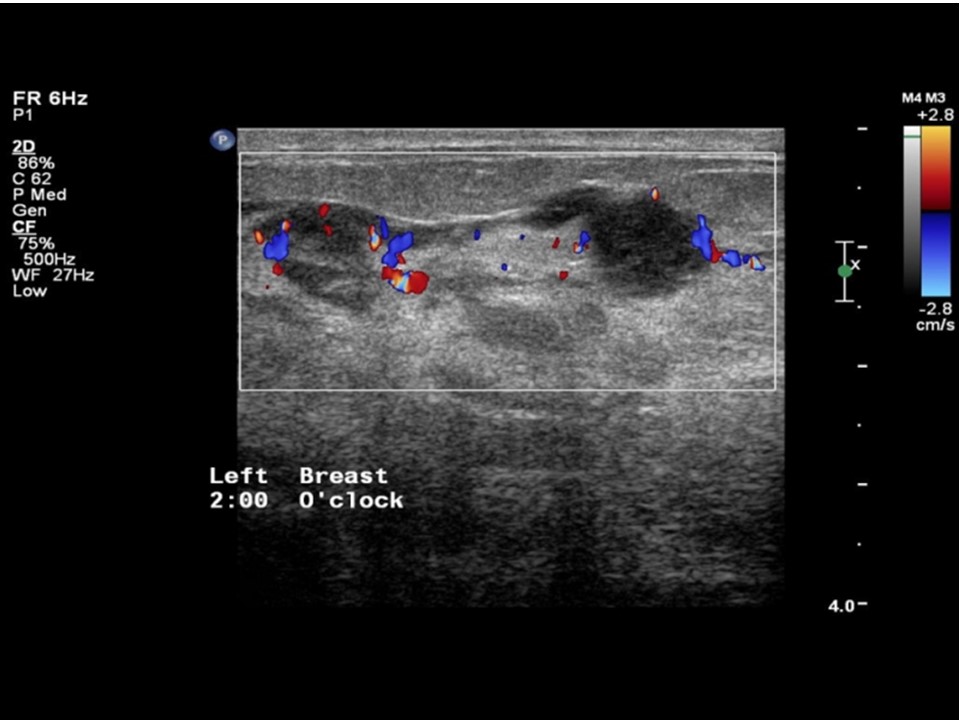
| Ultrasound features: April 2013: Left breast, outer quadrants at 2–6 o’clock | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | April 2013: Left breast, outer quadrants at 2–6 o’clock |
| • Number: | Multiple |
| • Size: | Largest 2.7 cm in greatest dimension |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Orientation: | Not parallel |
| • Margins: | indistinct |
| • Echo pattern: | Hypoechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | Fine microcalcifications |
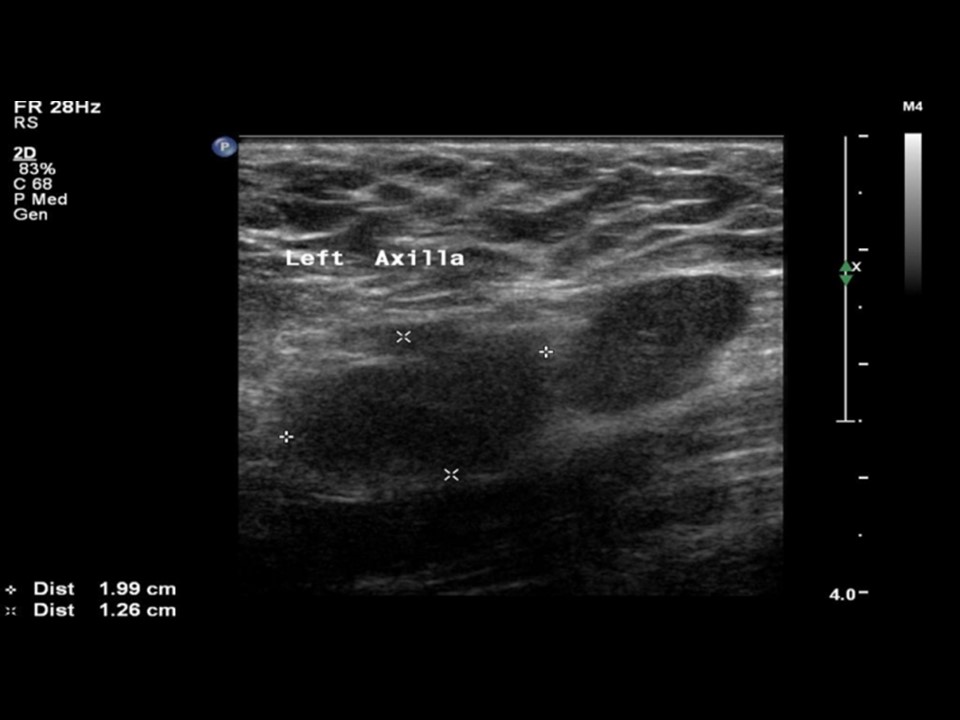
| ‣ Associated features: | Architectural distortion, duct changes, skin thickening, oedema, internal vascularity, and axillary lymphadenopathy with loss of central fatty sinus. Largest node is 2.0 × 1.3 cm |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category (April 2013): 5 (highly suggestive of malignancy)BI-RADS Category (July 2013): 6 (known biopsy-proven malignancy)
Further assessment:
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytologyCytology:
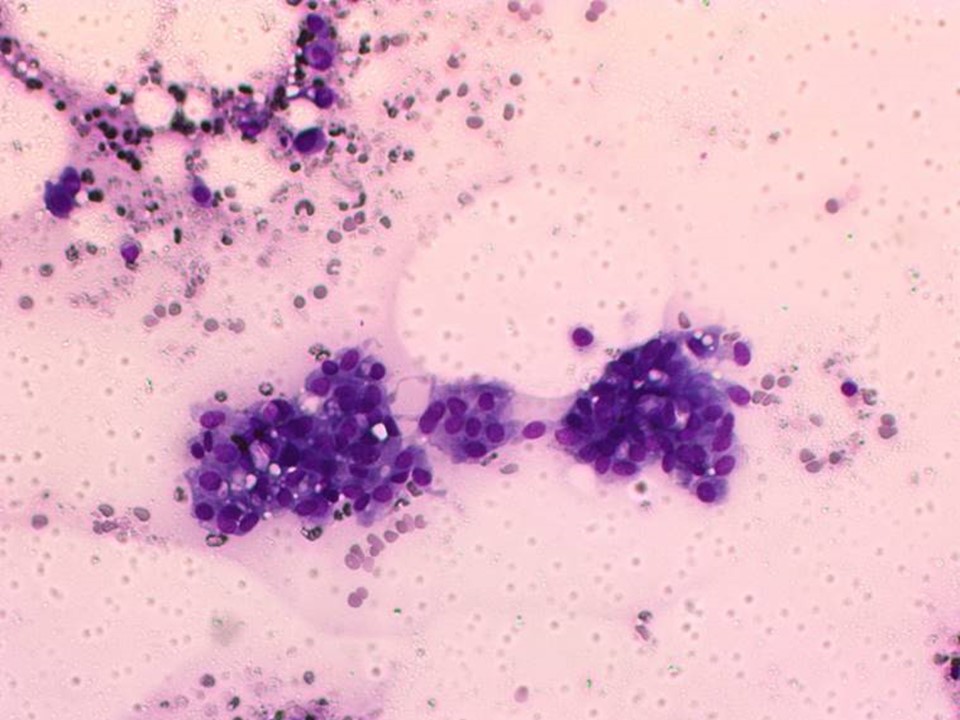
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC (solid lesion) |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Left |
| • Quadrant: | Upper outer |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | whitish |
| ‣ Cytological description: | Loosely cohesive sheets of malignant ductal cells with nuclear pleomorphism and prominent nucleoli |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Malignant |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Carcinoma – high grade |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
Histopathology:
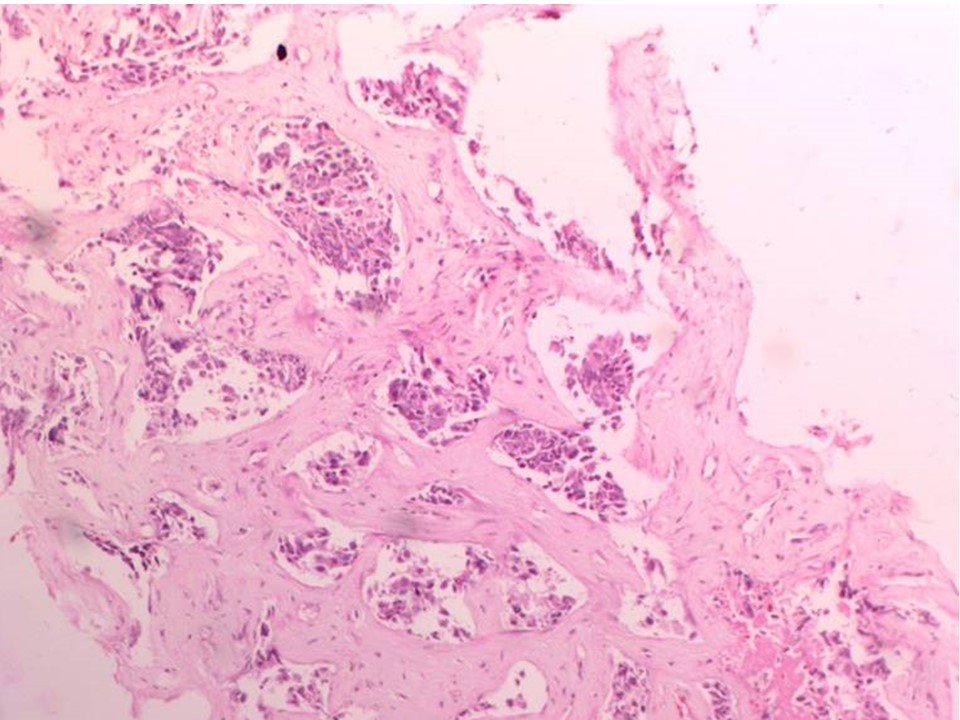
Core needle biopsy
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | Core needle biopsy |
| ‣ Laterality: | Left |
| ‣ Macroscopy: | 5 cores of size 5 mm, 5 mm, 8 mm, 10 mm, and 12 mm |
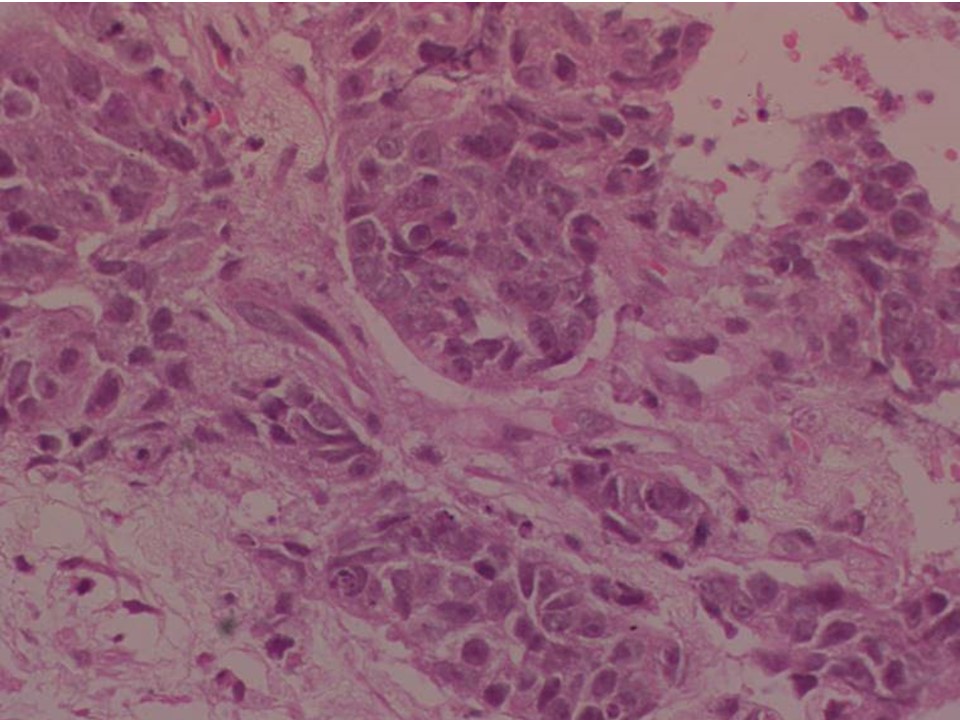
| ‣ Histological type: | Invasive carcinoma of no special type |
| ‣ Histological grade: | Grade 2 (3 + 2 + 2 = 7) |
| ‣ Mitosis: | 12 |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | |
| ‣ Margins: | |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | |
| ‣ Comments: |
After neo-adjuvant chemotherapy and breast-conserving surgery
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | After neo-adjuvant chemotherapy and breast-conserving surgery |
| ‣ Laterality: | Left (after neo-adjuvant chemotherapy ) |
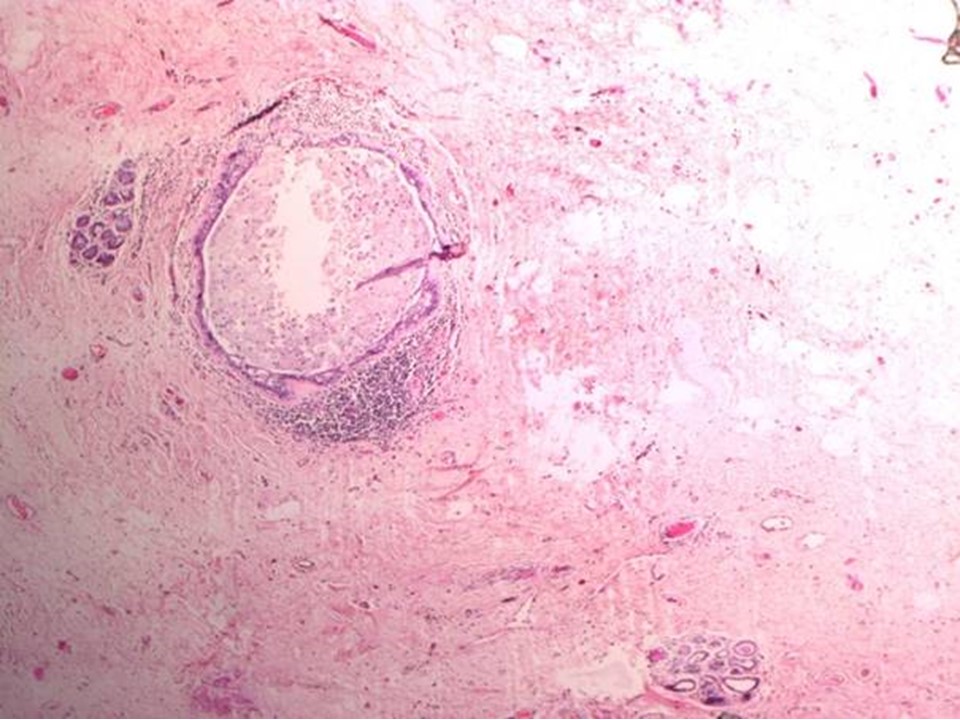
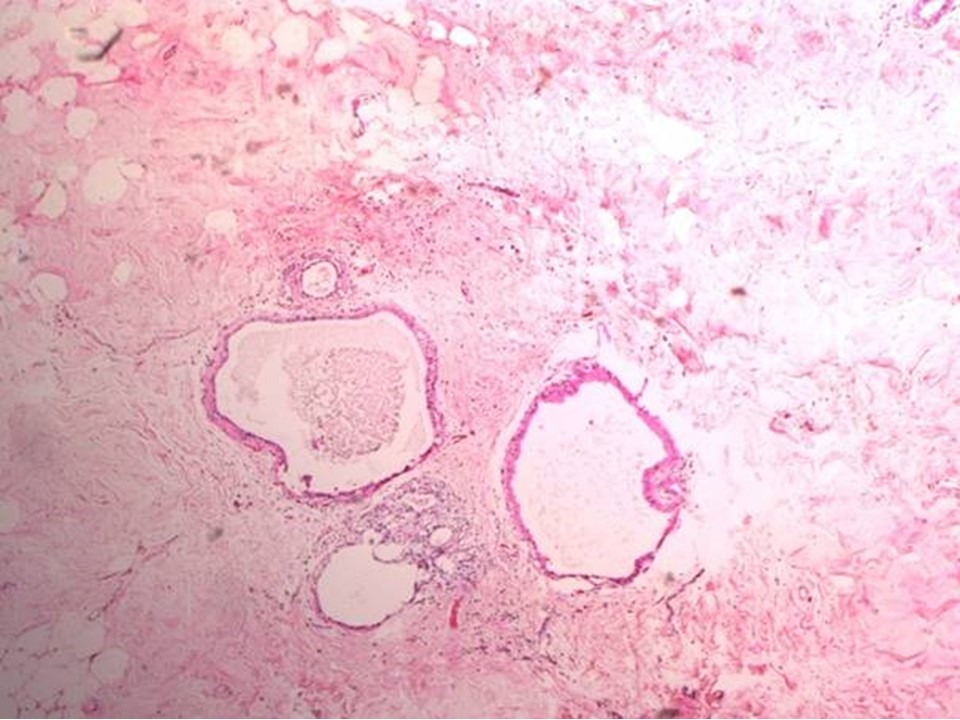
| ‣ Macroscopy: | On serial cut sections of the specimen whitish firm areas, 4.0 × 3.0 × 2.0 cm and 3.0 × 3.0 × 1.0 cm. Rest of the breast tissue shows fibrosis |
| ‣ Histological type: | No residual carcinoma in multiple sections of the breast tissue |
| ‣ Histological grade: | |
| ‣ Mitosis: | |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | No invasive carcinoma |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | 3/22 |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | Not identified |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | Not identified |
| ‣ Margins: | Free of tumour |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | yT0yN1 |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | |
| ‣ Comments: | Pathological complete response in the breast with tumour bed showing poorly cellular oedematous connective tissue, dilated ducts, dense sclerosis, and chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate |
Post NACT follow up:
| Breast composition: | ACR Category b (scattered areas of fibroglandular density). | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of lesion: | Left breast upper outer quadrant 2-5 o’clock |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Number: | No |
| • Size: | No |
| • Shape: | No |
| • Margins: | No |
| • Density: | No |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | No |
| • Suspicious: | Fine pleomorphic |
| • Distribution: | segmental |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | Present |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | Focal |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | No |
| ‣ Skin Lesion: | No |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | No |
| ‣ Associated features: | Skin thickening, Axillary lymphadenopathy, Architectural distortion Calcifications |
| ‣ Location of lesion: | Left breast upper outer quadrant 2-5 o’clock |
Case summary:
| Postmenopausal woman presented with mastalgia and unilateral left breast enlargement. Diagnosed as inflammatory carcinoma of the left breast with breast oedema, trabecular thickening, skin thickening, and segmental fine pleomorphic microcalcifications, BI-RADS 5 on imaging, as carcinoma on cytology, and as invasive breast carcinoma of no special type on needle core biopsy. Follow-up after neo-adjuvant chemotherapy showed significant tumour regression, BI-RADS 6 on imaging. Operative specimen after neo-adjuvant chemotherapy showed no residual carcinoma in breast, yT0N1 on histopathology. |
Learning points:
|