Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Filter by language: English / Русский
Go back to the list of case studies
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
| Case number: | 040 |
| Age: | 57 |
| Clinical presentation: | Postmenopausal woman with average risk of developing breast carcinoma presented with bilateral breast lumps. Examination revealed two lumps in the left breast and one lump in the upper outer quadrant of the right breast. Axillae were normal. |
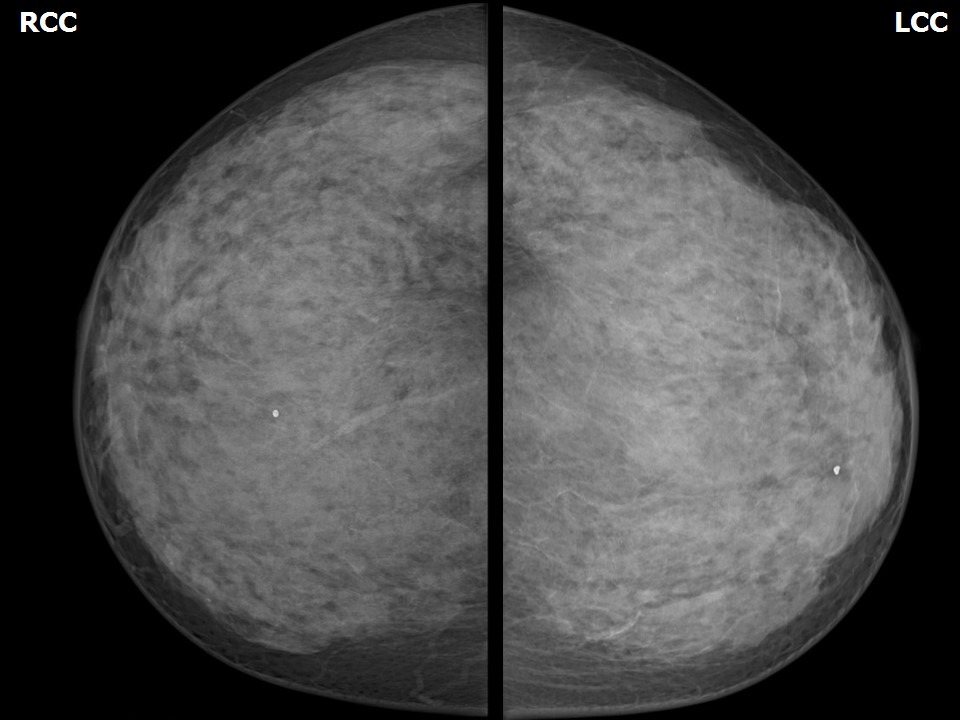
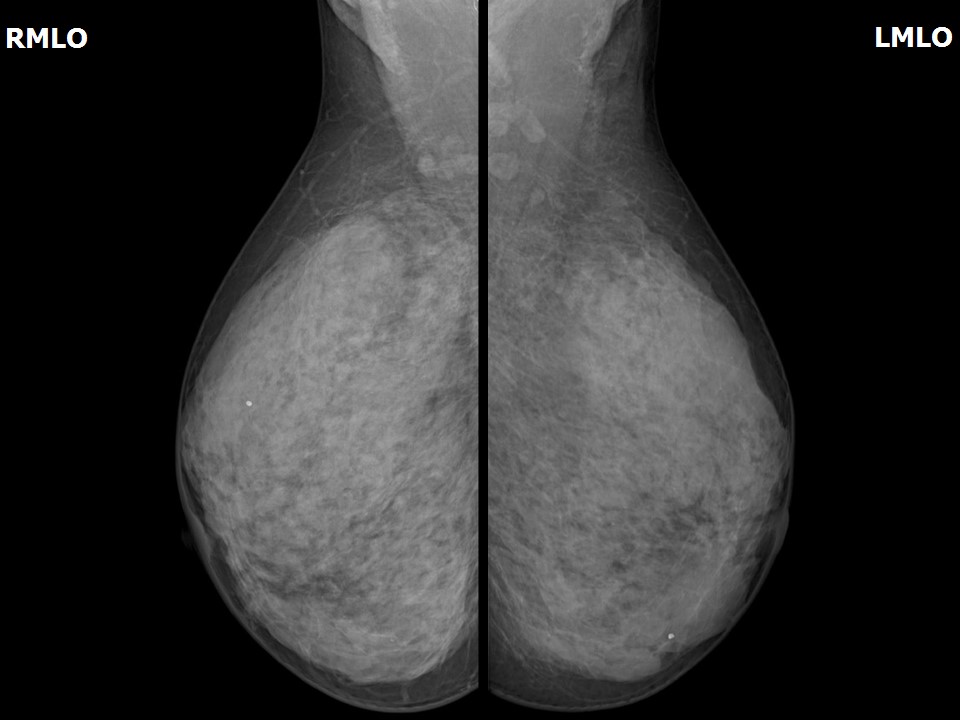
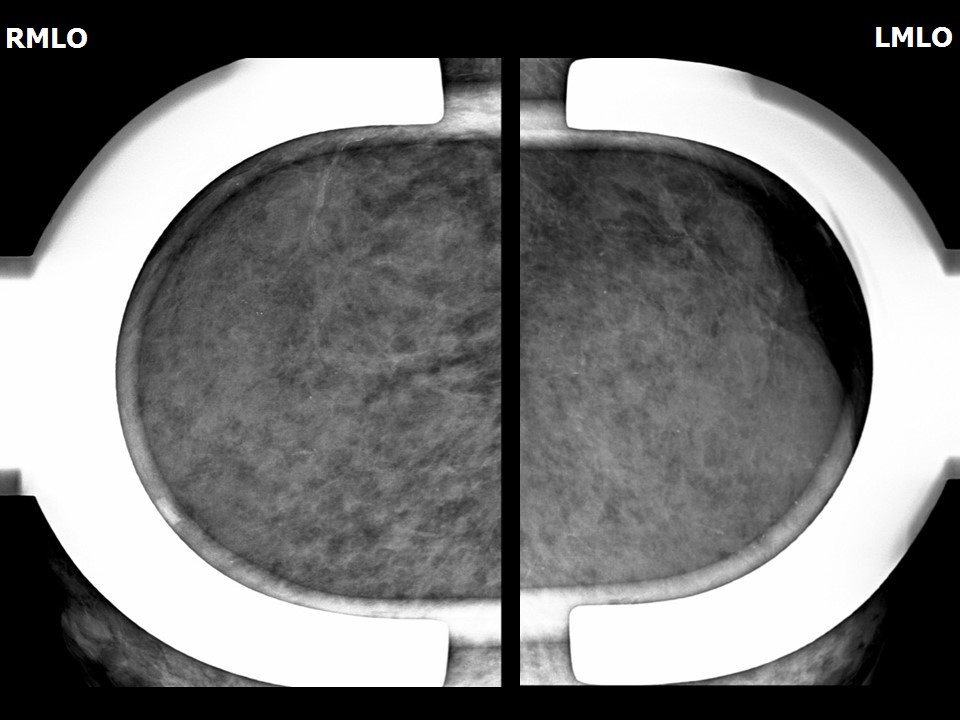
Mammography:
| Breast composition: | ACR category d (the breasts are extremely dense, which lowers the sensitivity of mammography) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Not identified in dense breast parenchyma |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | Mass not seen in extremely dense breasts which reduces the sensitivity of mammography |
| • Size: | Mass not seen in extremely dense breasts, which reduces the sensitivity of mammography |
| • Shape: | None |
| • Margins: | None |
| • Density: | None |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | Both breasts |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | Diffuse |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | Present |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | Focal, right breast, upper outer quadrant |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | None |
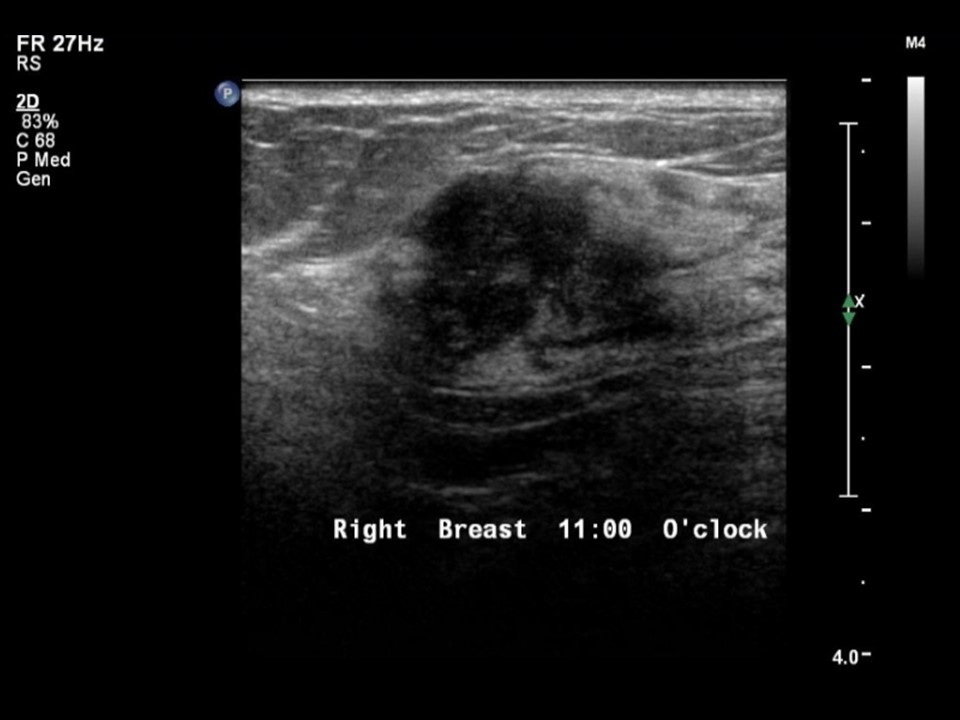
Ultrasound:
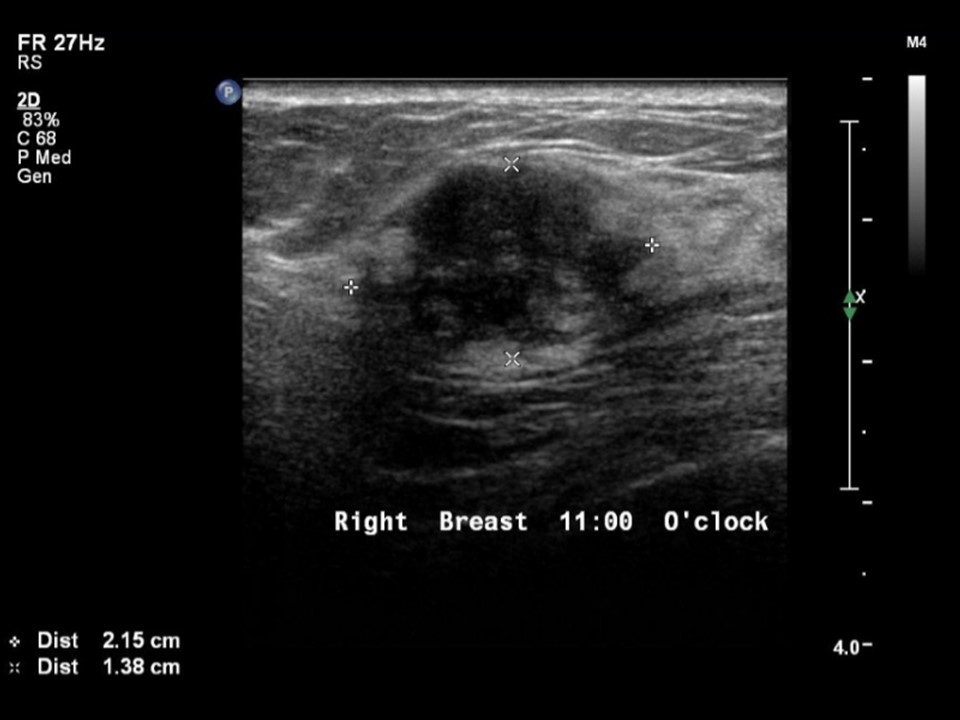
| Ultrasound features: Right breast, upper outer quadrant at 11 o’clock | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Right breast, upper outer quadrant at 11 o’clock |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 2.2 × 1.4 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Orientation: | Parallel |
| • Margins: | Spiculated |
| • Echo pattern: | Heteroechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
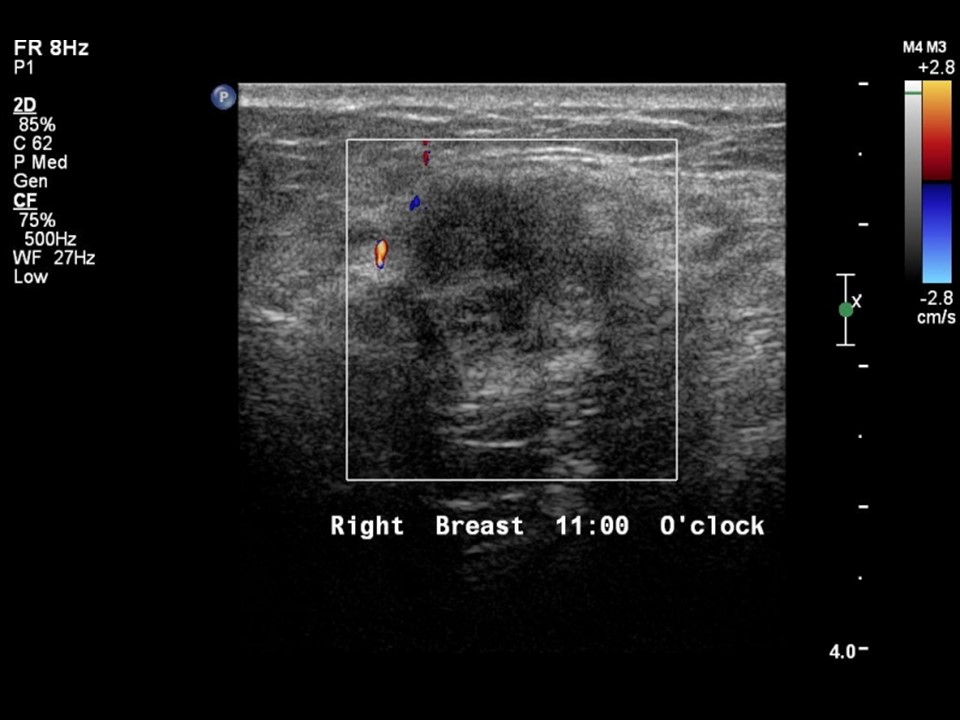
| ‣ Associated features: | Vascularity on colour flow mapping |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: 4C (high suspicion for malignancy)Further assessment:
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytologyCytology:
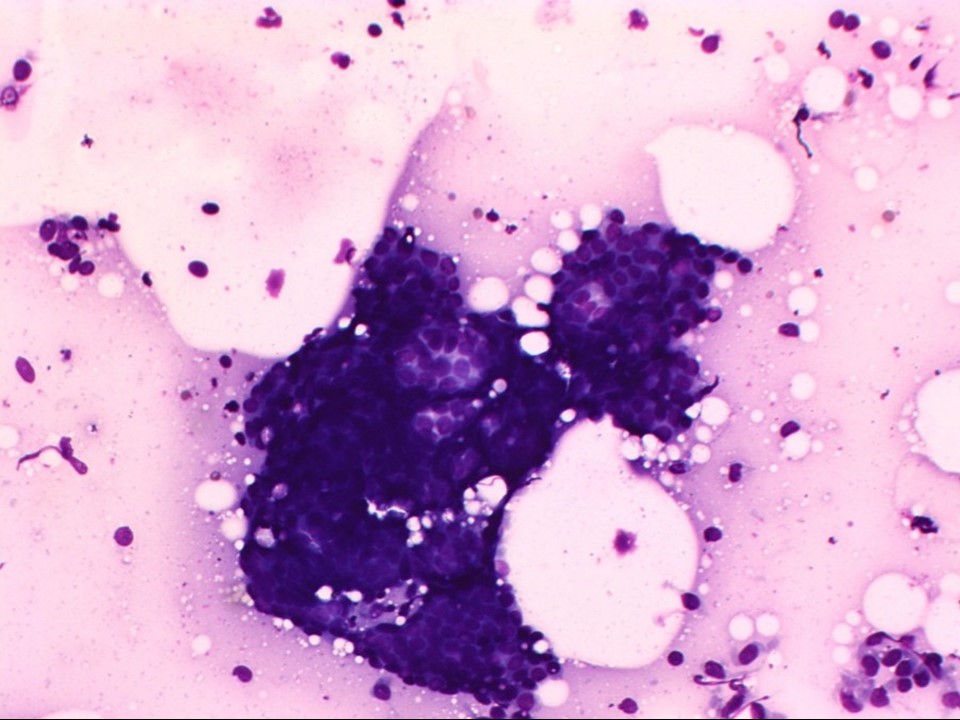
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Right |
| • Quadrant: | Upper outer |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | Whitish |
| ‣ Cytological description: | Smears reveal tightly cohesive sheets of benign ductal epithelial cells with myoepithelial cells against a background of bare nuclei, proteinaceous material, and blood |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Benign |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Benign proliferative breast lesion |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
Histopathology:
Breast-conserving surgery
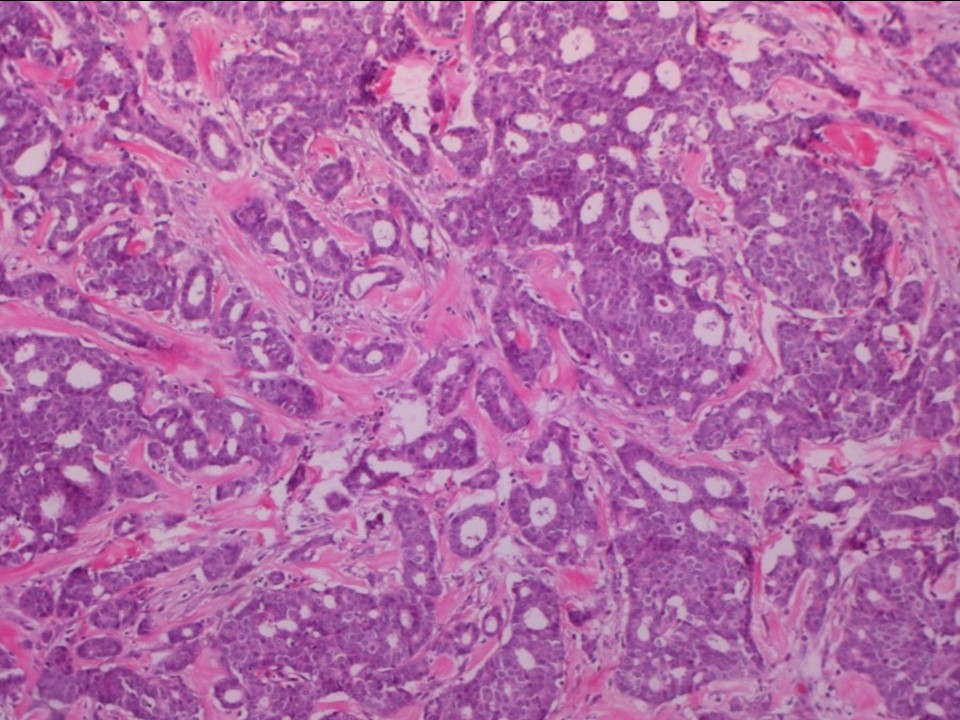
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | Breast-conserving surgery |
| ‣ Laterality: | Right |
| ‣ Macroscopy: | Specimen (7.5 × 6.5 × 3.0 cm) with overlying skin (2.8 × 0.8 cm). Cut section shows a grey white tumour (2.2 × 1.8 × 1.4 cm), 1.7 cm from the superior margin, 1.8 cm from the inferior margin, 0.8 cm from the lateral margin, and 3.0 cm from the medial margin. The tumour is 0.7 cm from the base. The surrounding breast shows extensive areas of fibrosis and appears firm and whitish |
| ‣ Histological type: | Invasive cribriform carcinoma, tubular carcinoma formed minor component |
| ‣ Histological grade: | Grade 1 (1 + 1 + 1 = 3) |
| ‣ Mitosis: | 4 |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | 2.2 cm |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | 0/31 |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | Absent |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | Cribriform type of low grade |
| ‣ Margins: | Free of tumour, nearest margin base is 0.7 cm from the tumour |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | pT2N0 |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | ER positive, PR positive, and HER2 negative |
| ‣ Comments: | Surrounding breast shows epithelial hyperplasia, adenosis, and lymphocytic lobulitis with extensive sclerosis |
Case summary:
| Postmenopausal woman presented with lumps in both breasts. Diagnosed as right breast mass of suspicious morphology, BI-RADS 4C on imaging, as benign proliferative breast lesion on cytology, and as invasive cribriform carcinoma admixed with tubular carcinoma pT2N0 and benign proliferative breast lesions on histopathology. Left breast shows diffuse fibrocystic changes. |
Learning points:
|
25 avenue Tony Garnier CS 90627 69366, LYON CEDEX 07 France - Tel: +33 (0)4 72 73 84 85
© IARC 2026 - Terms of use - Privacy Policy.
© IARC 2026 - Terms of use - Privacy Policy.