Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Filter by language: English / Русский
Go back to the list of case studies
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
| Case number: | 088 |
| Age: | 48 |
| Clinical presentation: | Premenopausal woman presented with right breast lump. She had no significant risk factors or family history of breast cancer. On examination, a firm breast lump in the lower quadrant of the right breast was found. |
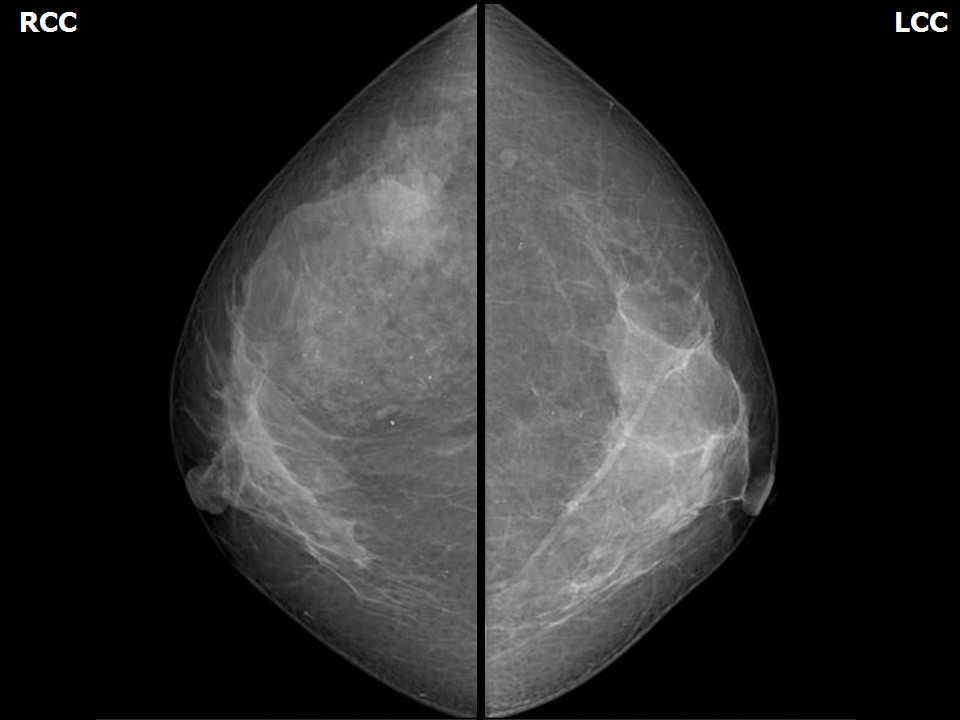
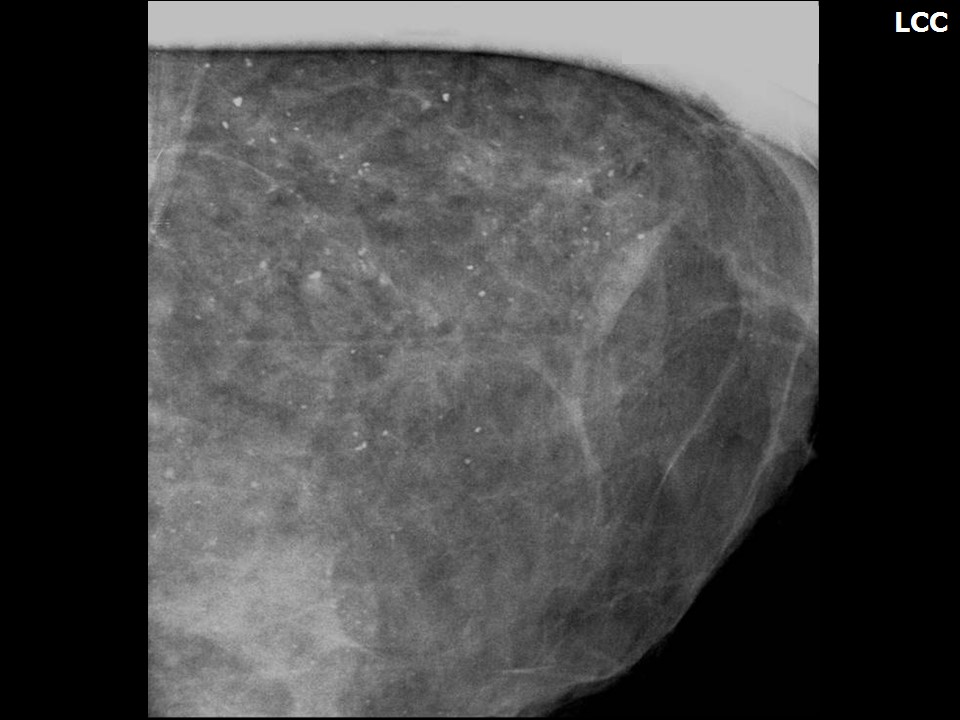
Mammography:
| Breast composition: | ACR category b (there are scattered areas of fibroglandular density) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Right breast, upper outer quadrant at 10 o’clock, middle third |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 3.5 × 1.5 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Margins: | Indistinct |
| • Density: | Equal |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | Typically benign, round and amorphous |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | Present in upper quadrant of the right breast |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | Focal |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Architectural distortion, calcifications, and enlarged right axillary node with calcification |
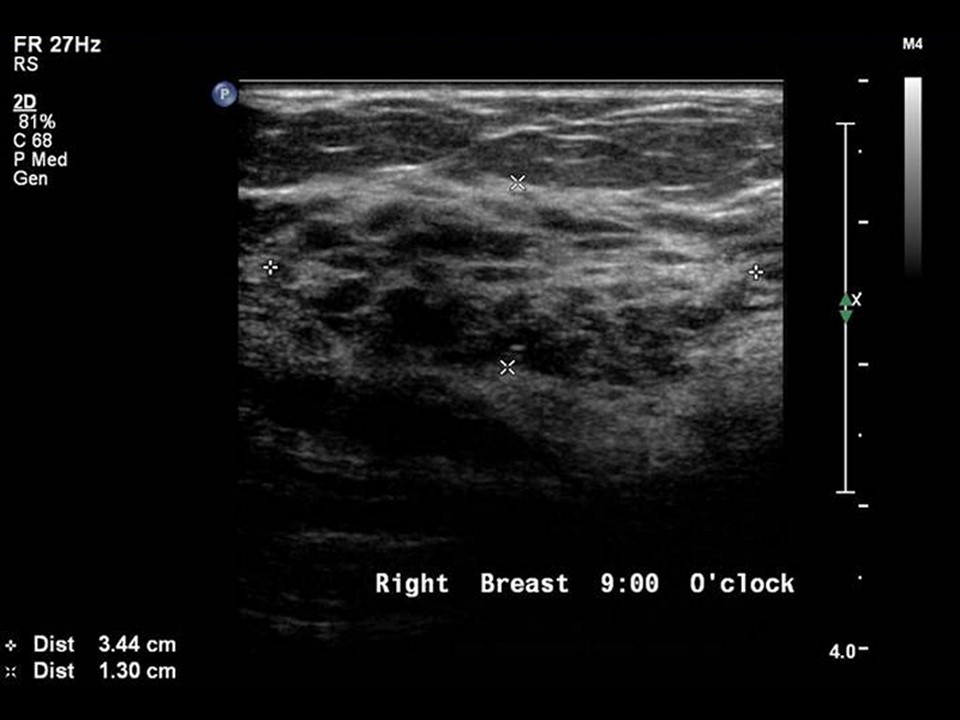
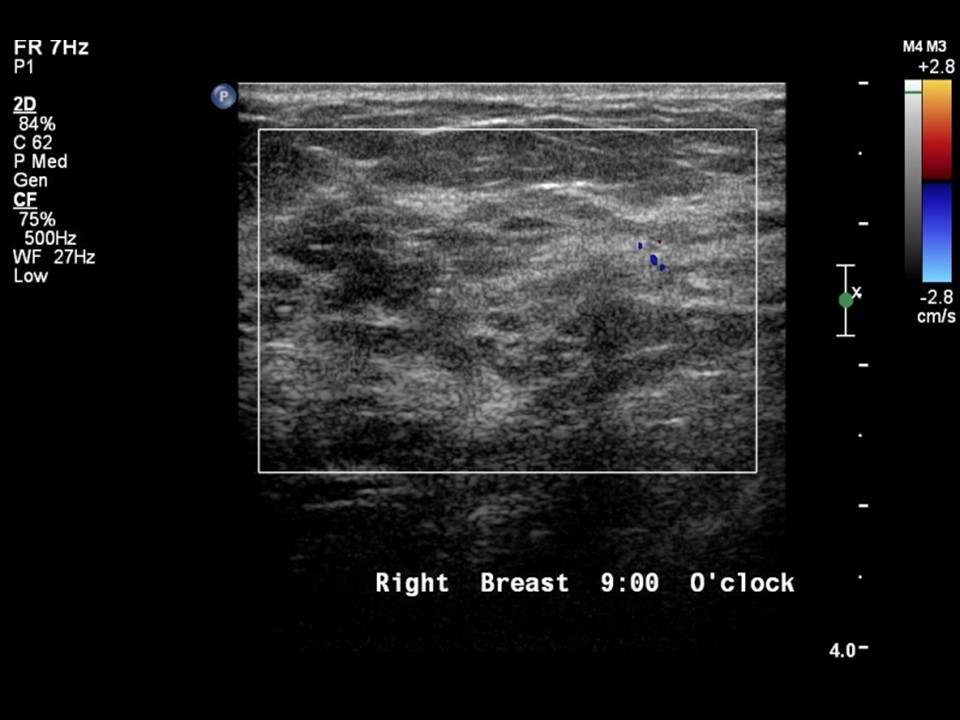
Ultrasound:
| Ultrasound features: Right breast, upper outer quadrant at 10 o’clock | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Right breast, upper outer quadrant at 10 o’clock |
| • Number: | 1 |
| • Size: | 3.4 × 1.3 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Orientation: | Parallel |
| • Margins: | Indistinct |
| • Echo pattern: | Heteroechoic with cystic areas |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Clustered microcysts |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: 4B (moderate suspicion of malignancy)Further assessment:
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytologyCytology:
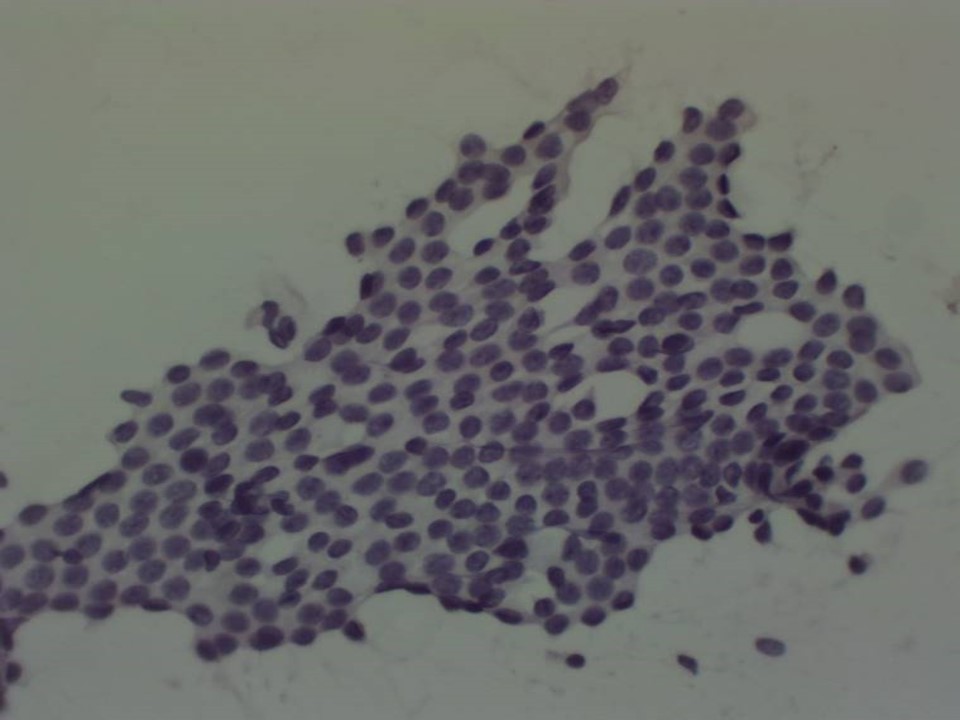
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC (solid lesion) |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Right |
| • Quadrant: | Upper outer |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | 0.5 mL of clear fluid |
| ‣ Cytological description: | Smears show flat cohesive sheets of benign ductal epithelial cells. Background shows proteinaceous fluid, foamy histiocytes, and occasional apocrine cells |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Benign |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Proliferative fibrocystic change |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
Histopathology:
breast Lumpectomy
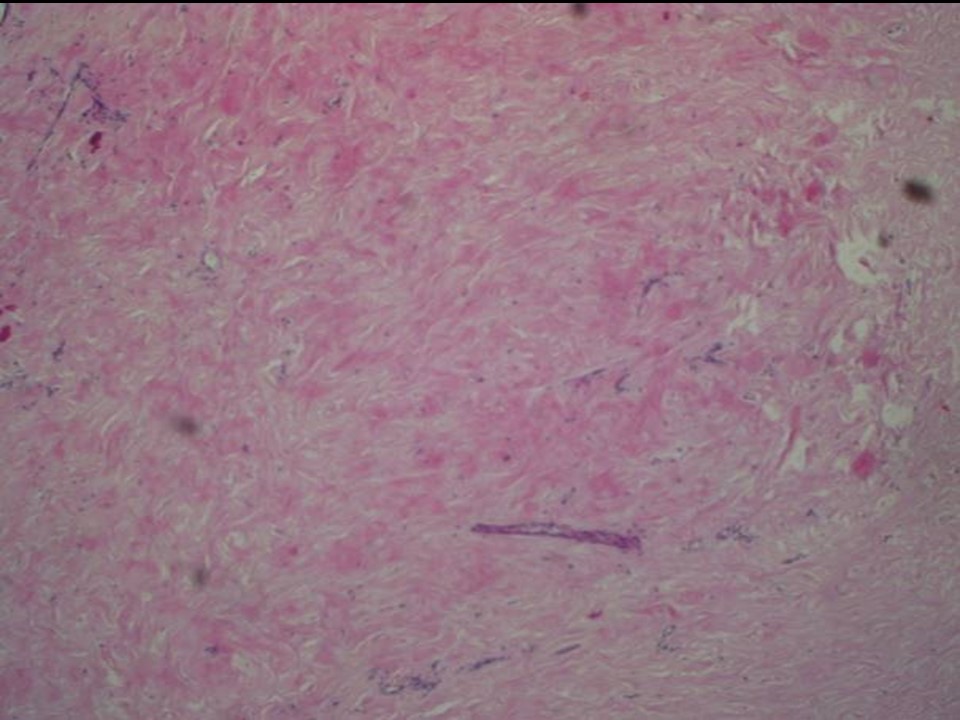
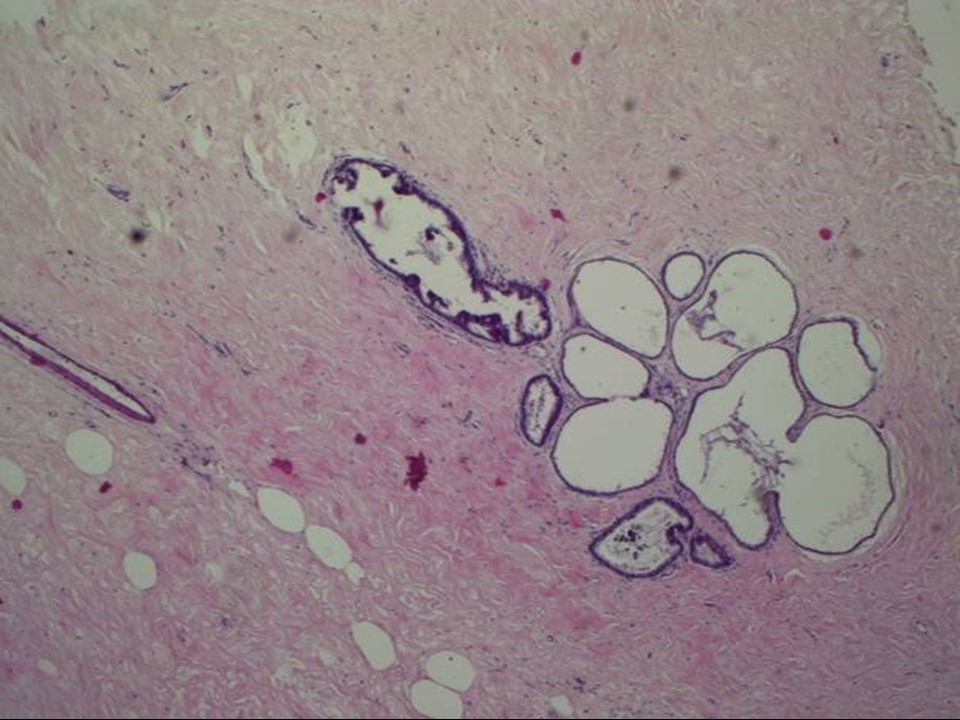
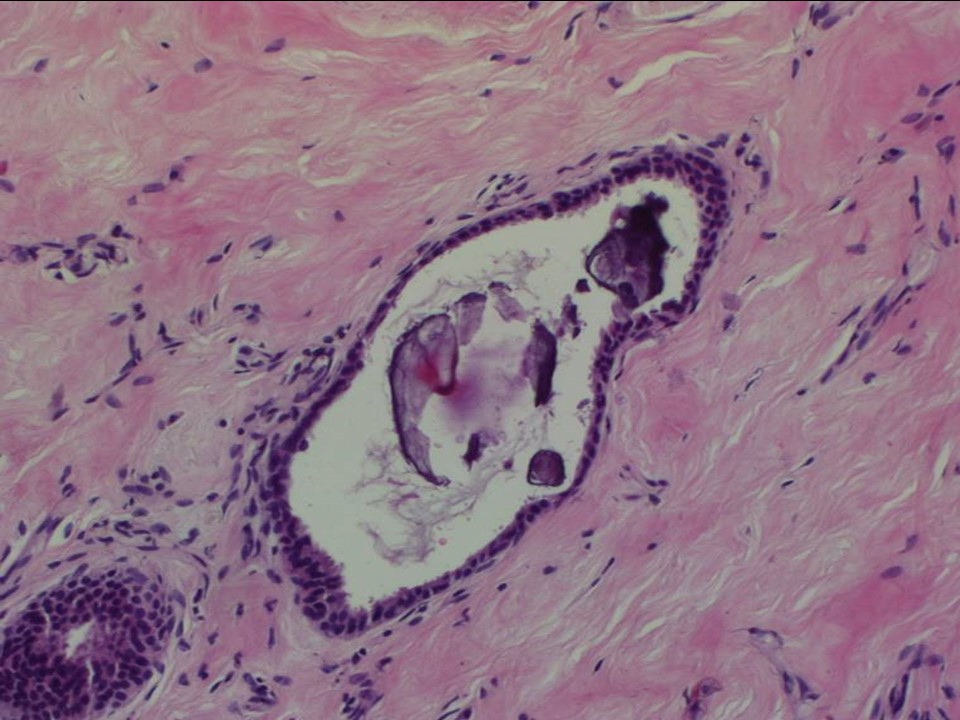
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | breast Lumpectomy |
| ‣ Laterality: | Right |
| ‣ Macroscopy: | Serial sectioning shows irregular whitish firm areas with no well-defined nodules |
| ‣ Histological type: | Sections from the whitish areas of the lumpectomy specimen show marked stromal fibrosis with hyalinization. Multiple microscopic cysts are seen in the breast parenchyma. The epithelial lining of most of these cysts are flattened. Occasionally, apocrine metaplasia is seen but there is no significant epithelial hyperplasia. There is no chronic inflammation surrounding these cysts. A few foci of calcification are seen within the ducts but no features of ADH, DCIS, or malignancy was seen in multiple sections studied |
| ‣ Histological grade: | |
| ‣ Mitosis: | |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | Not identified |
| ‣ Margins: | |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | |
| ‣ Comments: | Impression – fibrocystic change. Negative for intraductal proliferative lesions, DCIS, and malignancy. |
Case summary:
| Premenopausal woman presented with right breast lump. Diagnosed as low-density mass with fat-containing areas and amorphous calcifications within, BI-RADS 4B on imaging and as fibrocystic change on cytology and histopathology. |
Learning points:
|