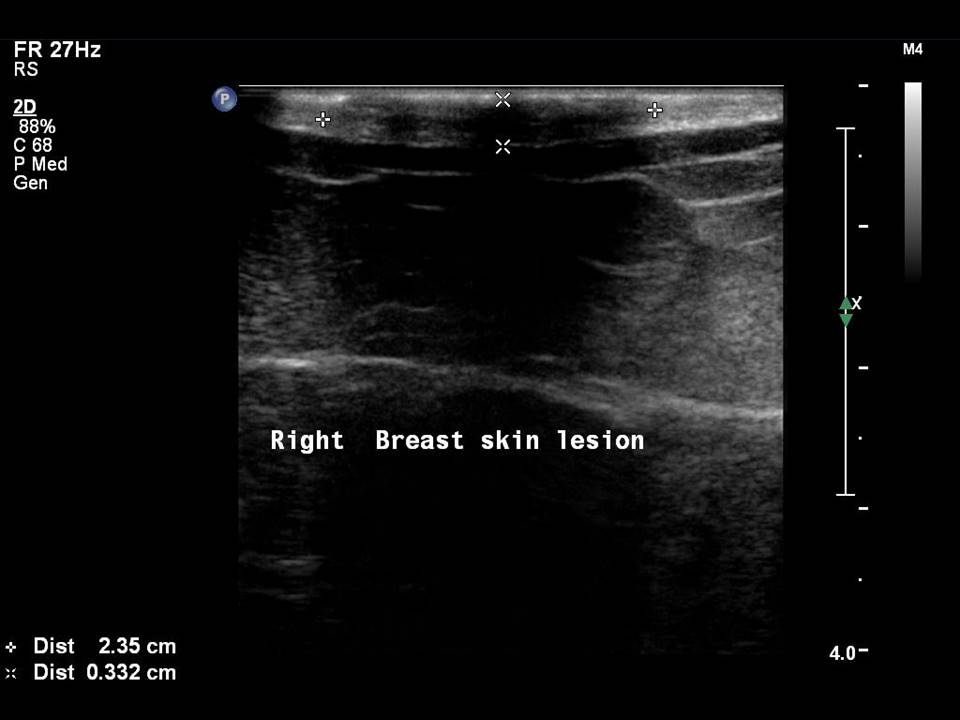
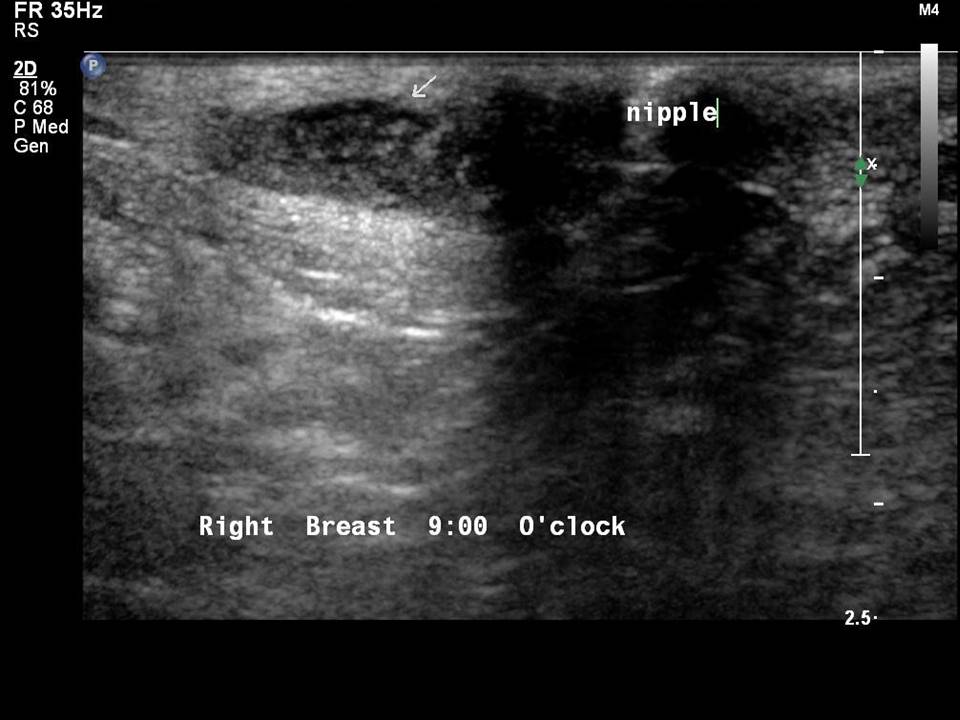
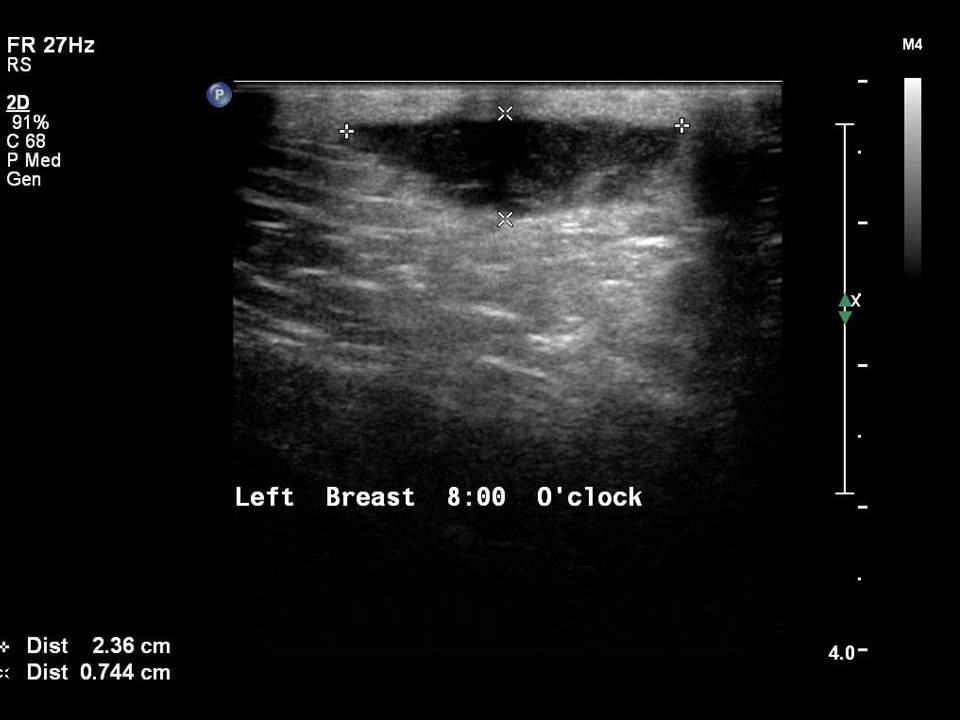
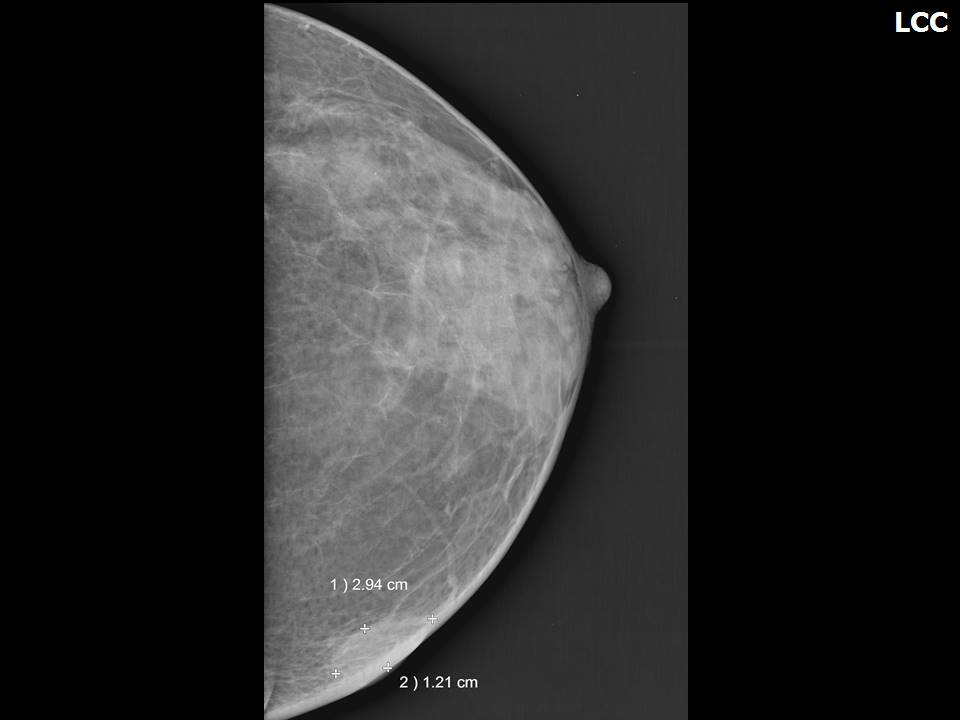
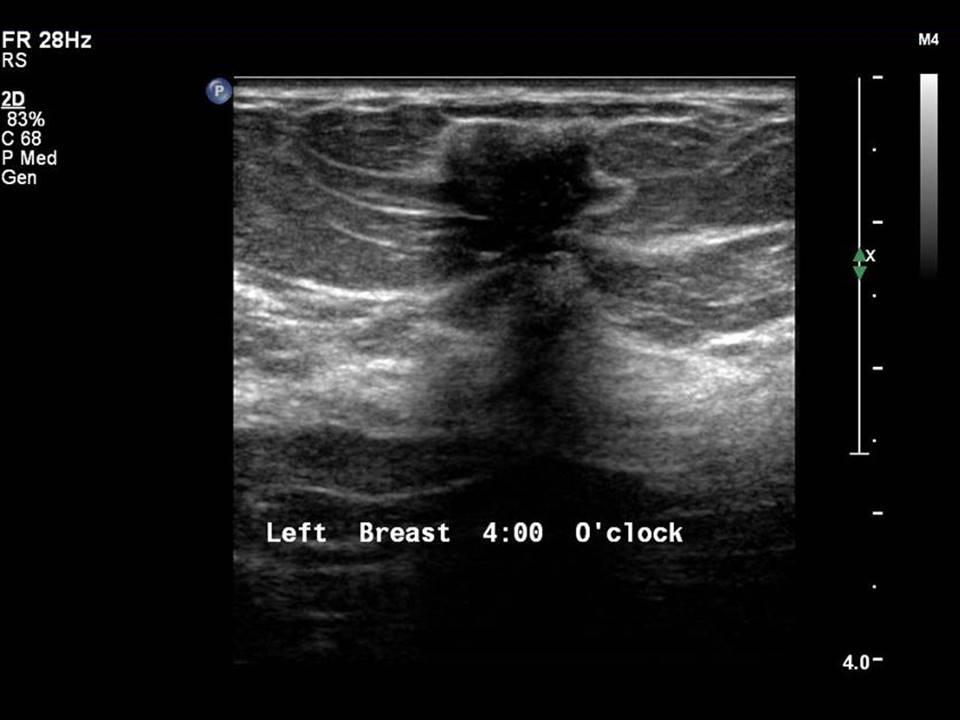
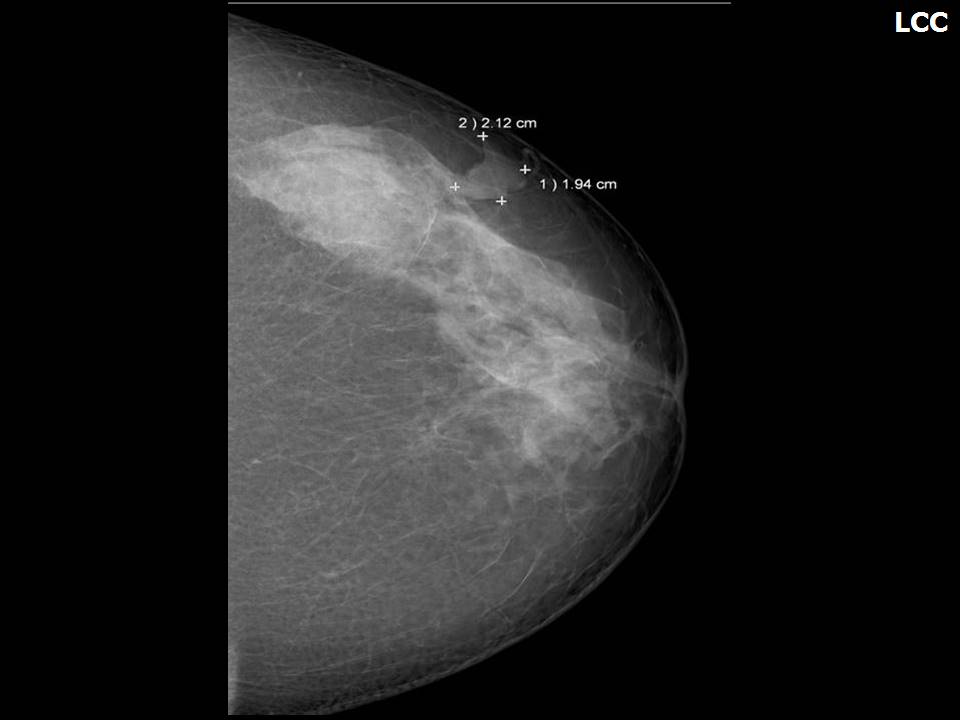
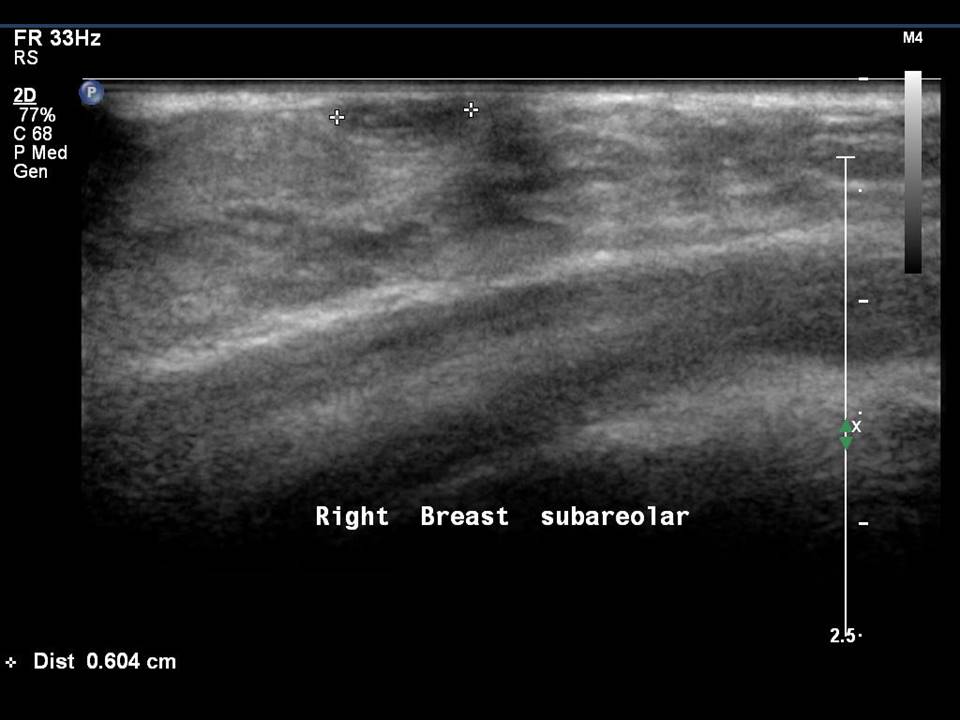
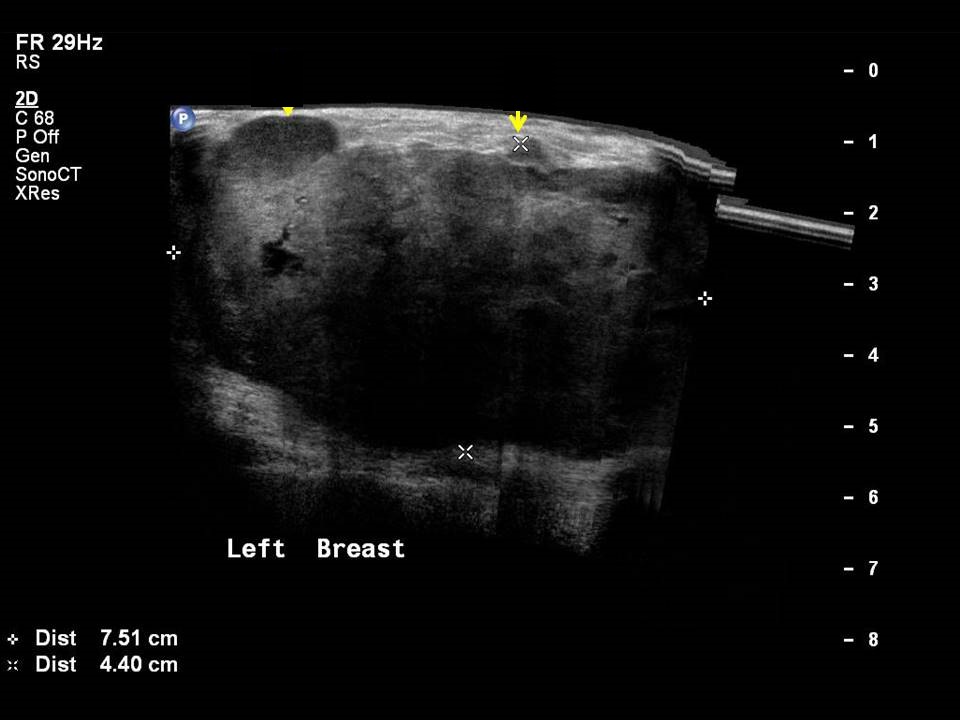
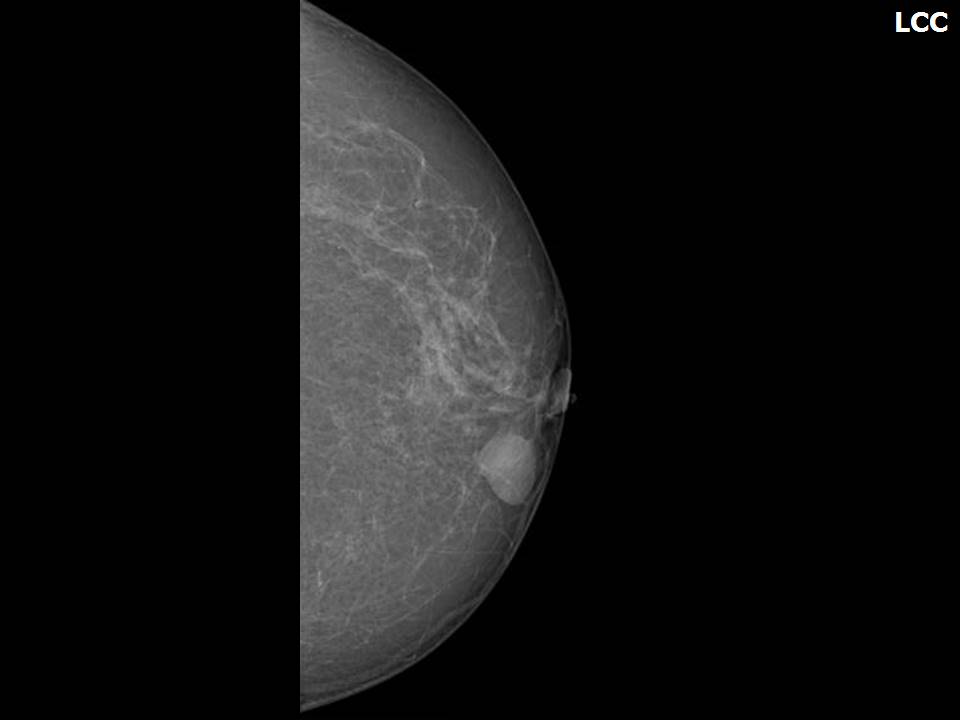
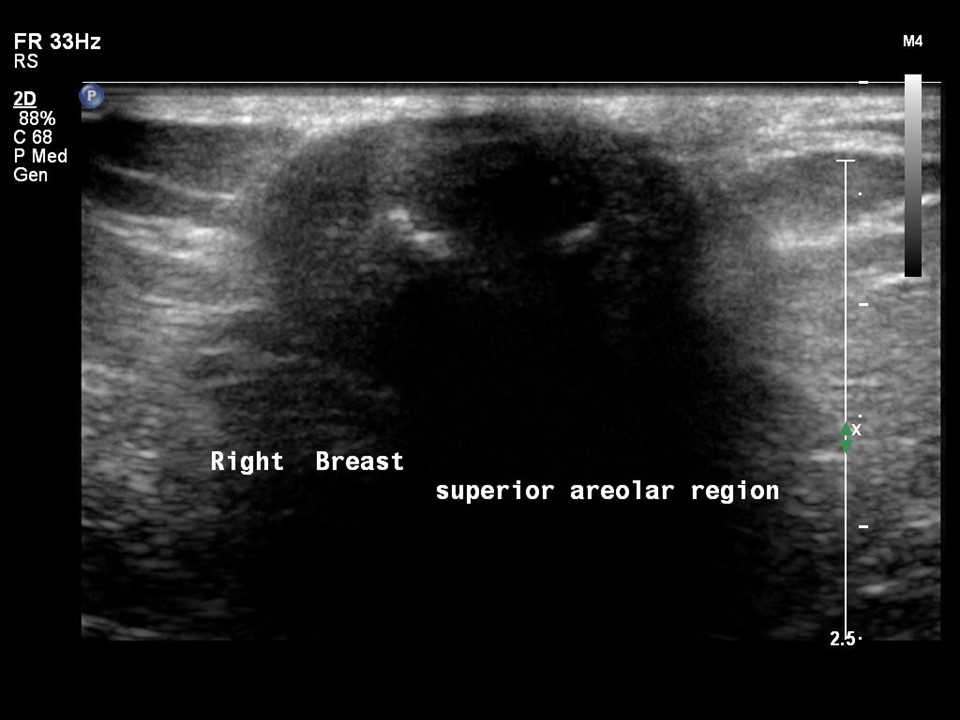
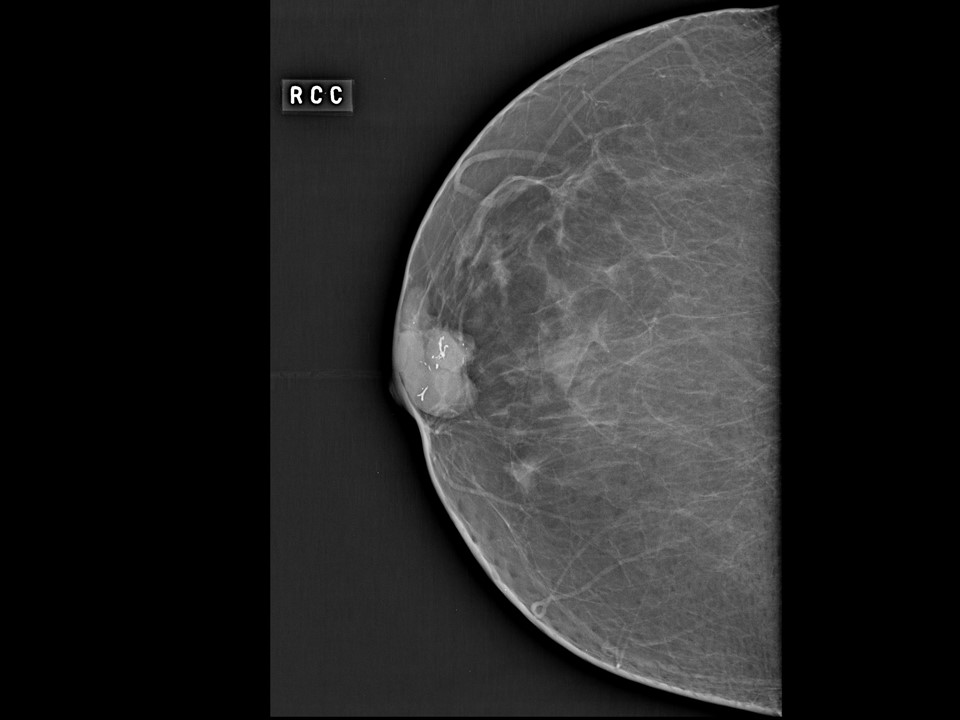
Mass in or on skin is also a special case in the ultrasound lexicon. Breast ultrasound is more accurate than mammography in localizing a lesion in the superficial tissues.
A superficial lesion may originate in:
- dermis,
- hypodermis (subcutaneous fat), or
- superficial mammary tissue (anterior TDLU).
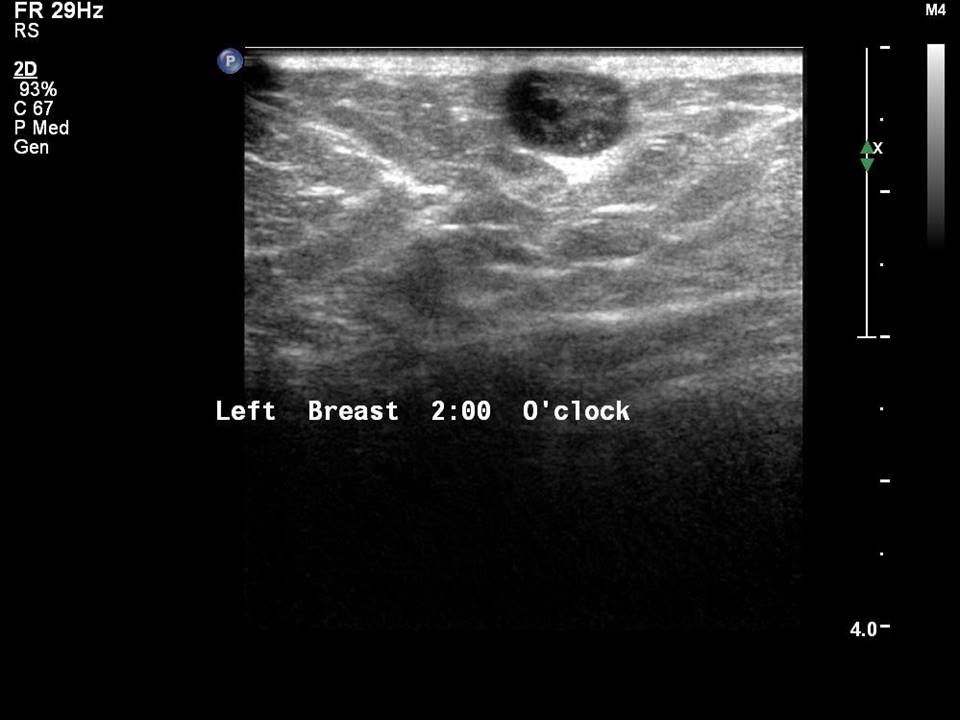
Skin lesions in the dermis
A dermal lesion has either some or all of the following diagnostic features on ultrasound:
- The lesion is contained entirely within the dermis.
- A tract is seen extending from the lesion to the skin.
- A claw of tissue surrounding the margin of the lesion is present in the dermis.
Differential diagnosis of lesions in the dermis includes sebaceous cysts, epidermal inclusion cysts (epidermoid cysts), and dermal calcifications.
Epidermoid cysts
Epidermoid cysts and sebaceous cysts are benign lesions. On ultrasound, they show similar morphology, but epidermoid cysts contain dead cells and sebaceous cysts have oily contents.
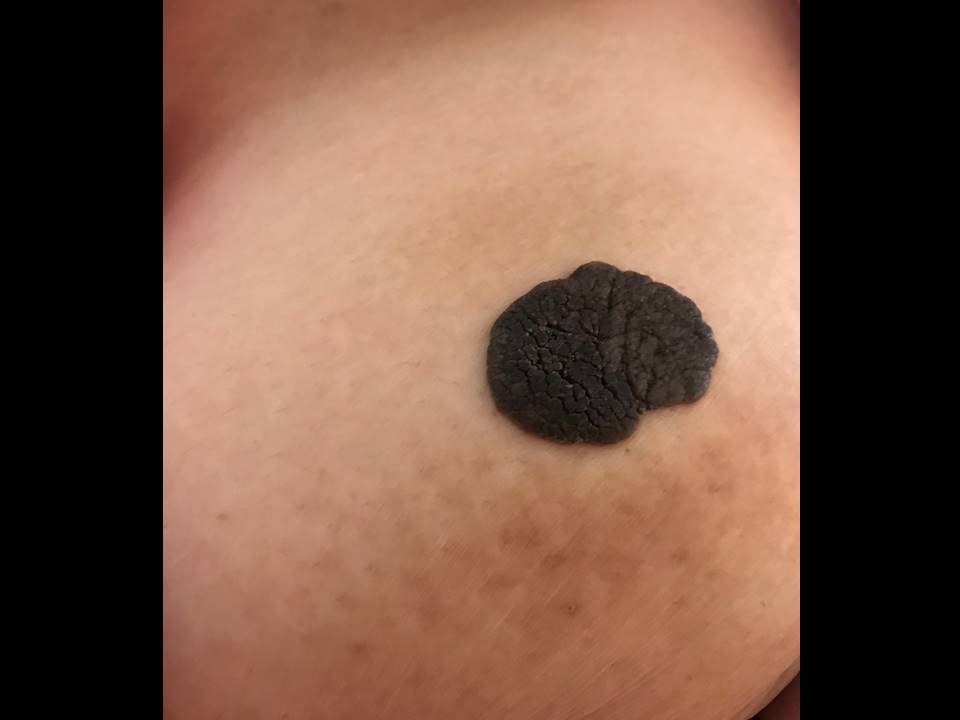
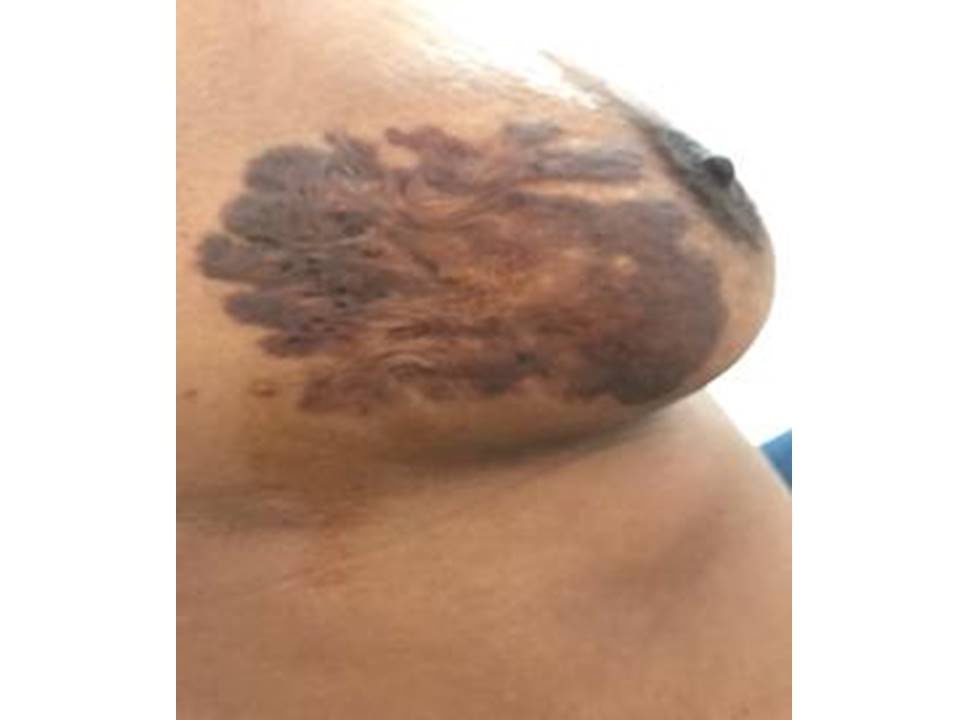
Other examples of dermal lesions of the breast with a “pasted-on-skin” appearance are seborrhoeic keratosis, naevus, warts, and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans.
Seborrhoeic keratosis
Seborrhoeic keratosis is a benign lesion. It should be distinguished from melanoma.
Naevus
A naevus is a pigmented chronic dermal lesion, commonly a birth identification mark, also known as a mole.
Warts
Warts are caused by infection of the skin by human papillomavirus (HPV).
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is a low-grade dermal malignant lesion with a high rate of local recurrence.
Skin lesions in the hypodermis
Skin lesions in the hypodermis include subcutaneous fat lesions and lesions in the anterior TDLU. Differential diagnoses include fat-containing lesions, haemangiomas, and lesions of neurogenic origin.
Fat-containing lesions
Lipomas, angiolipomas, and fat necrosis are all examples of fat-containing lesions.
Vascular malformations: Haemangiomas and thrombosed vessels
Lesions of neurogenic origin
Anterior TDLU
Anterior TDLU lesions in the subcutaneous tissues include papilloma, adenosis, fibroadenoma, and breast cancer.
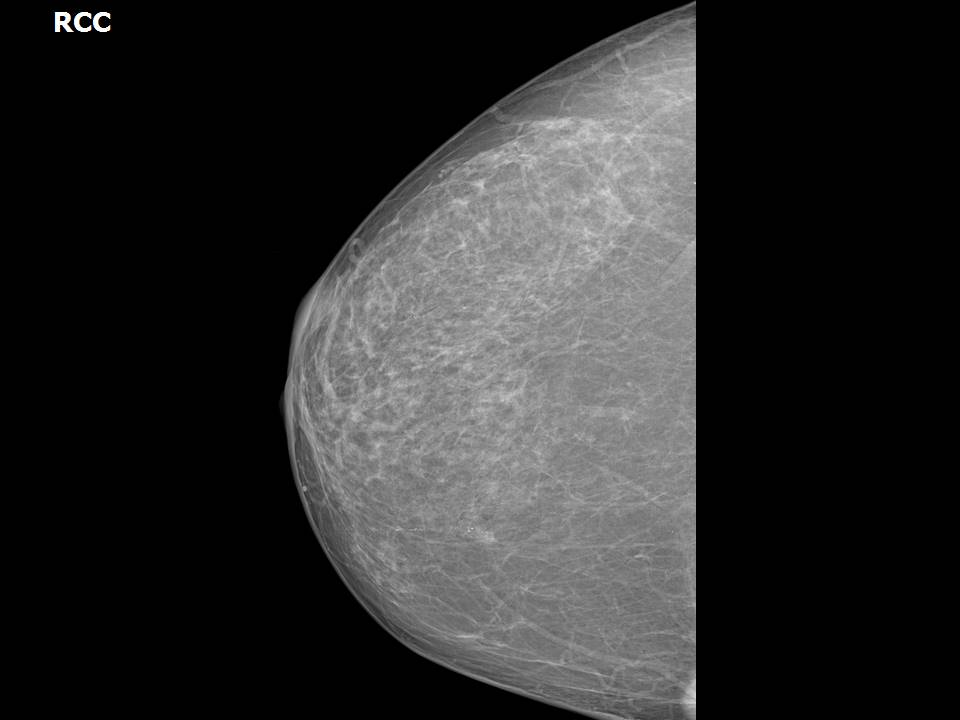
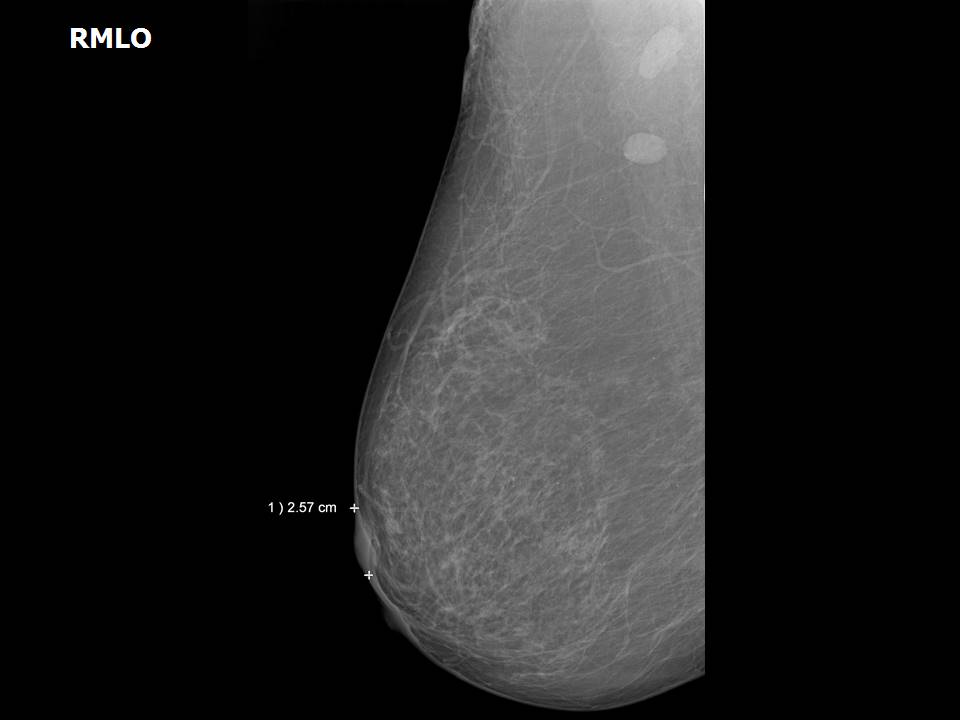
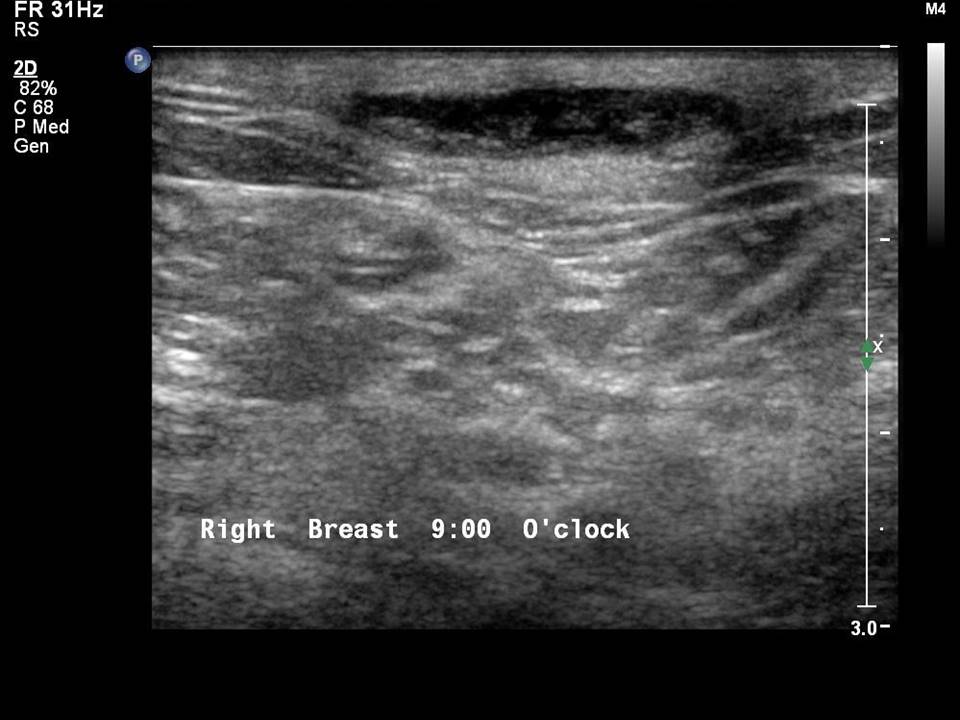
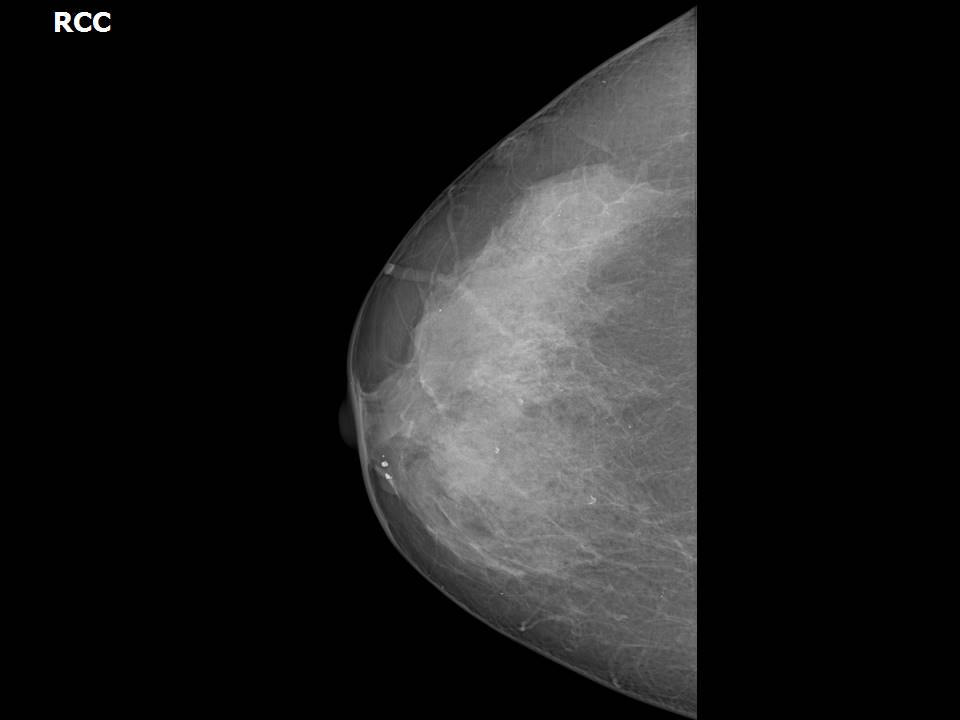
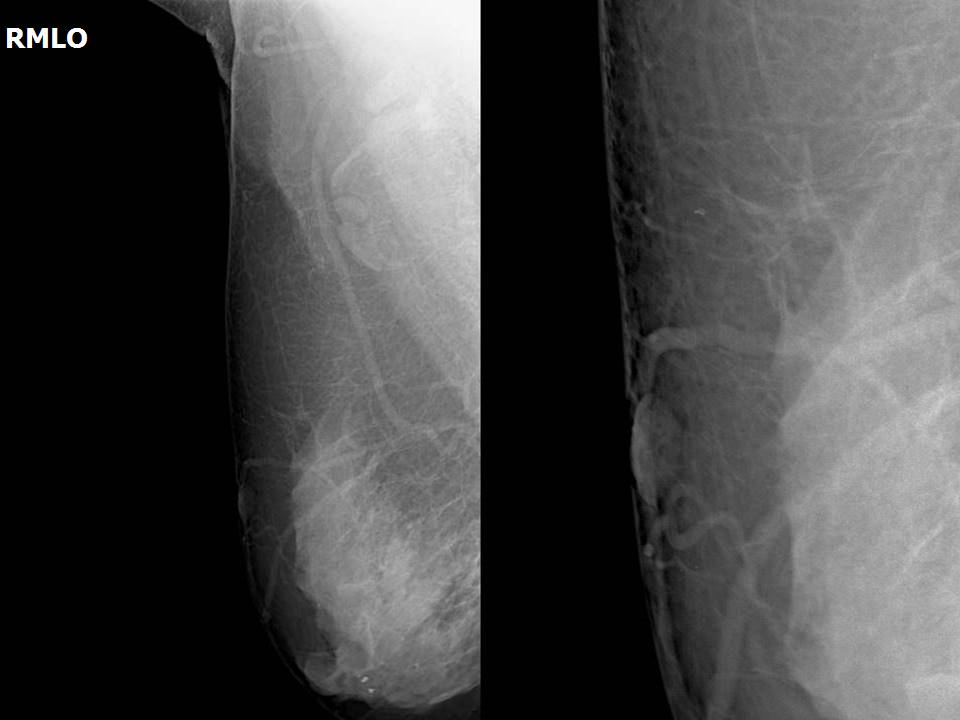
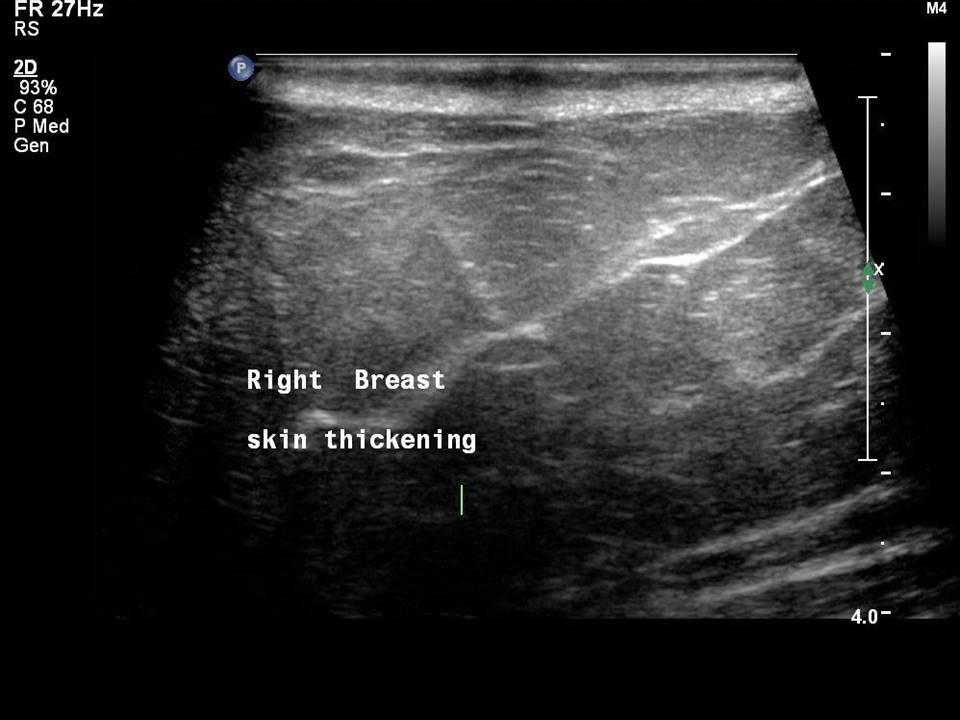
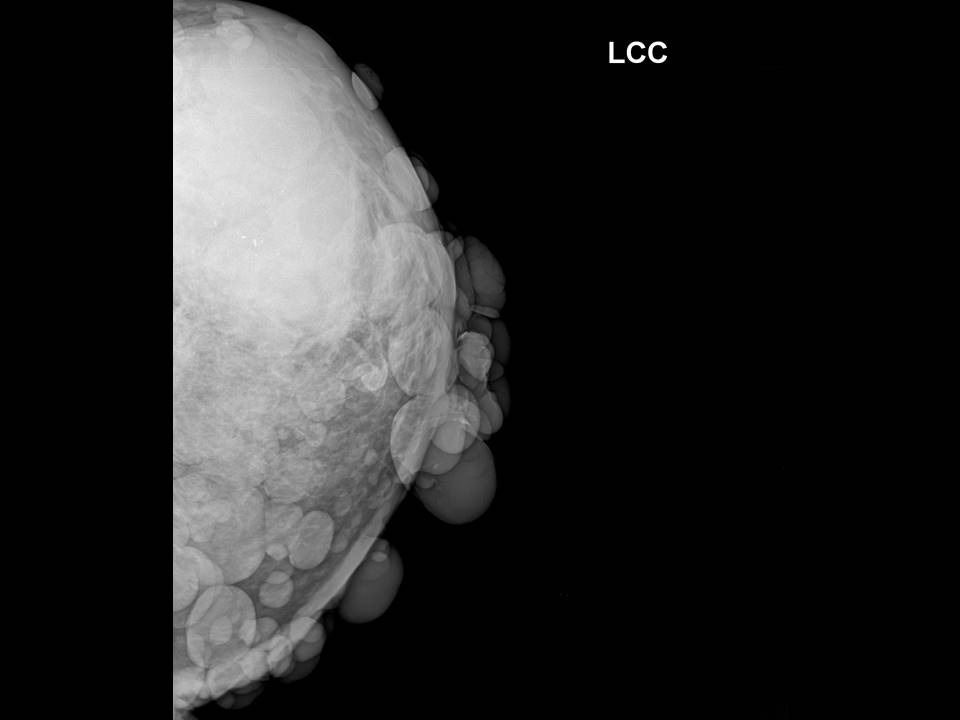
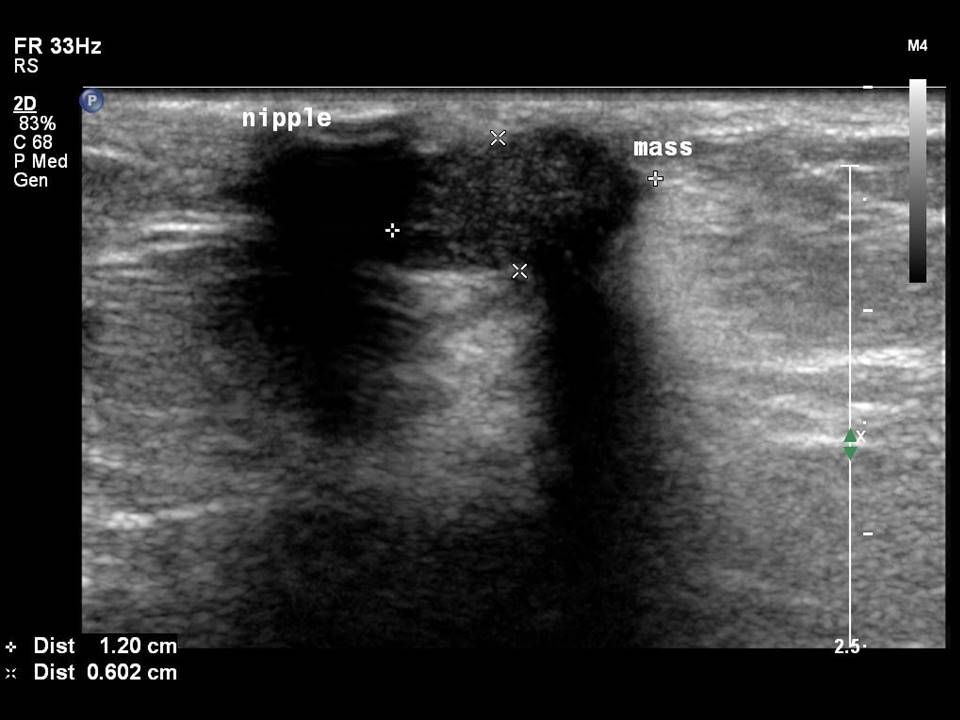
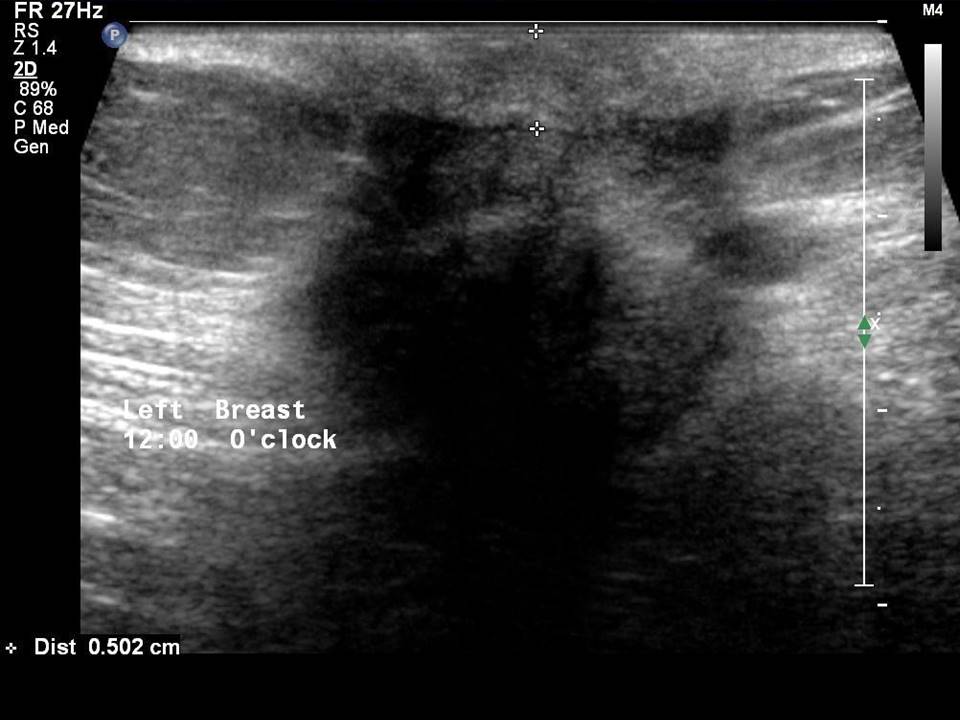
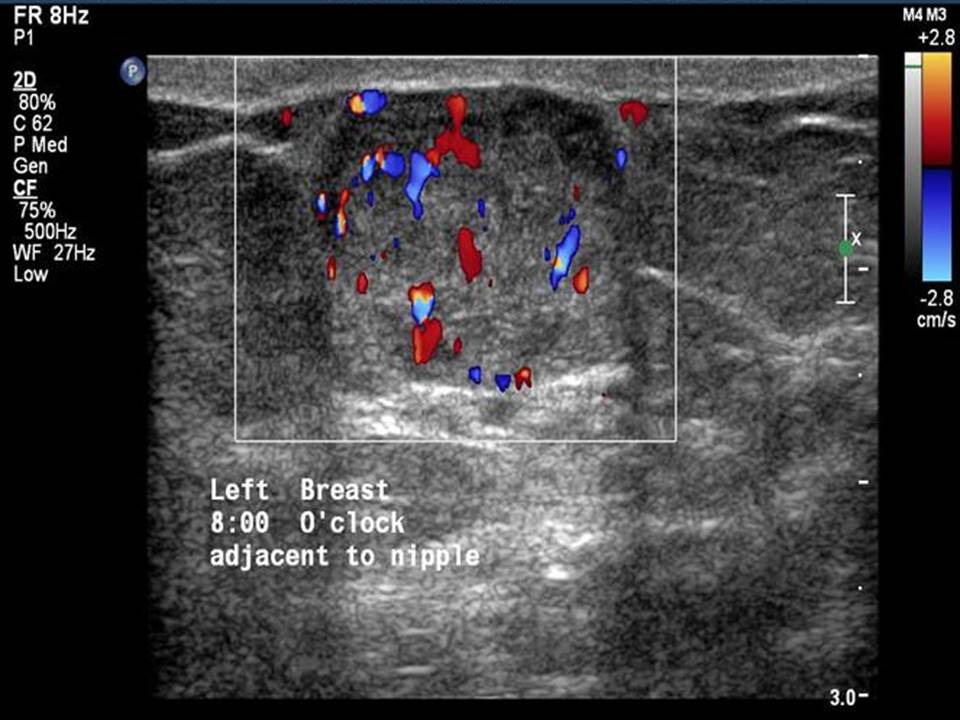
Breast cancer seen in the hypodermis with skin thickening and infiltrations
Papilloma (peripheral)
Fibroadenoma
Accurate anatomical localization and categorization of the superficial mass by lexicon terminology is important to differentiate the probable superficial cancers and benign lesions. Lexicon features including shape, margins, echotexture, associated features. Biopsy may be warranted to complete the triple assessment of the mass.
| .png)