Chapters
Introduction
Visual inspection after application of acetic acid (VIA)
Determining eligibility for ablative treatment after application of acetic acid
Anatomical considerations
Cervical epithelium
Physiological changes of cervical epithelium
Neoplastic changes of the cervical epithelium
Changes in the cervical epithelium after application of acetic acid
Instruments, consumables, and setup required for examination after application of acetic acid
VIA procedure
Interpretation of VIA test results
Preventing errors in VIA
Management of women with an abnormal VIA test
Steps to determine eligibility for ablative treatment
Role of Lugolís iodine in identifying the transformation zone for treatment
Treatment by cryotherapy
Treatment by thermal ablation
Videos
Preparation of Monselís solution
Infection prevention
Case study
Quiz
Acknowledgement
Suggested citation
Copyright
Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of visual inspection of the cervix with acetic acid for screening, triage, and assessment for treatment / Cases
Atlas of visual inspection of the cervix with acetic acid for screening, triage, and assessment for treatment
Filter by language: English / FranÁais / EspaŮol / Русский / українська
VIA-negative cases  Click to return to the atlas
Click to return to the atlas
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
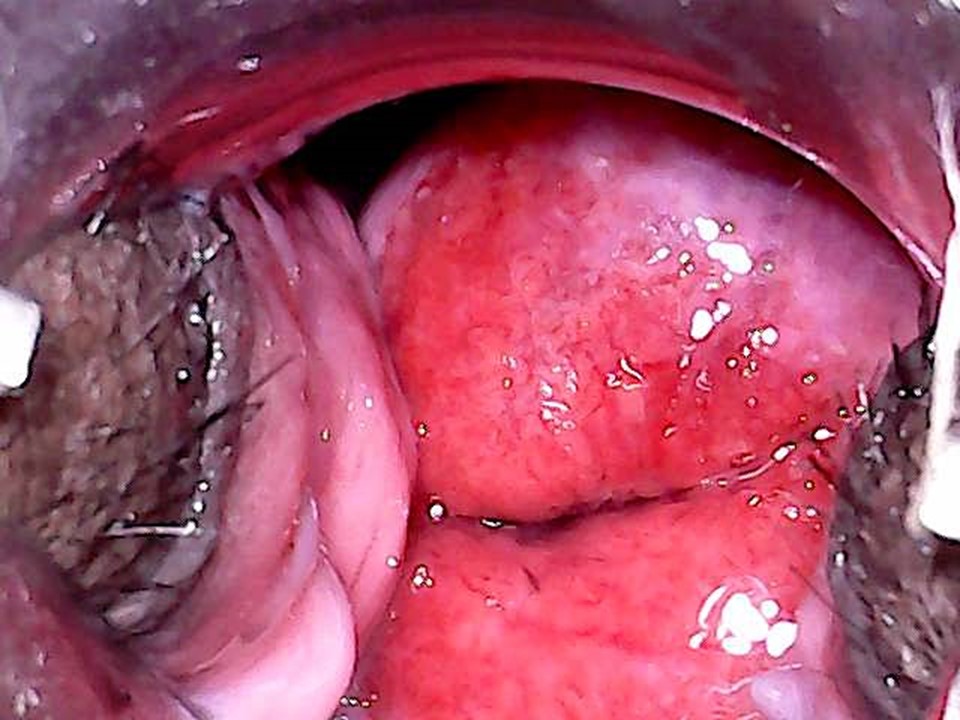
Before application of acetic acid: Red columnar epithelium covers most of the ectocervix. Pink squamous epithelium is seen at the periphery. Note the light reflections on the cervix.
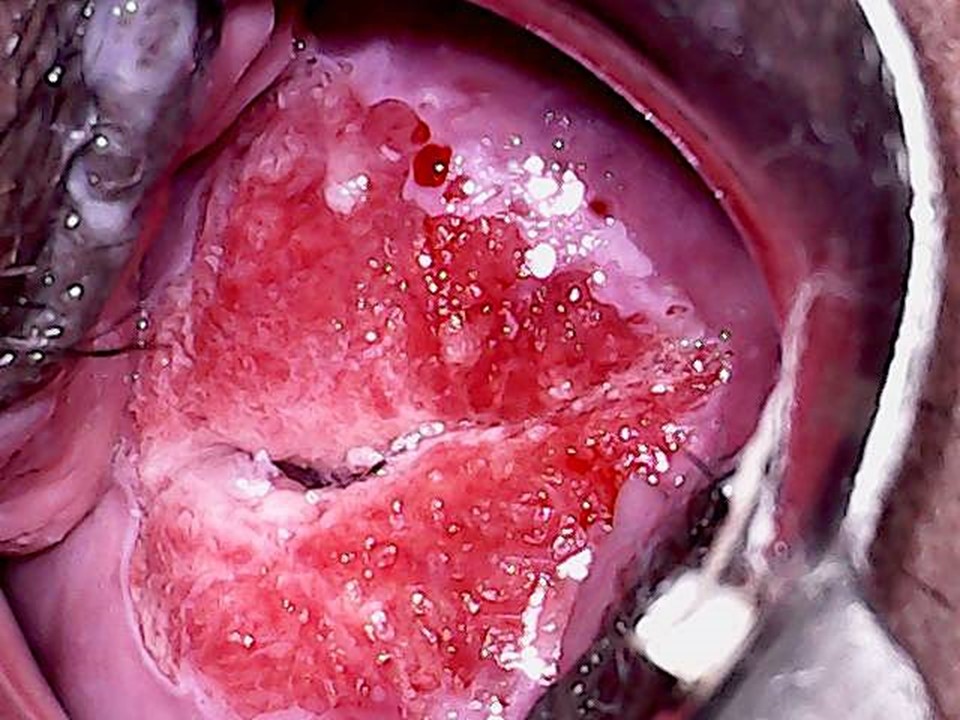
After application of acetic acid: Diffuse acetowhite areas of squamous metaplasia are seen at the 1 oíclock position. Note that the light reflections are still there but have shifted to other locations.
|