Learning colposcopy
Colposcopic appearance of normal cervix
The colposcopic examination
Detection of infections & benign conditions of cervix
Detection of cervical neoplasias
Treatment of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
Treatment by cryotherapy
Treatment by thermal ablation
Treatment by LLETZ (LEEP)
Treatment by cold-knife conization (CKC)
Cases
Normal
Squamous metaplasia and ectropion
Inflammation and cervicitis
Low grade
High grade
Early and advanced cancers
Miscellaneous
Post treatment
Search with IFCPC criteria
Search with Swede score criteria
Quiz Foreword
Acknowledgement
Authors
Suggested citation
Home
Atlas of Colposcopy: Principles and Practice
Filter by language: English / 中文 / Français / Español / Português / Русский
High grade / CIN2 / CIN3
Go back to the list
Colposcopy report (2011 IFCPC nomenclature):
Swede score:
Final Swede score: 7
Case Summary
Go back to the list
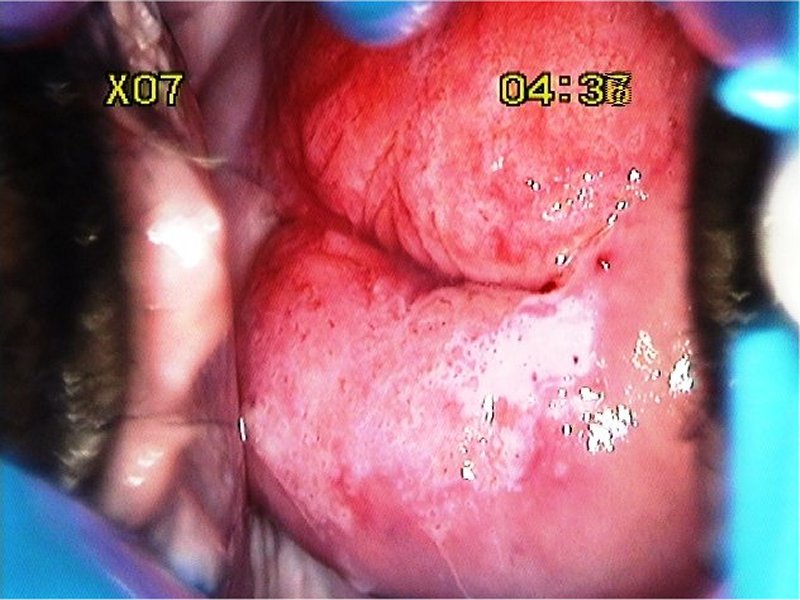
| After acetic acid |
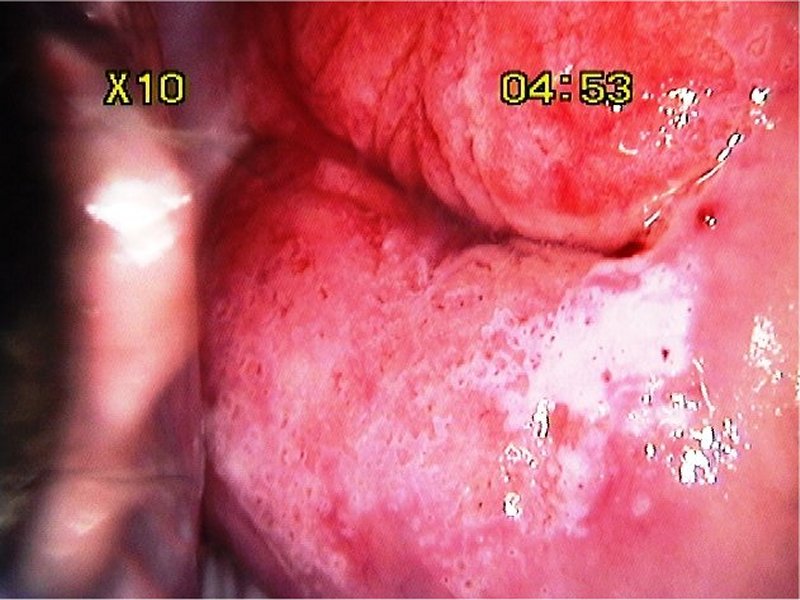
| After acetic acid |
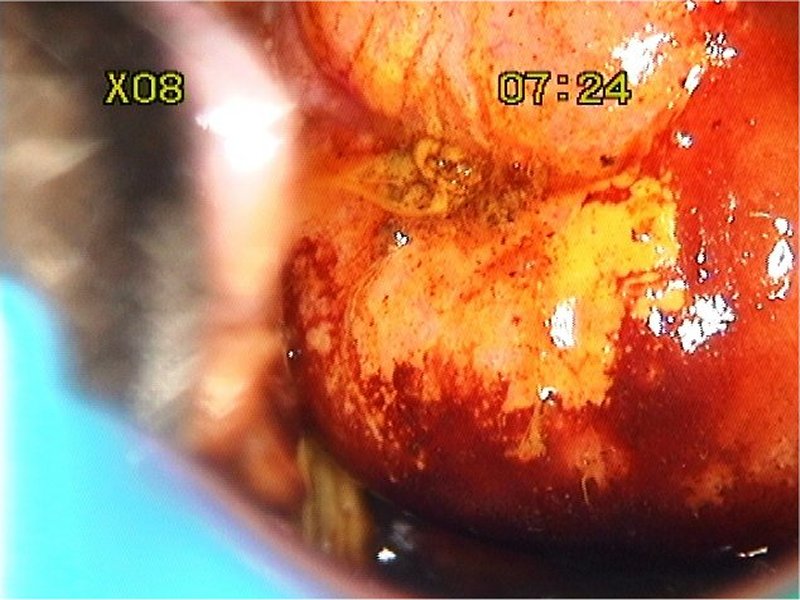
| After acetic acid with green filter |
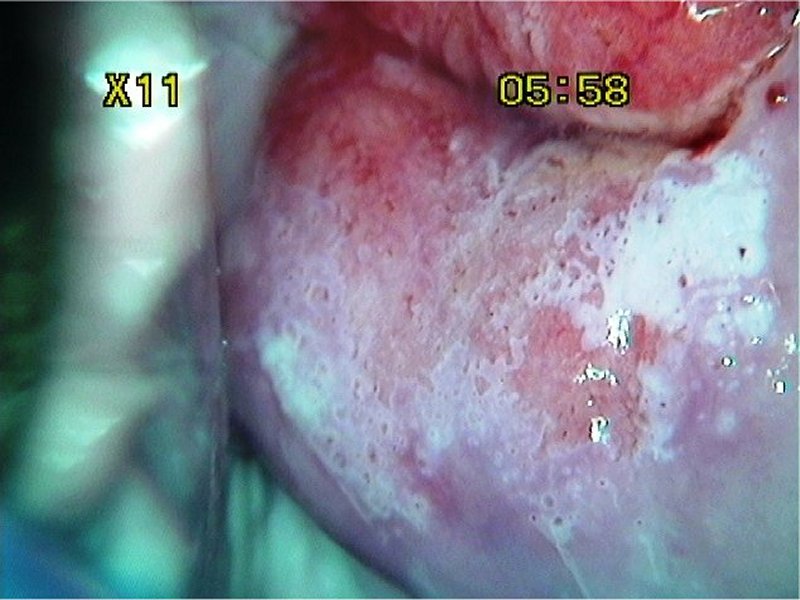
| After Lugol’s iodine |
 General assessment General assessment | |||||||||||||||||
 Normal colposcopic findings Normal colposcopic findings | |||||||||||||||||
 Abnormal colposcopic findings Abnormal colposcopic findings | |||||||||||||||||
 General principles General principles | |||||||||||||||||
 Position and size Position and size | |||||||||||||||||
 Grade 1 (minor) Grade 1 (minor)
|  Grade 2 (major) Grade 2 (major)
|  Non-specific Non-specific
|  Suspicious for invasion Suspicious for invasion
|  Miscellaneous finding Miscellaneous finding
| |
Swede score:
| Nil or transparent | Thin, milky | Distinct, stearin | |
| Nil or diffuse | Sharp but irregular, jagged, satellites | Sharp and even, difference in level | |
| Fine, regular | Absent | Coarse or atypical vessels | |
| < 5 mm | 5-15 mm or 2 quadrants | >15 mm, 3-4 quadrants, or endocervically undefined | |
| Brown | Faintly or patchy yellow | Distinctly yellow |
Final Swede score: 7
Case Summary
| Provisional diagnosis: | Type 1 transformation zone; high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL). |
| Management: | Cryotherapy or thermal ablation after taking punch biopsy from the lesion. |
| Histopathology: | HSIL-CIN2. |
| Comment: | The thin acetowhite area in the posterior lip with multiple crypt openings is due to immature metaplasia. The high grade lesion is limited to only one quadrant. |