Image | Caption |
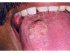 | Figure 1: Lymphangioma of the tongue. Note the exophytic, sessile growth on the right side of the dorsum of tongue in this 24–year-old patient. The diagnosis of lymphangioma was confirmed on excision biopsy. |
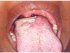 | Figure 2: Lymphangioma dorsum of the tongue. A raised irregular lesion on the posterior aspect of the tongue in this 13–year-old boy. Histopathological examination showed lymphangioma. |
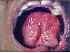 | Figure 3: Lymphangioma of the tongue. Note the prominent pebbly appearance with a central groove involving the ventral surface of the tongue. |
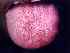 | Figure 4: Lymphangioma of the tongue. Note the macroglossia with crenation on left periphery and dorsum of the tongue showing pebbly appearance in the centre and multiple hypertrophied fungiform papillae. |
 | Figure 5: Lymphangioma of the tongue. |