Image | Caption |
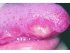 | Figure 1: Granular cell tumour. The typical presentation of granular cell tumour: a sessile swelling on the tongue covered by normal appearing epithelium. |
25 avenue Tony Garnier CS 90627 69366, LYON CEDEX 07 France - Tel: +33 (0)4 72 73 84 85
© IARC 2026 - Terms of use - Privacy Policy.
© IARC 2026 - Terms of use - Privacy Policy.




