Image | Statistics | Caption |
 |  | Adenocarcinoma in situ: sharp transition between normal (+) and neoplastic endocervical epithelium (arrow). |
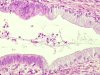 |  | Adenocarcinoma in situ (left) coexisting with normal endocervical epithelium (right). |
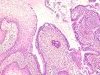 |  | Adenocarcinoma in situ: substitution of normal endocervical epithelium by neoplastic epithelium at the TZ. |
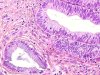 |  | Adenocarcinoma in situ: contrast between a normal gland (left) and a neoplastic gland (right). |
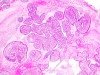 |  | Papillary adenocarcinoma in situ. |
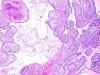 |  | Papillary adenocarcinoma in situ. |
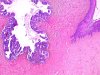 |  | Adenocarcinoma in situ developed in adenosis. |
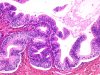 |  | Adenocarcinoma in situ developed in adenosis. |
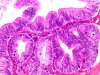 |  | Adenocarcinoma in situ developed in adenosis with a gland in gland formation. |
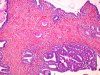 |  | Adenocarcinoma in situ developed in adenosis. |
 |  | Coexisting adenocarcinoma in situ (arrow) and CIN 3 (star). |
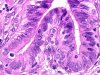 |  | Adenocarcinoma in situ: marked cellular abnormalities with typical and atypical mitoses. |
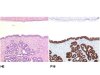 |  | HE staining: In situ adenocarcinoma of the endocervix (bottom). Normal endocervical mucosa (top). Immunolabelling anti-p16: heavy staining of the glandular neoplastic epithelium (nuclei and cytoplasm - bottom). The normal epithelium is not labelled (top). |
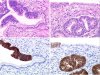 |  | In situ adenocarcinoma of the endocervix : A1 & A2: strong positivity of the glandular neoplastic epithelium. The normal endocervical epithelium is not labelled. There is a sharp transition between the normal and neoplastic epithelium. B1 & B2 : Same lesion with superficial glandular dysplasia with low p16 immuno-reactivity (arrows). |