Home / Training / Manuals / Histopathology of the uterine cervix - digital atlas / Glossary Definitions
Histopathology of the uterine cervix - digital atlas
Glossary Definitions
Filter by language: English / Franšais / Portugues / 中文|
|
 |
|
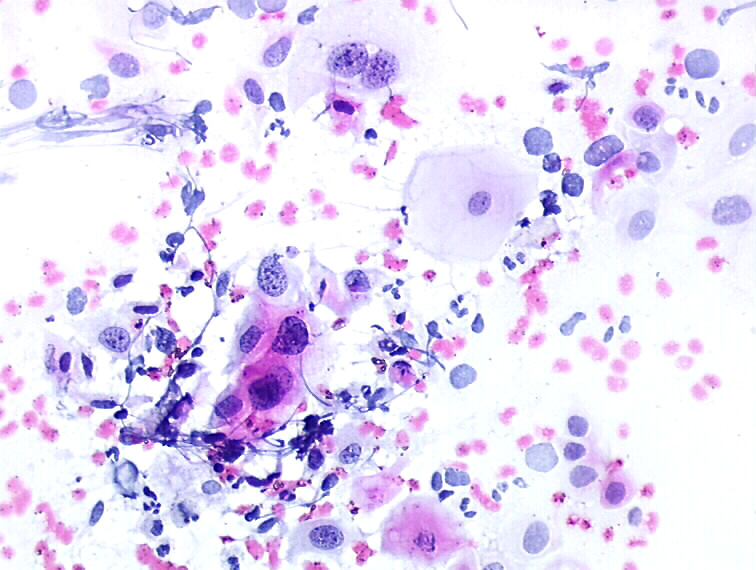
Anisokaryosis This is one of the main features of cancer cells: variation of nuclear size and shape from cell to cell. Referred to as nuclear pleomorphism and anisonucleosis. Cytopathology atlas |
25 avenue Tony Garnier CS 90627 69366, LYON CEDEX 07 France - Tel: +33 (0)4 72 73 84 85
© IARC 2026 - Terms of use - Privacy Policy.
© IARC 2026 - Terms of use - Privacy Policy.



