Image | Statistics | Caption |
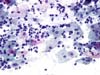 |  | Inflammatory smear with intermediate squamous cells having enlarged nuclei: the cause of this change is inflammatory and is not typical of ASC-US. The term ASC-US should be avoided in an inflammatory context with small halos. (obj. 20x) |
 |  | Inflammatory smear with intermediate squamous cells having enlarged nuclei: the cause of this change is inflammatory and is not typical of ASC-US. The term ASC-US should be avoided in an inflammatory context with small halos. (obj. 20x) |
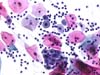 |  | Inflammatory exocervical smear: metaplastic cells with slightly enlarged nuclei. This change, of inflammatory origin, is not typical of ASC-US. (obj. 20x) |
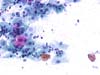 |  | Inflammatory smear with intermediate squamous cells having enlarged nuclei: this change is not typical of ASC-US. The term ASC-US should be avoided in an inflammatory context with small halos. (obj. 20x) |
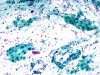 |  | Atrophic menopausal smear: moderately enlarged nuclei: this change, of inflammatory origin, is not typical of ASC-US. Possibility of ASC-US in A because of hyperchromatic and irregular nuclei. (same slide A, B, C and D: obj. 20x) |
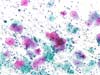 |  | Inflammatory smear with intermediate and superficial squamous cells having enlarged nuclei: look for Trichomonas or Gardnerella. The term ASC-US should be avoided in an inflammatory context with small halos. (obj. 10x) |
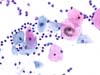 |  | Moderate inflammatory smear: an intermediate squamous cell with enlarged nuclei with normal chromatin (ellipse): metaplastic cell. (obj. 20x) |
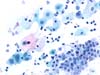 |  | Metaplastic cells with enlarged nuclei and clear chromatin. This change, of inflammatory origin, is not typical of ASC-US. (obj. 20x) |
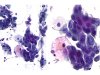 |  | Sheet of metaplastic cells with enlarged and clear nuclei. This change is not typical of ASC-US. Repair change. (A: obj. 20x, B: obj. 40x) |
 |  | Inflammatory smear: pseudo-koilocyte. (obj. 20x) |
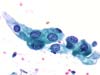 |  | Metaplasia: enlarged nuclei with regular chromatin and abundant cytoplasm. This change is not typical of ASC-US. Repair change. (obj. 40x) |
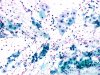 |  | Atrophic menopausal smear: moderately enlarged nuclei: this change is of inflammatory origin and not typical of ASC-US. (same slide A, B, C and D: obj. 20x) |
 |  | Atrophic menopausal smear: moderately enlarged nuclei in deep intermediate or parabasal cells: this change is not typical of ASC-US, because chromatin is clear. (same slide A and B: obj. 40x) |
 |  | Liquid based preparation: metaplastic cells with enlarged nuclei. This change is not typical of ASC-US. (obj. 20x) |
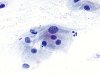 |  | Squamous cell with a nucleus more than twice the normal diameter, with a normal chromatin. This change, of inflammatory origin (yeast: arrow), is not typical of ASC-US. (obj. 40x) |
 |  | Metaplastic cells with cellular changes of inflammatory origin, not typical of ASC-US. Look for Trichomonas. (A and B: obj. 20x) |
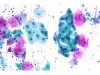 |  | Mature metaplastic cells with a moderately enlarged nucleus. This change, of inflammatory origin (look for Trichomonas or Gardnerella), is not typical of ASC-US. (obj. 20x) |
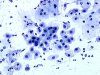 |  | Parabasal cells with enlarged nuclei. This change is not typical of ASC-US. (obj. 20x) |
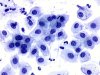 |  | Parabasal cells with enlarged nuclei. This change is not typical of ASC-US. (obj. 40x) |
 |  | Metaplastic cells with an enlarged nucleus. This change is not typical of ASC-US. (obj. 10x) |
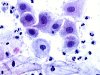 |  | Metaplastic cells with enlarged nuclei and moth-eaten degenerating borders. These changes, of inflammatory origin (look for Trichomonas), are not typical of ASC-US. (obj. 40x) |
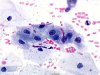 |  | Metaplastic cells with an enlarged nucleus. This change, of inflammatory origin, is not typical of ASC-US. (obj. 40x) |
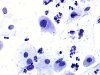 |  | Metaplastic cells with enlarged nuclei. This change is not typical of ASC-US. (obj. 40x) |
 |  | Atrophic, inflammatory smear: changes induced by atrophy and inflammation. This change is not typical of ASC-US. (A and B: obj. 10x) |
 |  | Atrophic, inflammatory smear: changes induced by atrophy and inflammation. These changes do not qualify for ASC-US. (A: obj. 20x, B: obj. 40x) |
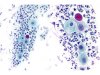 |  | Changes induced by atrophy and inflammation. These changes do not qualify for ASC-US. (A: obj. 20x, B: 40x) |
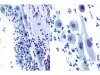 |  | Changes induced by atrophy and inflammation. These changes do not qualify for ASC-US. (A: obj. 20x, B: 40x) |
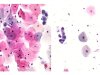 |  | Small metaplastic cells with nuclear enlargement and a binucleated cell, non-specific perinuclear halos. This change is not typical of ASC-US. (obj. 20x) |
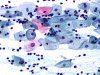 |  | Eosinophilic squamous cell with an enlarged nucleus (arrow). This change is not typical of ASC-US. (obj. 20x) |