Image | Statistics | Caption |
 |  | Exocervical smear, slightly inflammatory: an intermediate cell with an enlarged nucleus and a homogenous chromatin: ASC-US (arrow). (obj. 10x) |
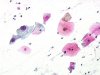 |  | Exocervical smear, slightly inflammatory: an intermediate cell with an enlarged nucleus and a homogenous chromatin: ASC-US (arrow). (obj. 20x) |
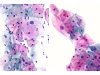 |  | A: ASC-US: eosinophilic squamous cell with enlarged and hyperchromatic nucleus. B: ASC-US: eosinophilic squamous cell with an enlarged nucleus but with pale chromatin. (A and B: obj. 20x) |
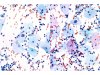 |  | ASC-US (A and B): intermediate cells with an enlarged nucleus and a chromatin slightly denser in B. (A and B: obj. 20x) |
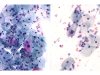 |  | A: Squamous cell with eosinophilic cytoplasm and an enlarged nucleus and a non densified chromatin: ASC-US. B: Intermediate squamous cell with an enlarged nucleus and a cytoplasmic clearing: ASC-US. (same slide for A and B: obj. 20x) |
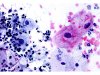 |  | A: ASC-US: basophilic squamous cells with enlarged and slightly hyperchromatic nuclei. Inflammatory background. B: Two eosinophilic squamous cells with enlarged nuclei and cytoplasmic clearing: ASC-US. (same slide A and B: obj. 40x) |
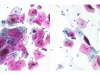 |  | A: Intermediate cell with an enlarged, regular nucleus and a homogenous chromatin, surrounded by an ill-defined clear halo: ASC-US. B: Slightly inflammatory exocervical smear: a binucleated eosinophilic cell with a dense, homogenous chromatin: ASC-US. (same slide A and B: obj. 20x) |
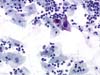 |  | Inflammatory ectocervix: Intermediate binucleated cell and deep intermediate cells with enlarged and densified nuclei: ASC-US. (obj. 20x) |
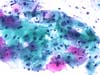 |  | Inflammatory ectocervix, some intermediate squamous cells with enlarged nuclei and narrow perinuclear halos: ASC-US. (obj. 20x) |
 |  | Inflammatory and bloody exocervical smear. A: intermediate mono or multinucleate squamous cells, with a clearcut enlargement (x3): ASC-US. B: intermediate squamous cell with an enlarged nucleus, to compare with columnar cell nuclei: ASC-US. (same slide A and B: obj. 20x) |
 |  | Some binucleated cells: ASC-US. (obj. 20x) |
 |  | A: Inflammatory smear: some parabasal squamous cell with an enlarged nucleus with regular chromatin surrounded by a clear cytoplasmic area with hazy limits: ASC-US. B: Inflammatory smear: parabasal squamous cell with an enlarged and irregular nucleus with perinuclear halo: ASC-US. (same slide A and B: obj. 20x) |
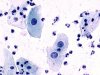 |  | Inflammatory exocervical smear: intermediate cells with enlarged nuclei without significant chromatin clumping: ASC-US. (same slide A and B: obj. 40x) |
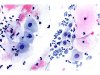 |  | A: Metaplastic cells with enlarged nuclei. This change is not typical of ASC-US. B: ASC-US: Metaplastic cells with definitely enlarged nuclei, irregular in shape and chromatin pattern. (same slide A and B: obj. 40x) |
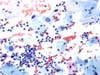 |  | ASC-US: two squamous metaplastic cells from the deep intermediate layers with nuclear enlargement, with one denser and slightly irregular chromatin (arrow). (obj. 20x) |
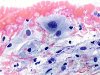 |  | Squamous cell with a nucleus more than twice the normal diameter and irregular: ASC-US. (obj. 40x) |
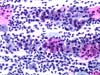 |  | Parabasal cells showing a clear perinuclear zone not always clearly delimited and an abnormal, enlarged and hyperchromatic nucleus (ASC-US). If the smear is atrophic, repeat after oestrogen treatment. The koilocytes are intermediate or superficial squamous cells. (obj. 20x) |
 |  | Normal intermediate basophilic and superficial basophilic and eosinophilic squamous cells. A superficial eosinophilic cell with enlarged and irregular nucleus: ASC-US. (obj. 40x) |
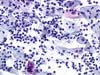 |  | Parabasal cells showing a perinuclear cytoplasmic clearing and an abnormal nucleus, enlarged, hyperchromatic (ASC-US). The koilocytes are intermediate or superficial squamous cells. (obj. 20x) |
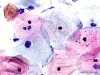 |  | Normal basophilic and eosinophilic squamous cells. Note the intermediate cell with a mildly densifiied and an enlarged nucleus with a small perinuclear halo:ASC-US. (obj. 40x) |