Image | Caption |
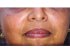 | Figure 1: Lip (vermilion border of the lip) is the lipstick area, extending from mucocutaneous junction to the area where both lips touch each other. |
 | Figure 2: Buccal mucosa is the inner lining of the cheeks. |
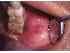 | Figure 3: Opening of the Stensen duct. |
 | Figures 4: The labial mucosa is part of the buccal mucosa lining the inner surface of the lips. |
 | Figures 5: The retromolar trigone (yellow circle) is a small triangular area, lying behind last lower molar teeth on either side. |
 | Figure 6: Gingiva (arrows) is the tissue that covers the neck of the teeth and alveolar bone. |
 | Figure 7: Bony ridge that forms the borders of the upper and lower jaws and contains the sockets for teeth. |
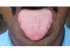 | Figure 8: Anterior two thirds of the tongue is the mobile part of the tongue. The dorsal surface is illustrated. |
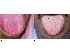 | Figures 9A and 9B: Filiform papillae appear as numerous, fine, pointed, cone-shaped papillae (blue arrow) and the fungiform papillae appear as mushroom-shaped reddish prominences on the dorsum of tongue (yellow arrow). |
 | Figure 10: Circumvallate papillae (arrows) appear as nodules (8-10 in number) on the posterior third of tongue. |
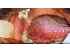 | Figure 11: Foliate papillae of the tongue. |
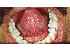 | Figure 12: Ventral surface of the tongue (yellow arrows), median lingual frenum (white arrow) and openings of the Wharton duct (blue arrows). |
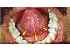 | Figure 13: The floor of mouth is a horseshoe-shaped area between the ventrum of the tongue medially and the gingivae of the lower teeth anteriorly and laterally, extending to the palatoglossal fold posteriorly. |
 | Figure 14: The hard palate (yellow arrows) forms the roof of the oral cavity and is continuous anteriorly with the maxillary alveolar arches and posteriorly with the soft palate (black arrow). |