Image | Statistics | Caption |
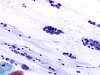 |  | Mucus with numerous naked nuclei in groups from reserve cell hyperplasia (RCH), with nuclear size variations: ASC-H. (obj. 20x) |
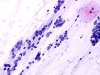 |  | Mucus with numerous naked nuclei in groups from reserve cell hyperplasia (RCH), with nuclear size variations: ASC-H. (obj. 20x) |
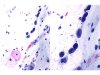 |  | Mucus with numerous naked nuclei in groups from reserve cell hyperplasia (RCH), with nuclear size variations: ASC-H. (A: obj. 20x, B: obj. 40x) |
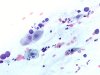 |  | Mucus with isolated naked nuclei from reserve cell hyperplasia (RCH), with nuclear size variations: ASC-H. (obj. 20x) |
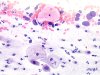 |  | Mucus with isolated naked nuclei, hypo or hyperchromatic, from reserve cell hyperplasia (RCH), with nuclear size variations: ASC-H. (obj. 20x) |
 |  | Large groups of immature atypical cells some with nucleoli (atypical immature metaplasia (arrow) or atypical repair?), sometimes more columnar-shaped (dotted line). Atypias of squamous cells (ASC-H) or glandular cells (AGC). (obj. 10x) |
 |  | A small group of immature atypical cells with enlarged nuclei and nucleoli: ASC-H. (A: obj. 20x, B: obj. 40x) |
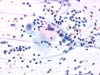 |  | Intermediate and parabasal (or histiocytes?) squamous cells with a regularly enlarged nucleus and a quiet normal appearing chromatin: ASC-H. (obj. 20x) |
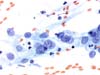 |  | ASC-H. some of these cells may be histiocyte. (obj. 40x) |
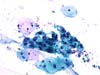 |  | A small cohesive cluster of atypical cells (immature metaplasia) with nuclear enlargement, hyperchromasia and anisokaryosis. ASC-H. (obj. 20x) |
 |  | Transition zone smear: bloody mucus containing cells resembling histiocytes. Possibility of atypical basal squamous cells (ASC-H). (obj. 10x) |
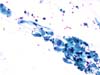 |  | A small cohesive cluster of atypical cells (immature metaplasia) with nuclear enlargement, hyperchromasia and anisokaryosis. ASC-H. (obj. 20x) |
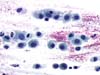 |  | Transition zone smear: bloody mucus containing cells resembling histiocytes. Possibility of atypical basal squamous cells (ASC-H). (obj. 40x) |
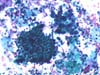 |  | Compare the small group of immature, atypical metaplastic cells with markedly enlarged nuclei, on the right, with the cluster of normal columnar cells on the left: ASC-H. (obj. 20x) |
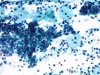 |  | A large group of immature, atypical cells with coarse and dense chromatin (circles). ASC-H. (obj. 20x) |
 |  | A group of immature, atypical cells with prominent nucleoli (arrows): ASC-H. (A: obj. 20x, B: obj. 40x) |
 |  | A small cohesive cluster of immature metaplasia, less atypical under high magnification (B) than under low magnification (A): this change is not typical of ASC-H. (obj. 20x) |
 |  | Large group of cells with prominent nucleoli (repair/immature metaplasia). One atypical basal isolated cell (arrow) : ASC-H. (obj. 20x) |
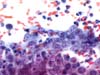 |  | Large group of cells with prominent nucleoli (repair/immature metaplasia). One isolated atypical basal cell (arrow) : ASC-H. (obj. 40x) |
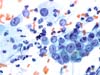 |  | Large group of cells with prominent nucleoli (repair/immature metaplasia): two atypical basal isolated cells (arrows) : ASC-H (HSIL?). (obj. 40x) |
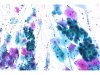 |  | Inflammatory smear with a sheet of immature metaplastic cells showing some degree of nuclear hypertrophy and irregular nuclear membrane. Under higher magnification: ASC-H. (A:obj. 10x, B: obj. 20x) |
 |  | Moderately inflammatory smear with two sheets of immature metaplastic cells showing some degree of nuclear hypertrophy. Under higher magnification: ASC-H. (A: obj. 10x, B: obj. 20x) |
 |  | A small cohesive cluster of immature, atypical metaplastic cells with nuclear enlargement, anisokaryosis and hyperchromasia. ASC-H. (A: obj. 20x, B: obj. 40x) |
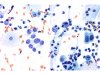 |  | Basal cells cells with enlarged nuclei, a coarse chromatin and a thickened nuclear membrane. Atypical but altered cells with possibility of histiocytic origin and naked nuclei. ASC-H on this field. Final diagnosis: HSIL. (A and B: obj. 40x) |
 |  | Some immature, metaplastic cells with nuclear outline irregularities without hyperchromasia : ASC-H may be discussed (A). Clear cut ASC-H in B (anisokaryosis). (A and B: obj. 20x) |
 |  | Isolated atypical cells with enlarged nuclei and nucleoli (arrows): ASC-US instead of ASC-H. (obj. 20x) |
 |  | A small cohesive cluster of metaplastic cells with slight nuclear hypertrophy, anisokaryosis and nuclear membrane irregularities without hyperchromasia. ASC-US instead of ASC-H . (obj. 20x) |
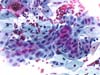 |  | Bloody smear: sheet of immature metaplasia showing mild nuclear hypertrophy. No definite criteria for ASC-H. (obj. 20x) |
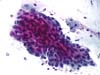 |  | Cohesive cluster of immature metaplasia with nuclear enlargement and anisokaryosis. No definite criteria for ASC-H. (obj. 20x) |
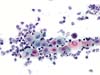 |  | ASC-H in an atrophic smear: only one parabasal cell with an enlarged nucleus with irregular outlines and hyperchromasia (arrow). (obj. 20x) |
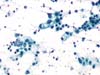 |  | ASC-H in an atrophic smear: parabasal cells with enlarged nuclei, sometimes with irregular outlines and chromatin texture (arrow). Repeat after local estrogenic and anti-inflammatory treatment. (obj. 20x) |
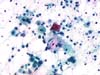 |  | ASC-H in an atrophic smear: deep squamous cells with enlarged nuclei, sometimes with irregular outlines and chromatin texture (arrows). Repeat after local estrogenic and anti-inflammatory treatment. (obj. 20x) |
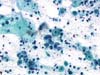 |  | ASC-H in an atrophic smear: deep squamous cells with enlarged nuclei, sometimes with irregular outlines and chromatin structure (arrow). Repeat after local estrogenic and anti-inflammatory treatment. (obj. 20x) |
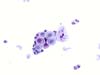 |  | Atrophic smear: parabasal cells with enlarged normal nuclei : no criteria for ASC-H (obj. 20x) |