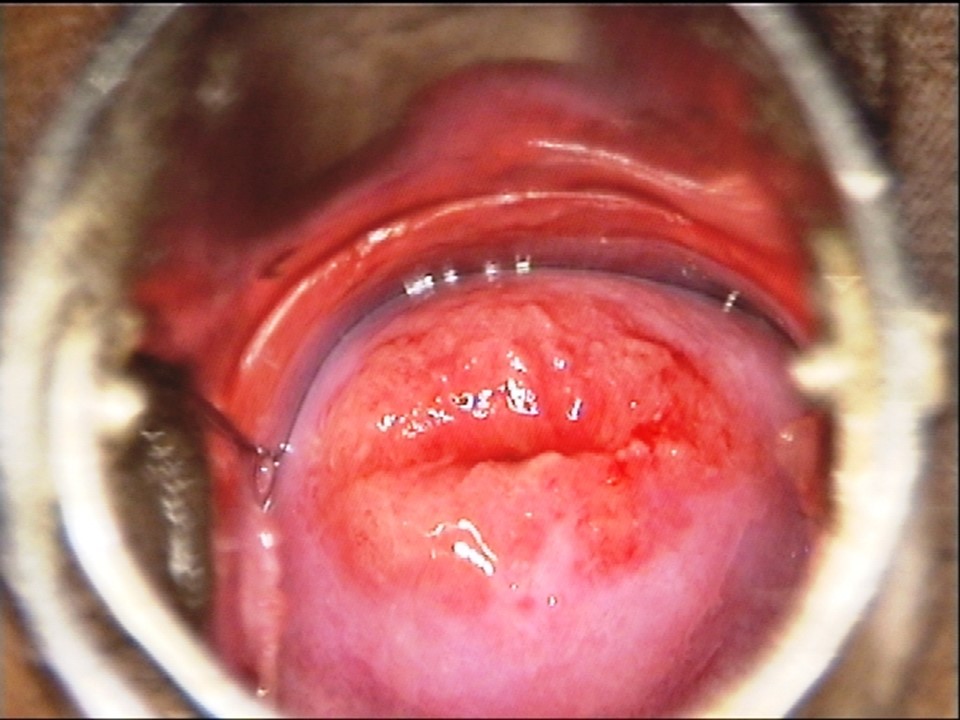
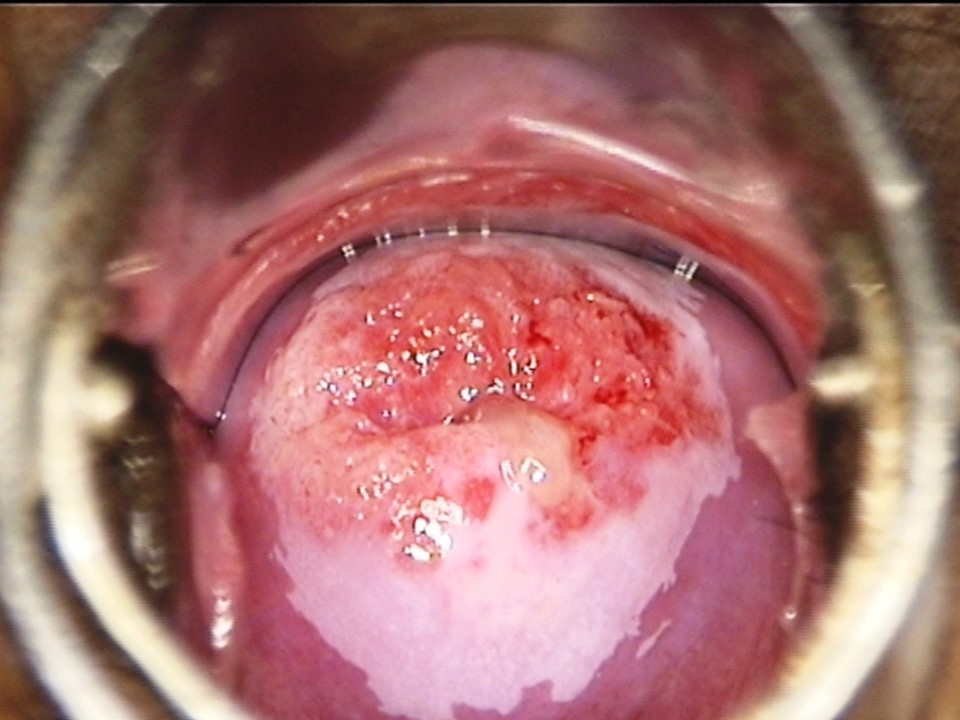
Atlas of visual inspection of the cervix with acetic acid for screening, triage, and assessment for treatment / Activity 1
Visual inspection after application of acetic acid (VIA) – VIA as a screening test for cervical cancer |
Visual inspection after application of acetic acid (VIA) involves naked-eye examination of the uterine cervix with appropriate illumination after application of freshly prepared 3%–5% acetic acid. The interpretation of the test is based on the detection of a well-defined dense acetowhite area on the transformation zone of the cervix one minute after application of acetic acid. VIA is a screening test that aims to detect cervical pre-cancers and early cervical cancers in apparently normal and asymptomatic women. The test is most suitable for women aged 30–49 years, because most of the high-grade precancers of the cervix are detected in this age range. The test sensitivity of VIA (the capability of the test to correctly detect the precancers and cancers) decreases in postmenopausal women. The test is suitable for screening women living with HIV, in whom screening should start at 25 years of age. Pregnancy is not the ideal time to perform a screening test. However, in many settings the antenatal visit is considered as an opportunity to screen women, especially in the first trimester. There is no contraindication to perform VIA test in a pregnant woman. VIA is widely used as a screening test in several low- and middle-income countries, especially in Africa and Asia. VIA will be useful as a triage test of HPV positive women even when HPV primary screening becomes widely available. Nurses, midwives, and general practitioners can perform the test in primary health-care settings. The next section describes the advantages of VIA. |
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends