HPV detection test has several advantages. It is much more sensitive than cytology or VIA. Therefore, HPV negative women have very low risk of developing cervical cancer in the next 10 years. Hence unlike VIA or cytology that has to be repeated every 3 to 5 years, it is quite acceptable to screen women with HPV test once every 10 years. Women may collect vaginal samples themselves (self-sampling) for HPV test and do not require any speculum examination by the health professionals. Thus, replacing VIA with HPV test can save resources for the screening programme. HPV test is not a subjective test like VIA or cytology. Common laboratory technicians can be trained to perform the test with high competency. Because of all these advantages, WHO has recommended HPV test as the screening test of first choice and many high-income countries have already switched from their cytology-based screening programmes to screening based on HPV detection. The test is expected to become more affordable in the future, when many low- and middle-income countries will also be able to introduce the test.
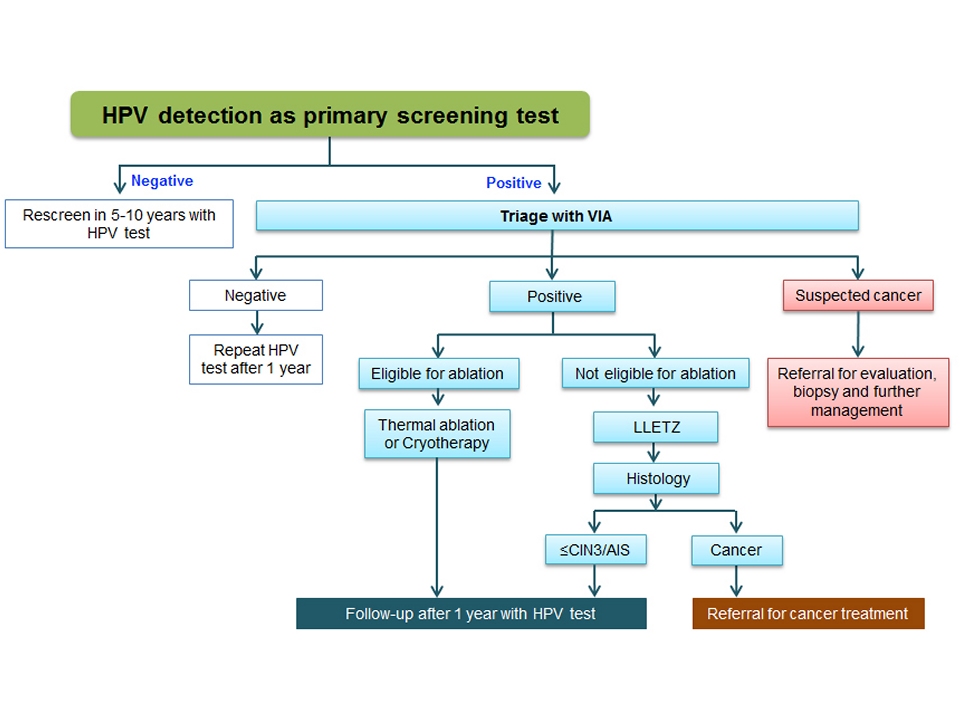
proportion of women with a positive HPV test will not have cervical precancer or cancer, especially among women living with HIV. To reduce unnecessary referral of a large number of HPV-positive women for colposcopy and/or treatment, a triage test is needed to identify those women who are at greatest risk of having the disease. Cytology is the most widely recommended triage test for HPV-positive women in high-resource countries.
In settings where high-quality cytology is not available, HPV-positive women may be triaged with VIA. HPV-positive but VIA-negative (triage-negative) women are advised to repeat the HPV test after 2 years for women in the general population, while women living with HIV should have HPV test repeated after 1 year. Women positive on both HPV and VIA tests (triage-positive) are immediately assessed for ablative treatment in a ‘screen, triage and treat’ setting. If eligible, they are treated with thermal ablation or cryotherapy. HPV and VIA positive women ineligible for ablative treatment or suspected to have invasive cancer need to be appropriately referred and managed.
Many of the HPV detection technologies also provide information on the presence or absence of HPV types 16 and 18 (the two most oncogenic types). When HPV 16/18 detection is integrated to the HPV detection technology, WHO recommends to treat all HPV 16/18 positive women and triage women positive for other genotypes with VIA in a ‘screen, triage and treat’ setting.
Please note that the principles, the consumables and instruments needed, the steps to be followed, and the interpretation of normal and abnormal changes before or after application of acetic acid are exactly the same when VIA is used as a primary screening test or as a triage test.
|
|