Atlas of Colposcopy: Principles and Practice / Activity 6
Case |
High grade / CIN2 / CIN3
Go back to the list
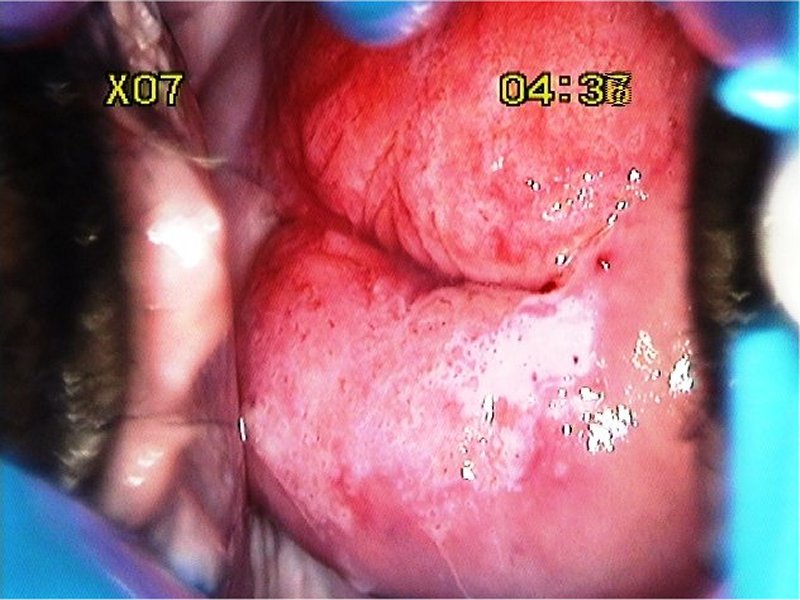
| After acetic acid |
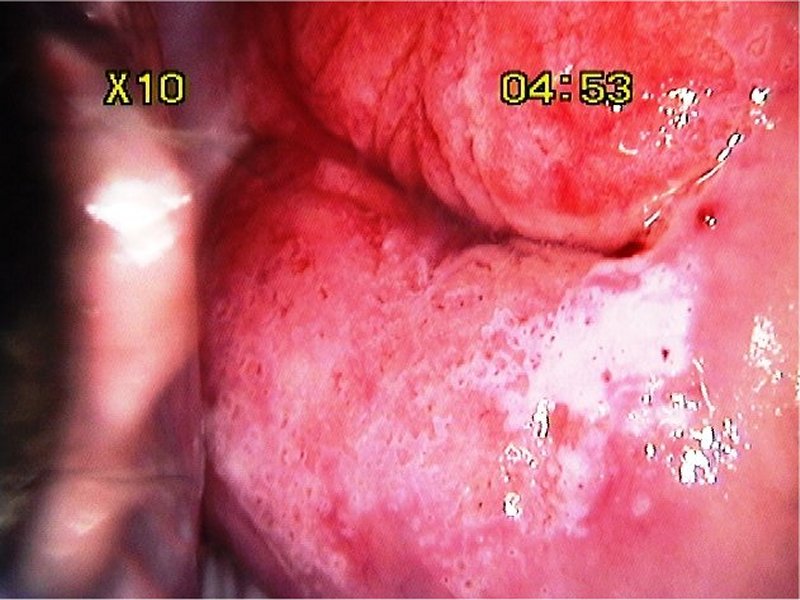
| After acetic acid |
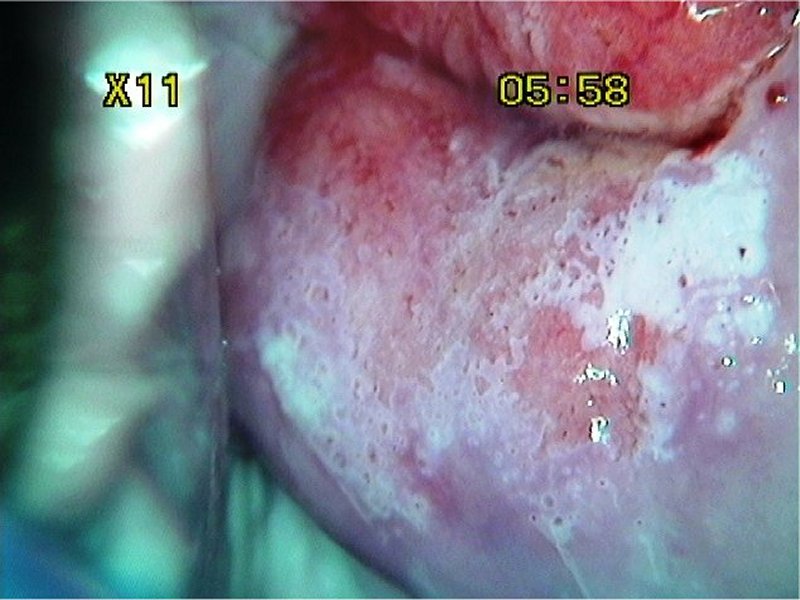
| After acetic acid with green filter |
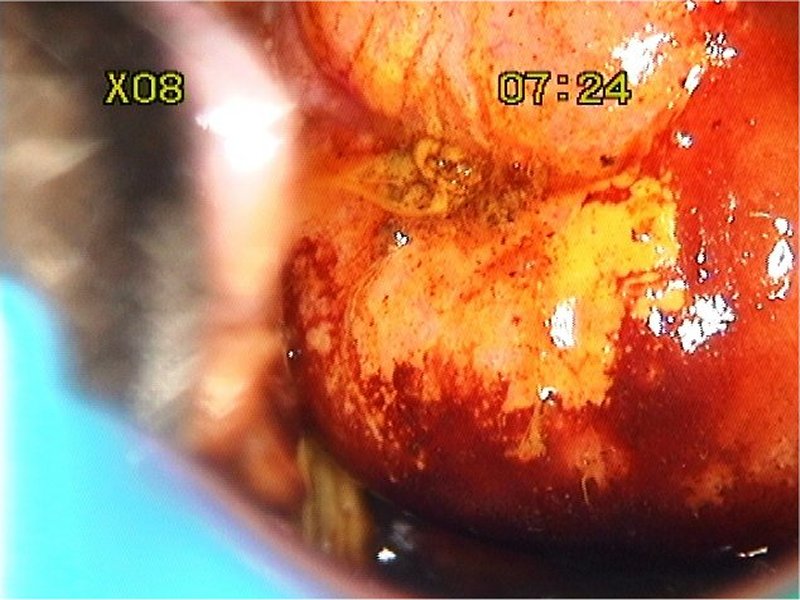
| After Lugolís iodine |
 General assessment General assessment | |||||||||||||||||
 Normal colposcopic findings Normal colposcopic findings | |||||||||||||||||
 Abnormal colposcopic findings Abnormal colposcopic findings | |||||||||||||||||
 General principles General principles | |||||||||||||||||
 Position and size Position and size | |||||||||||||||||
 Grade 1 (minor) Grade 1 (minor)
|  Grade 2 (major) Grade 2 (major)
|  Non-specific Non-specific
|  Suspicious for invasion Suspicious for invasion
|  Miscellaneous finding Miscellaneous finding
| |
Swede score:
| Nil or transparent | Thin, milky | Distinct, stearin | |
| Nil or diffuse | Sharp but irregular, jagged, satellites | Sharp and even, difference in level | |
| Fine, regular | Absent | Coarse or atypical vessels | |
| < 5 mm | 5-15 mm or 2 quadrants | >15 mm, 3-4 quadrants, or endocervically undefined | |
| Brown | Faintly or patchy yellow | Distinctly yellow |
Case Summary
| Provisional diagnosis: | Type 1 transformation zone; high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL). |
| Management: | Cryotherapy or thermal ablation after taking punch biopsy from the lesion. |
| Histopathology: | HSIL-CIN2. |
| Comment: | The thin acetowhite area in the posterior lip with multiple crypt openings is due to immature metaplasia. The high grade lesion is limited to only one quadrant. |