Atlas of Colposcopy: Principles and Practice / Activity 6
Case |
Early and advanced cancers / Squamous cell cancer
Go back to the list
| Speculum examination |
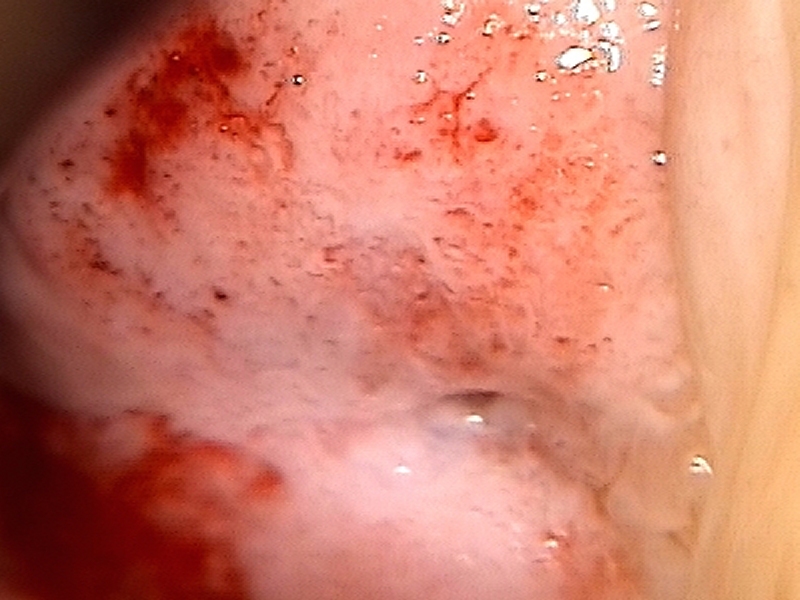
| After normal saline |
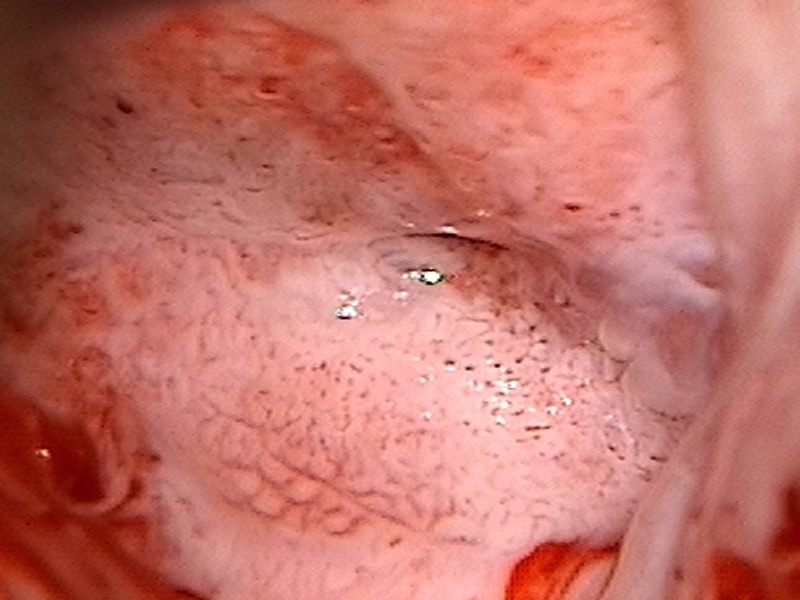
| After acetic acid |
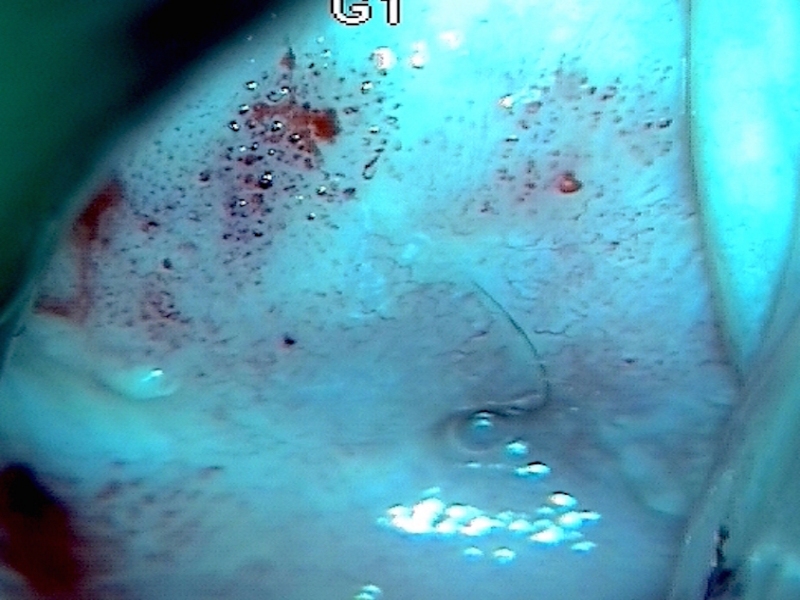
| After acetic acid with green filter |
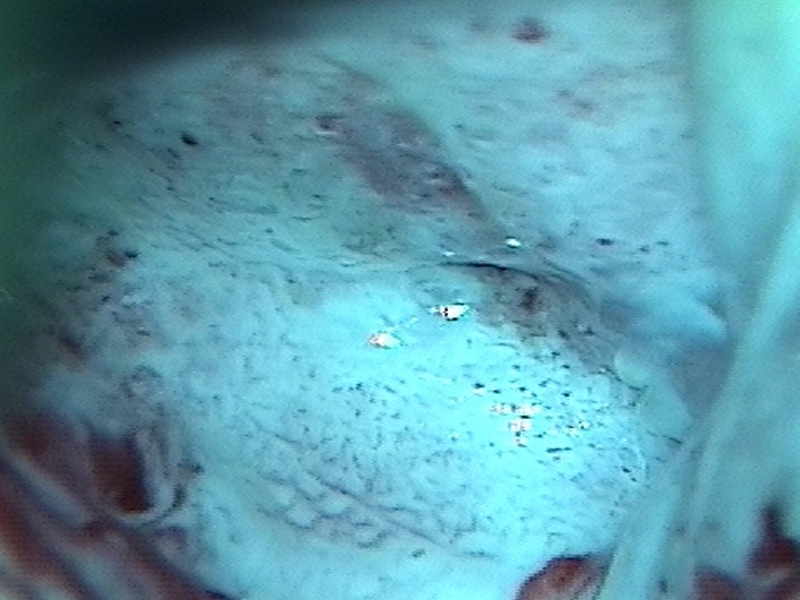
| After acetic acid with green filter |
 General assessment General assessment | |||||||||||||||||
 Normal colposcopic findings Normal colposcopic findings | |||||||||||||||||
 Abnormal colposcopic findings Abnormal colposcopic findings | |||||||||||||||||
 General principles General principles | |||||||||||||||||
 Position and size Position and size | |||||||||||||||||
 Grade 1 (minor) Grade 1 (minor)
|  Grade 2 (major) Grade 2 (major)
|  Non-specific Non-specific
|  Suspicious for invasion Suspicious for invasion
|  Miscellaneous finding Miscellaneous finding
| |
Swede score:
| Nil or transparent | Thin, milky | Distinct, stearin | |
| Nil or diffuse | Sharp but irregular, jagged, satellites | Sharp and even, difference in level | |
| Fine, regular | Absent | Coarse or atypical vessels | |
| < 5 mm | 5-15 mm or 2 quadrants | >15 mm, 3-4 quadrants, or endocervically undefined | |
| Brown | Faintly or patchy yellow | Distinctly yellow |
Case Summary
| Provisional diagnosis: | Type 3 transformation zone; suspicion of invasive cancer. |
| Management: | Multiple punch biopsies. |
| Histopathology: | Squamous cell carcinoma. |
| Comment: | The lesion is suspicious of invasive cancer because of its large size covering the entire cervix and extensive coarse mosaics and punctations. If invasive disease was not diagnosed on punch biopsies, diagnostic excision by LLETZ or cold-knife conization would have been necessary. |