Atlas of Colposcopy: Principles and Practice / Activity 6
Case |
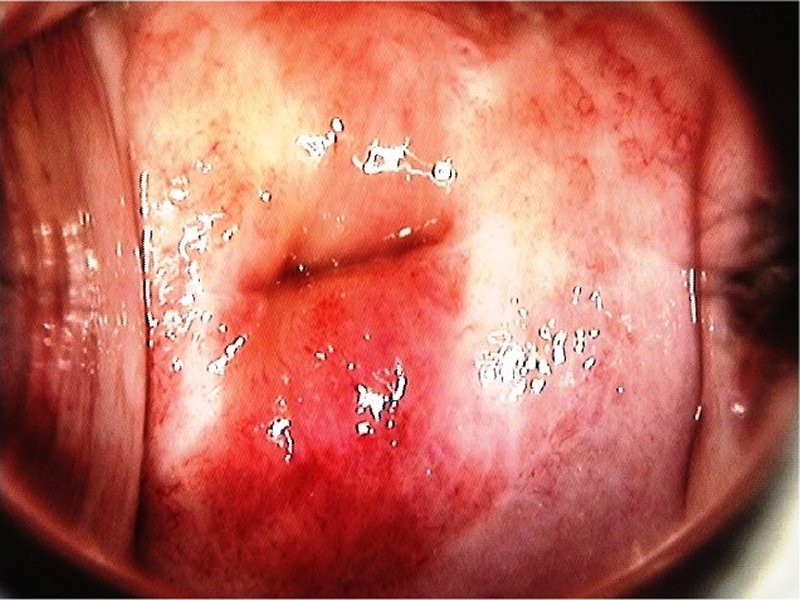
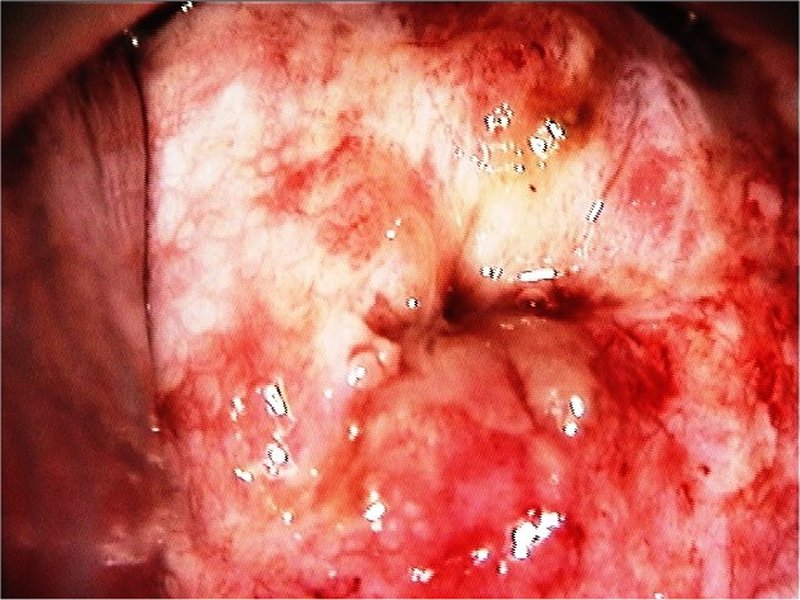
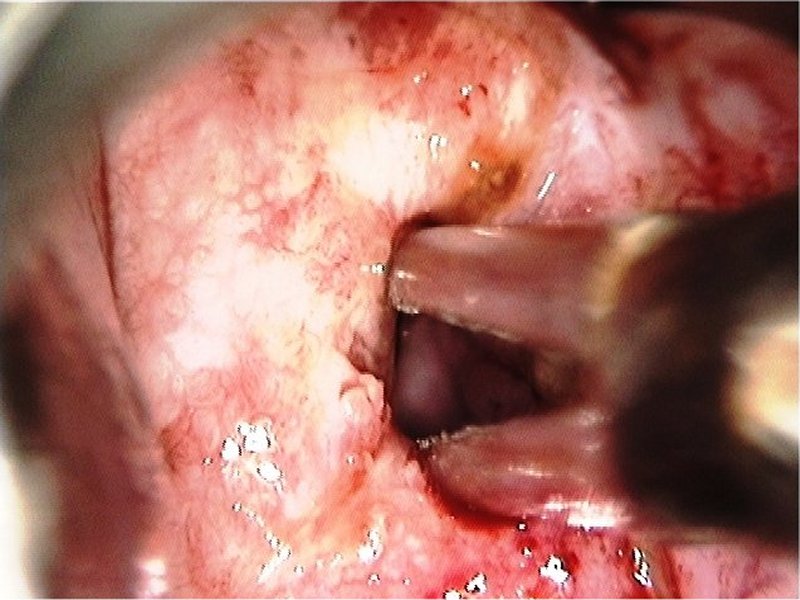
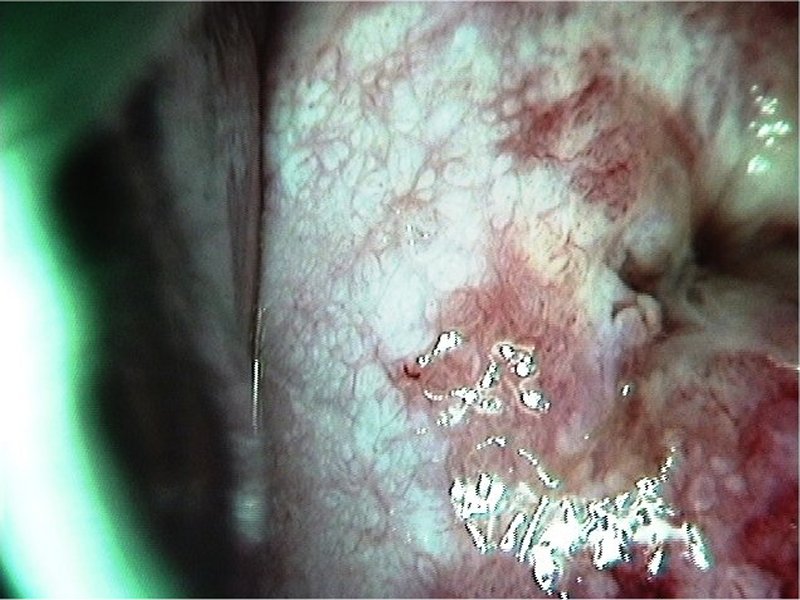
Early and advanced cancers / Squamous cell cancer
Go back to the list
| After normal saline |
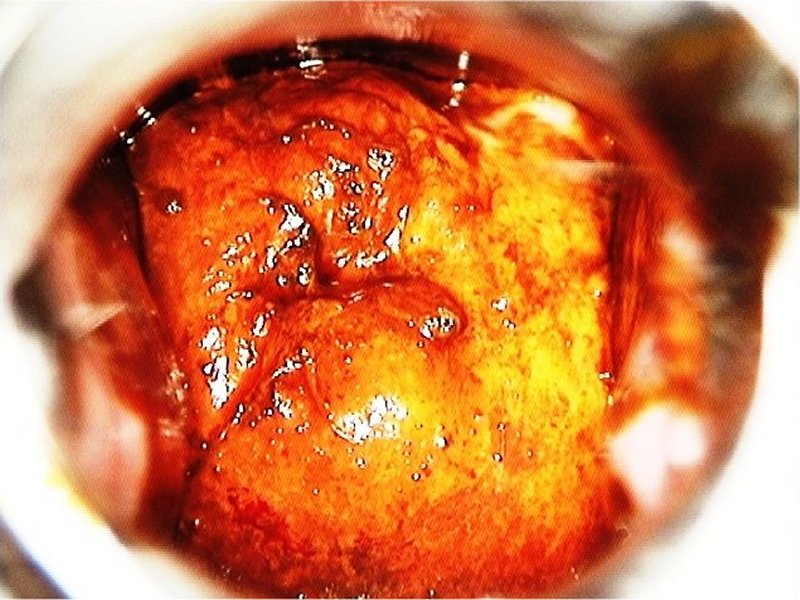
| After acetic acid |
| Visualization of the SCJ |
| After acetic acid with green filter |
| After Lugolís iodine |
 General assessment General assessment | |||||||||||||||||
 Normal colposcopic findings Normal colposcopic findings | |||||||||||||||||
 Abnormal colposcopic findings Abnormal colposcopic findings | |||||||||||||||||
 General principles General principles | |||||||||||||||||
 Position and size Position and size | |||||||||||||||||
 Grade 1 (minor) Grade 1 (minor)
|  Grade 2 (major) Grade 2 (major)
|  Non-specific Non-specific
|  Suspicious for invasion Suspicious for invasion
|  Miscellaneous finding Miscellaneous finding
| |
Swede score:
| Nil or transparent | Thin, milky | Distinct, stearin | |
| Nil or diffuse | Sharp but irregular, jagged, satellites | Sharp and even, difference in level | |
| Fine, regular | Absent | Coarse or atypical vessels | |
| < 5 mm | 5-15 mm or 2 quadrants | >15 mm, 3-4 quadrants, or endocervically undefined | |
| Brown | Faintly or patchy yellow | Distinctly yellow |
Case Summary
| Provisional diagnosis: | Type 3 transformation zone; suspicion of early invasive squamous cell carcinoma. |
| Management: | Multiple punch biopsies. |
| Histopathology: | Squamous cell carcinoma. |
| Comment: | Such extensive lesions with vascular abnormalities should be considered invasive disease. The central part of the transformation zone may be excised with a loop to ensure adequate biopsy material for histopathology. Alternatively, a diagnostic excision can be done by LLETZ or cold-knife conization. |