|
Using Human Papillomavirus (HPV) detection tests for cervical cancer screening and managing HPV-positive women – a practical guide / Activity 7Steps to determine eligibility for ablative treatment – Criteria used to determine eligibility for ablative treatment |   | .png)
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
|
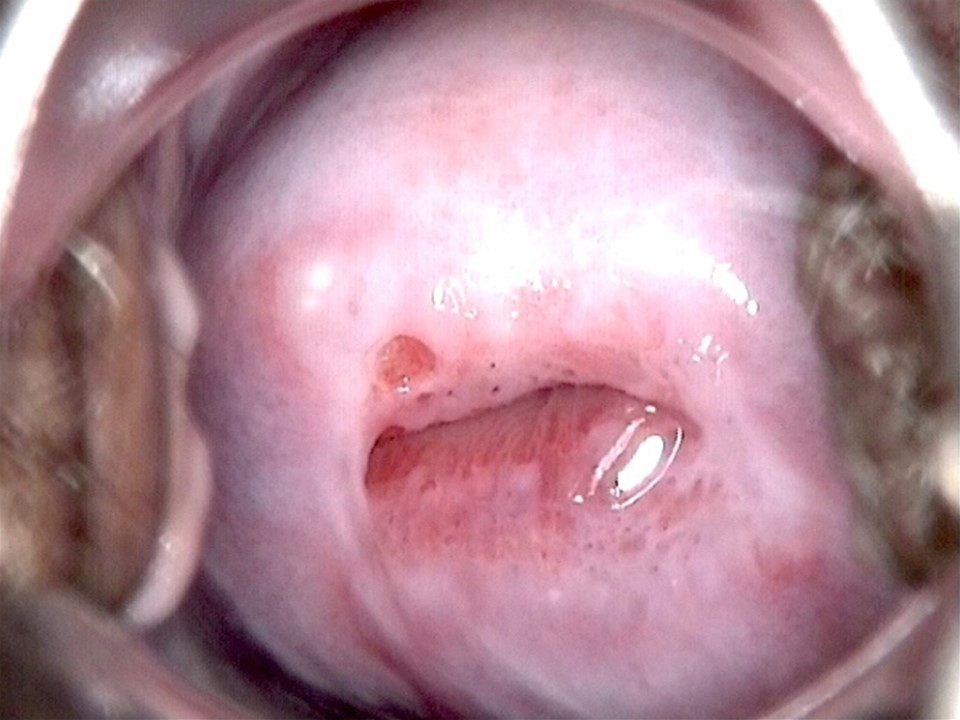
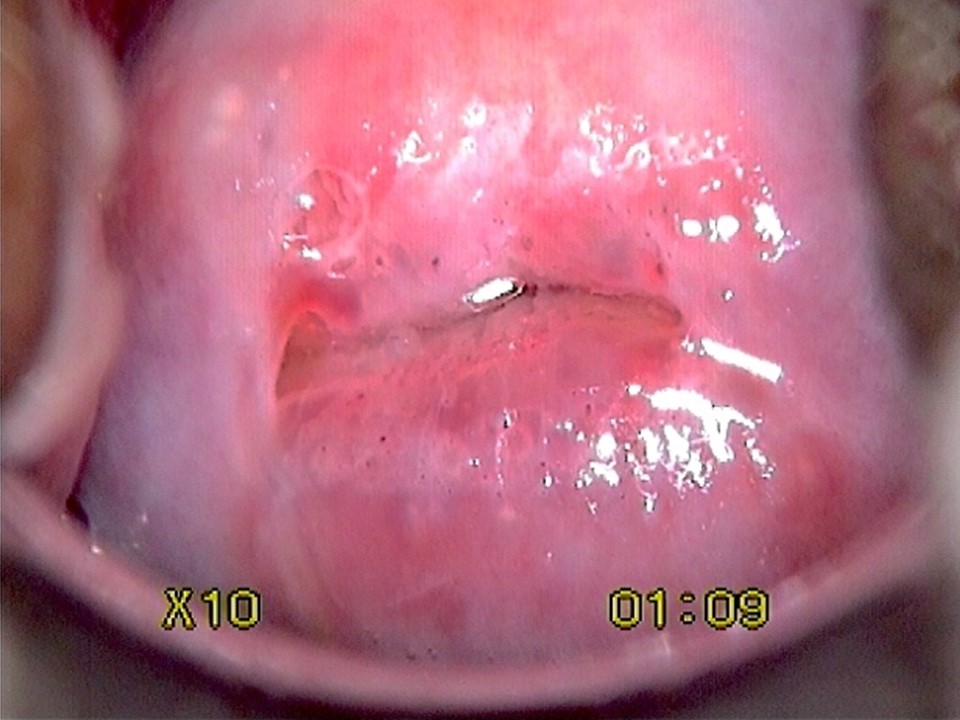
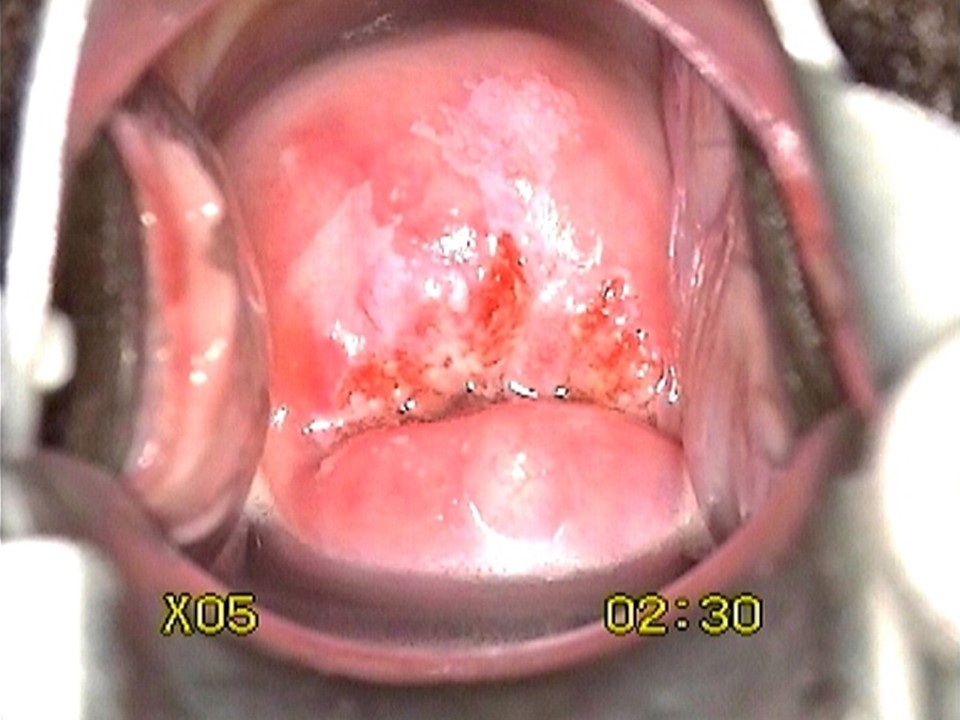
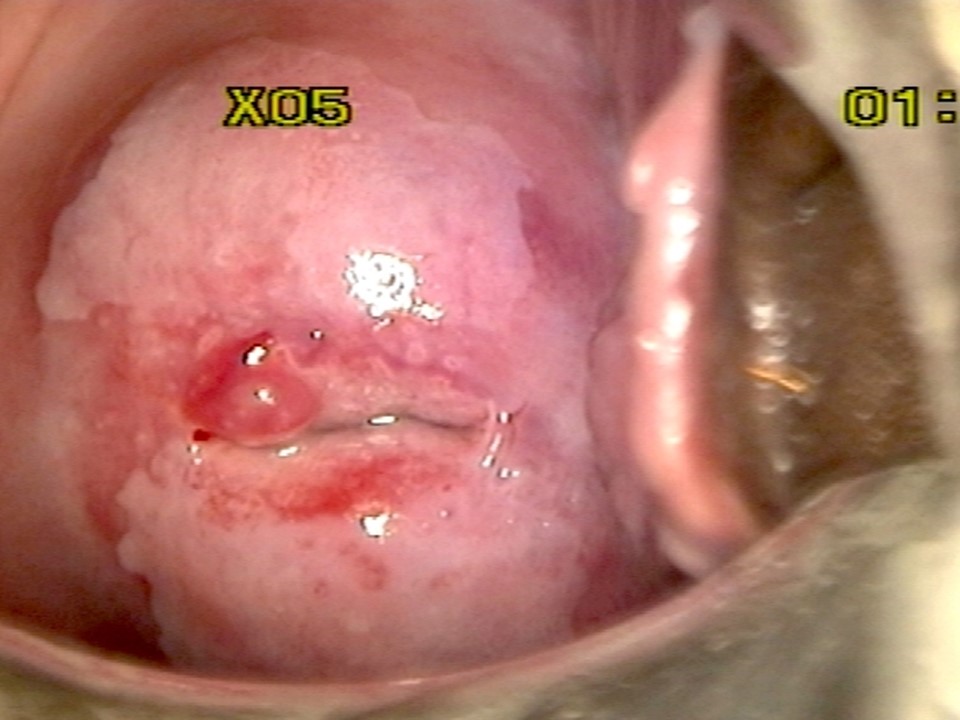
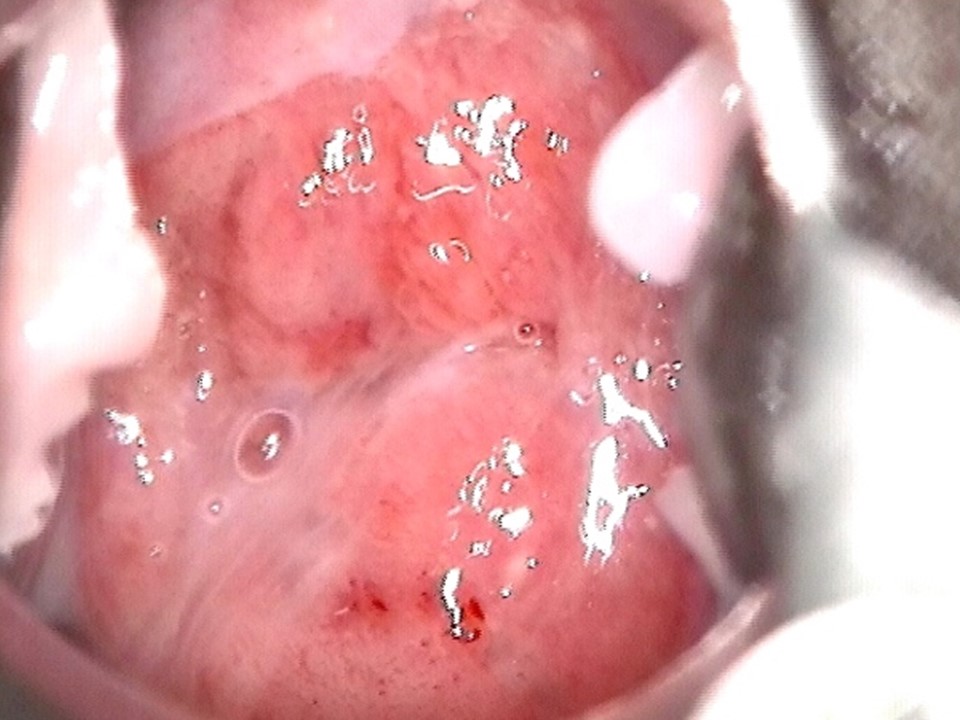
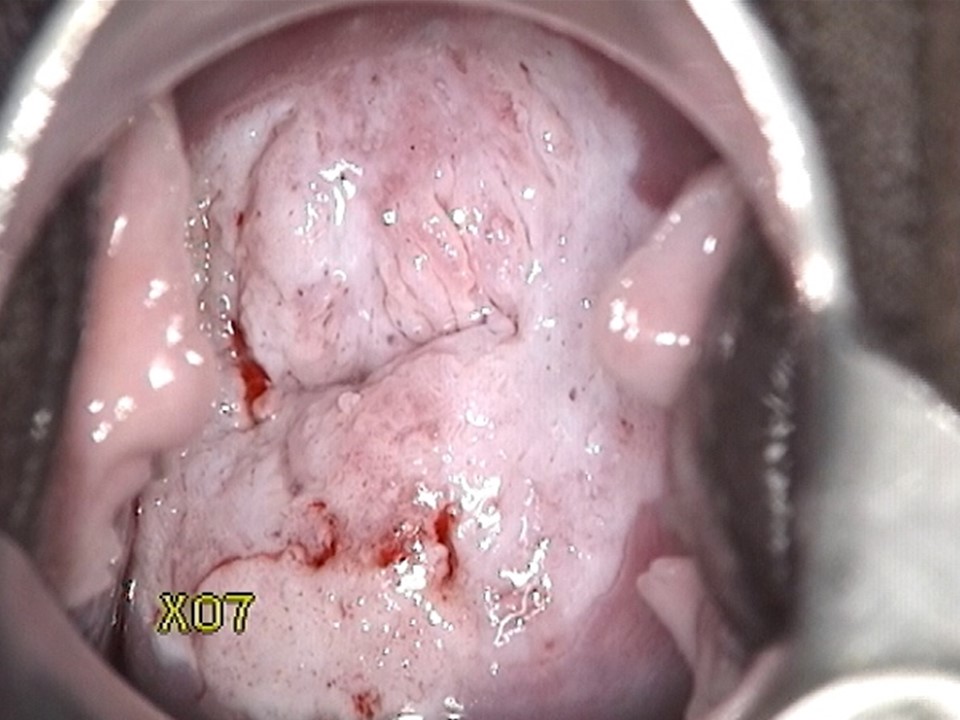
Ablative treatment can be used to treat an abnormal transformation zone or a normal transformation zone in an HPV-positive woman provided the following criteria are fulfilled:
- The squamocolumnar junction (SCJ) should be fully visible and should be on the ectocervix or at the external os.
- If there is a visible lesion, it should be on the ectocervix without any extension to the endocervix or to the vagina.
- If there is a visible lesion, it should not occupy more than 75% of the ectocervix.
- The size of the transformation zone or the size and location of the lesion (when a lesion is present) should be such that it can be fully covered by the tip of the largest cryotherapy probe (applicable for cryotherapy only).
- There should not be any suspicion of invasive cancer.
- There should not be any suspicion of adenocarcinoma in situ (e.g. a cytology report suggesting abnormal glandular cells).
Please note that an HPV-positive cervix may appear normal even after application of acetic acid. Some of the criteria mentioned above will not be applicable.
|
|  |  |
|
|