Using Human Papillomavirus (HPV) detection tests for cervical cancer screening and managing HPV-positive women – a practical guide / Activity 6
Management of women with a positive HPV test result – Triage with colposcopy | Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends |
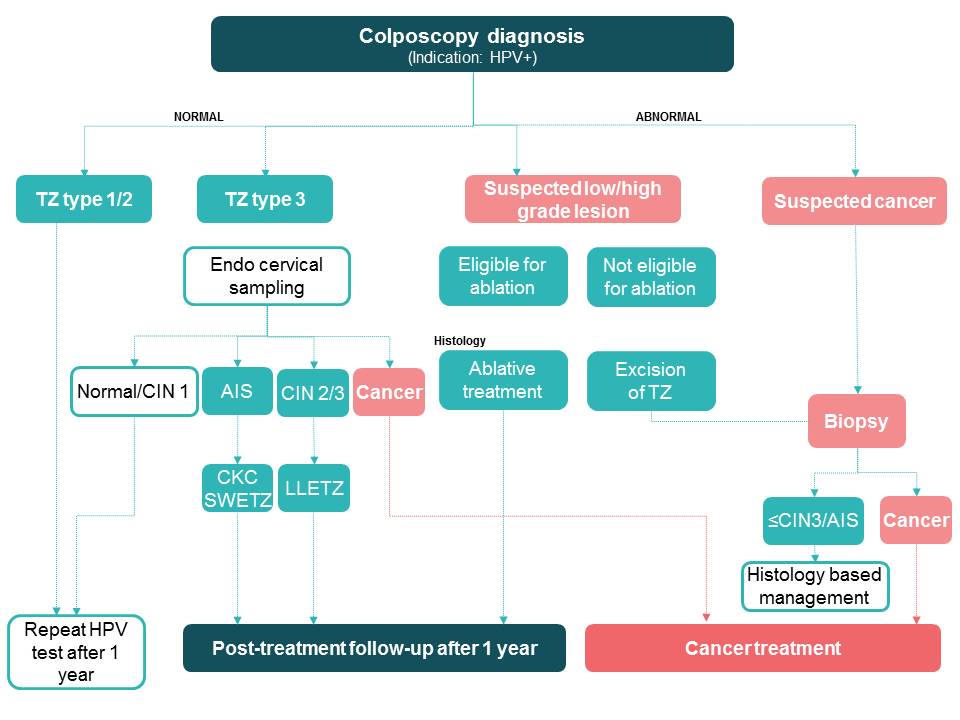
In some settings, women with a positive HPV test result may be directly referred for colposcopy. Women with no abnormalities detected on colposcopy are advised to repeat the HPV test after 1 year.
The colposcope enables examination of the cervix under a good light source and with different levels of magnification. Depending on the results of the colposcopic examination, a colposcopist may decide to either take a biopsy from the abnormal area or proceed directly to treatment. HPV-positive women with a normal colposcopy result should be reassured and advised to repeat the HPV test after 1 year. In women with a suspected precancerous lesion of the cervix, the colposcopist may decide to take a biopsy and wait for the histopathology result before making a treatment decision. However, to reduce the number of visits to the clinic by a woman, the colposcopist may immediately assess the women with suspected precancers for treatment (especially if high-grade lesions are suspected) and treat them with ablation (thermal ablation or cryotherapy) or large loop excision of the transformation zone (LLETZ). Women who are suspected to have cancer on colposcopy undergo cervical biopsy and are managed depending on the histopathology reports. To learn more about colposcopy, access the Atlas of Colposcopy: Principles and Practice. |