|
Using Human Papillomavirus (HPV) detection tests for cervical cancer screening and managing HPV-positive women – a practical guide / Activity 5Procedure to collect samples for HPV testing – Steps for inspection of the external genitalia |   | .png)
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
|
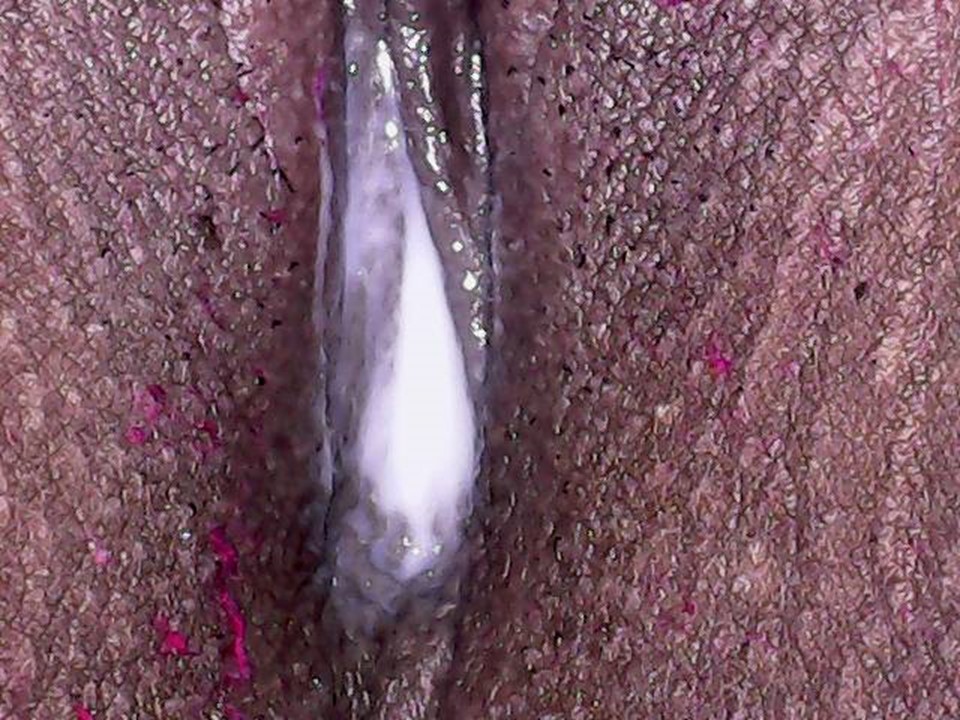
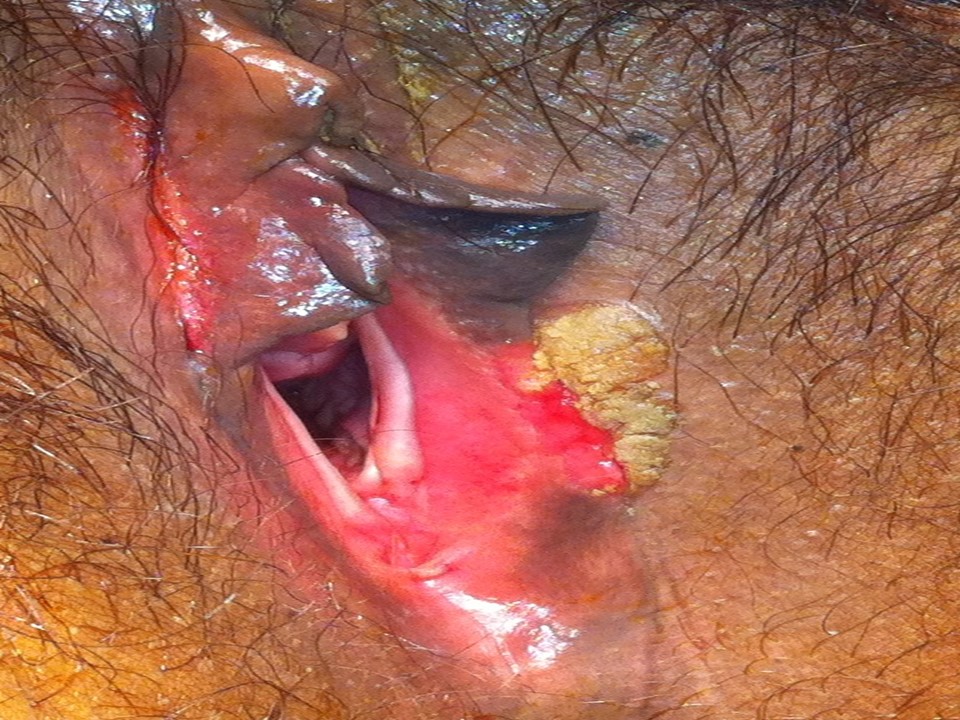
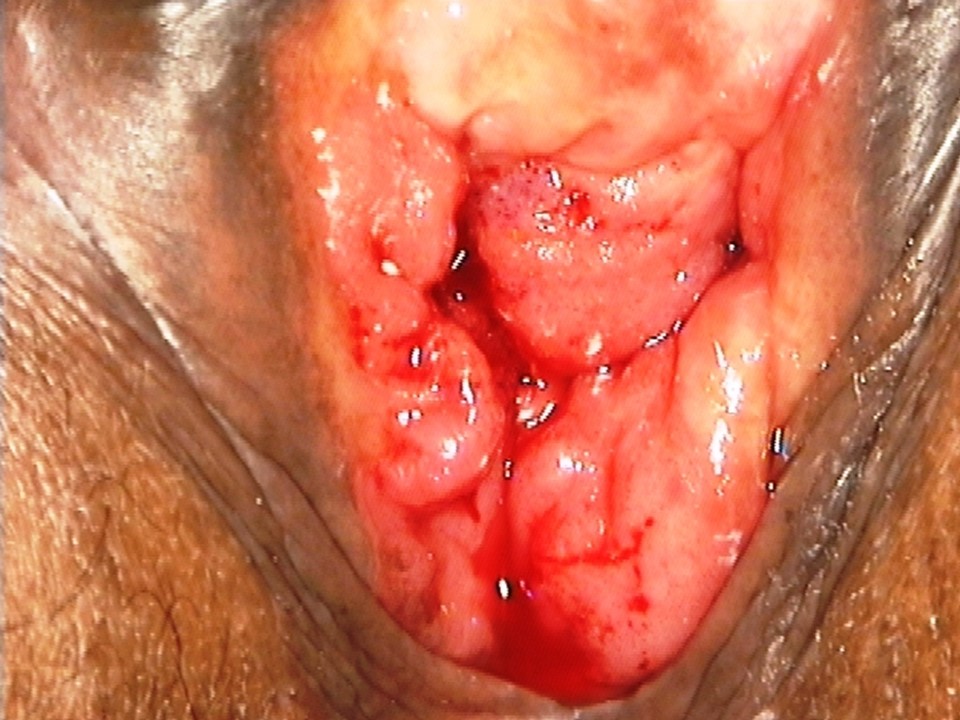
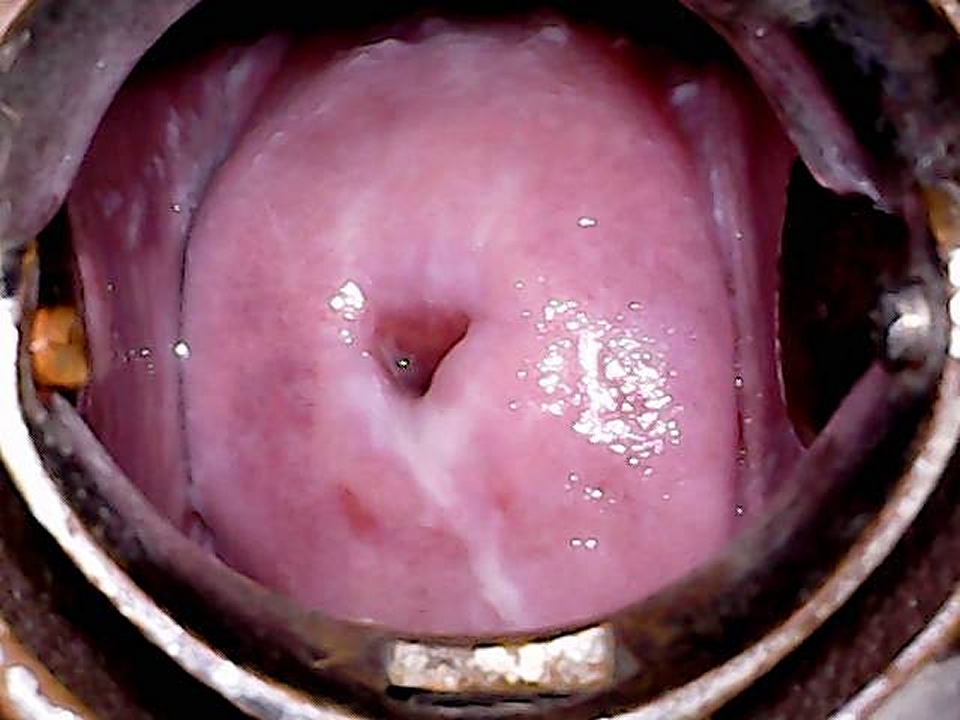
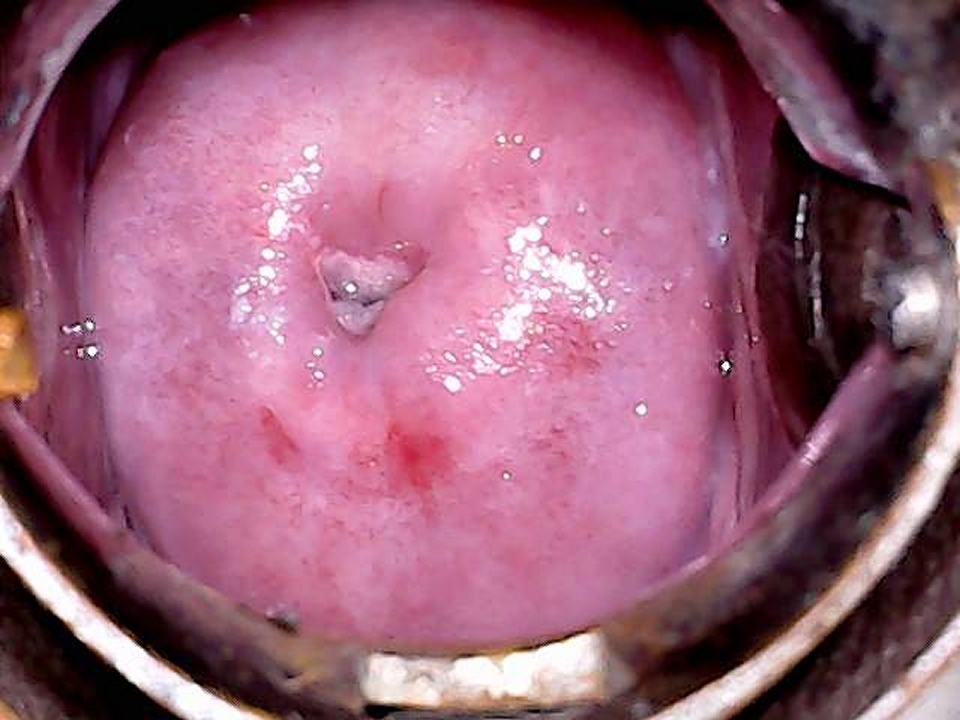
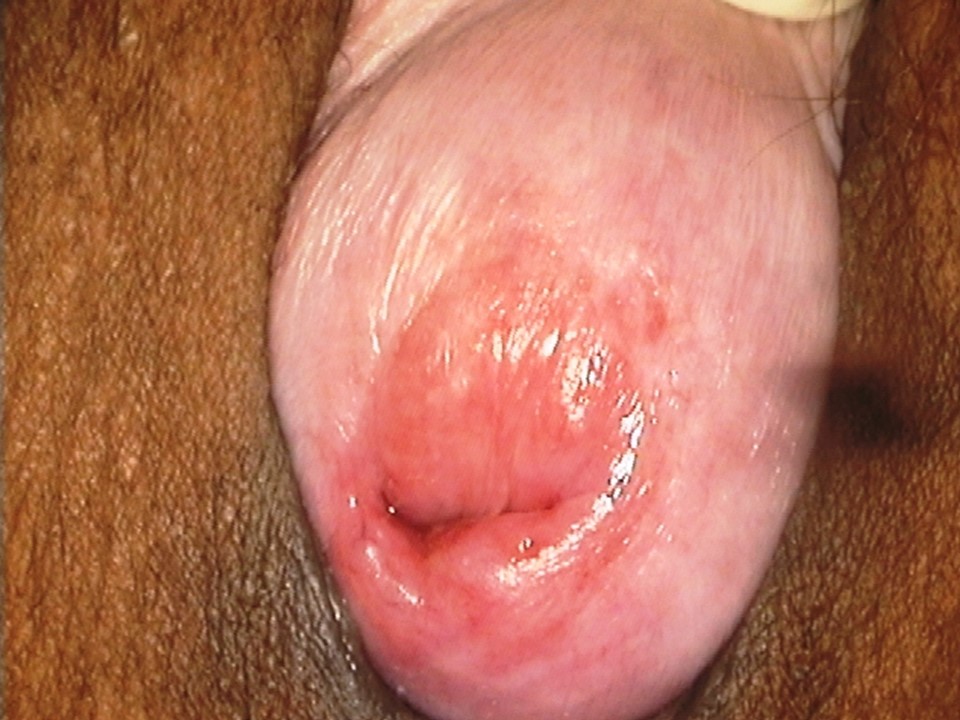
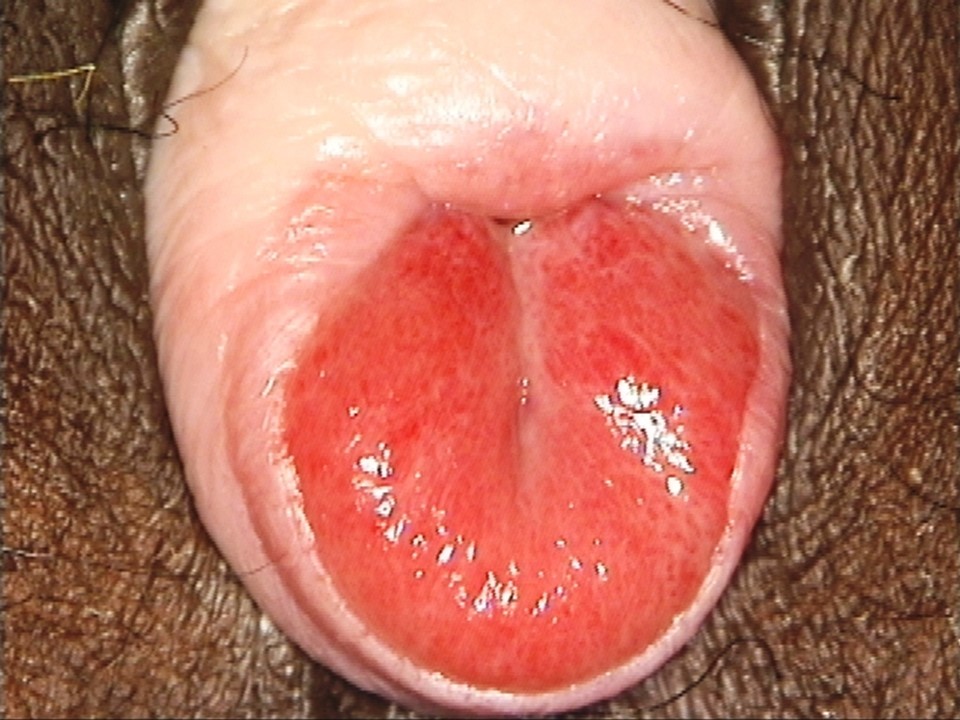
- Inspect the external genitalia and the perineal region for any signs of excoriations, oedema, white or red patches, vesicles, papules, sores, ulceration, warts, and growths.
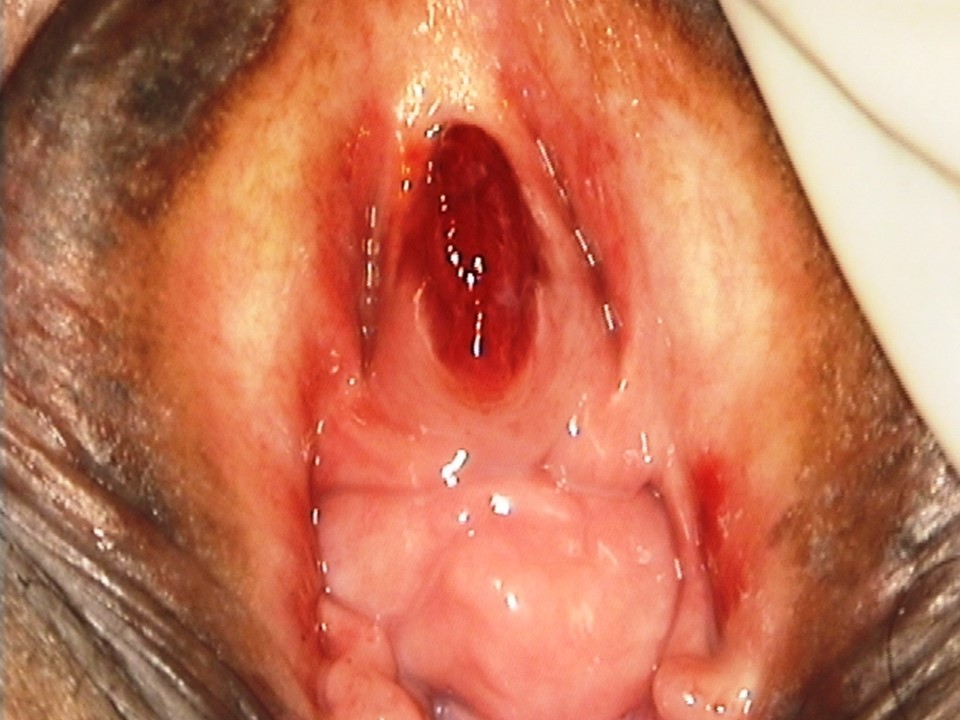
- Spread the labia minora gently, and check for any fleshy mass, discharge, or bleeding from the urethral opening or the introitus.
- In some women the uterus may slip down from its normal position because of laxity of the muscles and ligaments that support the uterus. In such a situation, the cervix may be seen protruding through the vaginal opening or may lie completely outside the vagina. This condition is known as uterovaginal prolapse.
- Women with long-standing prolapse can present with ulcers on the prolapsed tissue. These are known as decubitus ulcers. A decubitus ulcer has a raw, smooth surface with sharply defined margins.
|
|
| .jpg)